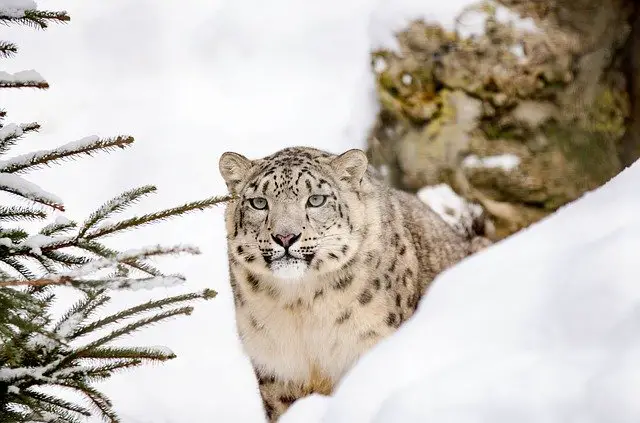
We have gathered a complete set of Snow Leopard Facts For Kids that will provide you with all the Snow Leopard Information For Kids you need. You are going to learn about its scientific name, taxonomy, importance, evolution, species, characteristics, appearance, size weight, height, body parts, speed, jump, habitat, biome, countries, lifespan, survival, diet, prey, hunting, predators, adaptations, endangerment, population and many other interesting facts about snow leopard.
Snow Leopard Facts For Kids
1. What Is A Snow Leopard
- The snow leopard is a beautiful and well-camouflaged big cat (a member of the genus Panthera).
- It is indigenous to the mountain ranges of South and Central Asia.
- It is also known as “Ounce”.
- Of all the big cat species in the world, the snow leopard is the most elusive one.
- It lives in alpine and subalpine zones at the altitudes of 9,800 to 14,800 feet (3,000 to 4,500 meters).
- Their natural habitat ranges from Eastern Afghanistan to Mongolia and China.
- The population of snow leopards is continuously decreasing. That is why it is included in the list of vulnerable animals of the IUCN Red List.

2. Snow Leopard Scientific Name
- “Panthera uncia” is the scientific name of the snow leopard.
3. Snow Leopard Classification – Snow Leopard Taxonomy
- The following is the taxonomy or scientific classification of the snow leopard:
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Subphylum | Vertebrata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Carnivora |
| Suborder | Faliformia |
| Family | Felidae |
| Subfamily | Pantherinae |
| Genus | Panthera |
| Species | Panthera uncia |
4. Where Do Snow Leopards Come From – Snow Leopard Evolution
- The phylogenetic analysis of the DNA sequence samples of the living Felidae revealed that snow leopards and tigers form a sister taxon (or sister group).
- The time when the genetic divergence of this group occurred is estimated as 4.62 to 1.82 million years ago.
- Probably, both species (snow leopard and tiger) diverged between 3.7 to 2.7 million years ago.
- North Central Asia is the most likely region where Panthera originated.
- The oldest known Panthera species excavated in Ngari Prefecture, Tibet, is Panthera blytheae, the skull of which shows characteristic resemblance with snow leopard.
- In 2016, research revealed that the mitochondrial genome of snow leopards, leopards, and lions has many similarities as compared to their nuclear genome. It indicates that the forefathers of snow leopards hybridized with those of leopards and lions at some stage of their ovulation.
5. Snow Leopard Species – Types Of Snow Leopards
- The snow leopard is the only species of its kind.
- However, a new study revealed three subspecies of snow leopards based on genetic distinctions, geographic separation, unambiguous population assignments, and low level of admixture.
- The subspecies are:
- Panthera uncia iribis (Northern group)
- Panthera uncia uncia (Western group)
- Panthera uncia uncioides (Central group)
6. Snow Leopard Characteristics – Snow Leopard Features
- The following are some of the snow leopard’s characteristics or features that help them to survive in the harsh mountainous habitat:
- A snow leopard has whitish-grey thick fur with a hair length of about 5 to 12 cm.
- They have large black rosettes on the body and black spots on the head that provide them excellent camouflage.
- Their long hind limbs and short stronger forelimbs allow them to jump for about 10 meters in the air.
- As compared to other cats of the genus Panthera, a snow leopard has a slightly smaller body size.
- Their overall body structure provides them good insulation in the snowy environment and minimizes heat loss.
- Snow leopards have large paws with fur which acts like natural snowshoes. It prevents them from sinking in the snow and also prevents heat loss.
7. What Does A Snow Leopard Look Like – Snow Leopard Appearance – Snow Leopard Physical Description
- Snow leopards have whitish-grey fur and a long tail of an average length of about 36 inches.
- They have short muzzles, a domed forehead, and large nasal cavities.
- They have thick fur, which grows extra thicker and denser in the winter season.
- Like jaguars, snow leopards have black spots on the head, neck, and lower limbs and rosettes on the back and tail.
- The color of their fur resembles the rocky and snowy environment of their habitat and provides them camouflage.
- Their paws have a covering of fur which acts like snowshoes.
- They have stocky and relatively small bodies than other big cats.
- Their average body size ranges between 4 to 5 feet.
- The weight of a male snow leopard ranges between 90 and 120 pounds and of a female between 70 to 90 pounds.
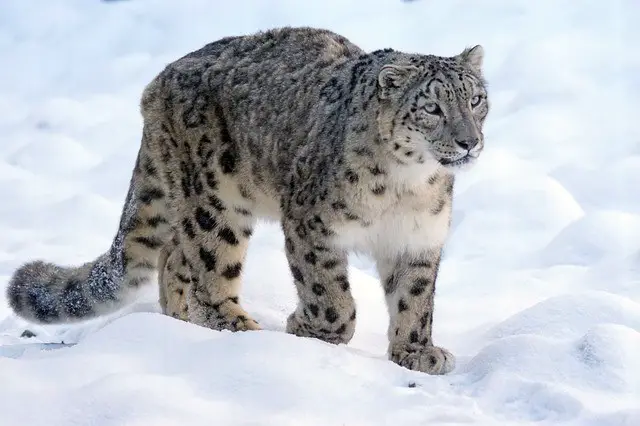

8. What Is The Size Of A Snow Leopard – Snow Leopard Size
- The average size of a leopard ranges between 4 to 5 feet.
- Their standing height at the shoulders is about 1.8 feet (22 inches).
How Tall Is A Snow Leopard – Snow Leopard Height
- The standing height of the snow leopard at the shoulder region is about 22 inches (56 cm).
How Long Is A Snow Leopard
- The average body length of the snow leopard is 4 to 5 feet.
- The tail has an average length of about 36 inches.
9. How Much Does A Snow Leopard Weigh – Snow Leopard Weight
- The average body weight of a snow leopard ranges between 49 and 121 pounds (22 and 55 kg).
- Sometimes, large males gain weight of up to 165 pounds (75 kg).
- While some small females weigh under 55 pounds (25 kg).
10. What Color Is A Snow Leopard – Snow Leopard Color
- The fur color of a snow leopard is whitish-grey.
- The belly side is white.
- The head has black spots, while the back, flank, and tail have rosettes.
Snow Leopard Eye Color
- The eye color of the snow leopard ranges from pale green to grey.
11. Snow Leopard Head
- The head of the snow leopard is relatively big and round with two small tears at the top.
- Its forehead is domed-shaped and the muzzle is short.
- The head is covered with whitish to grey fur.
- Its head has a pattern of black spots at the forehead, around the eyes, and at the mustache region.
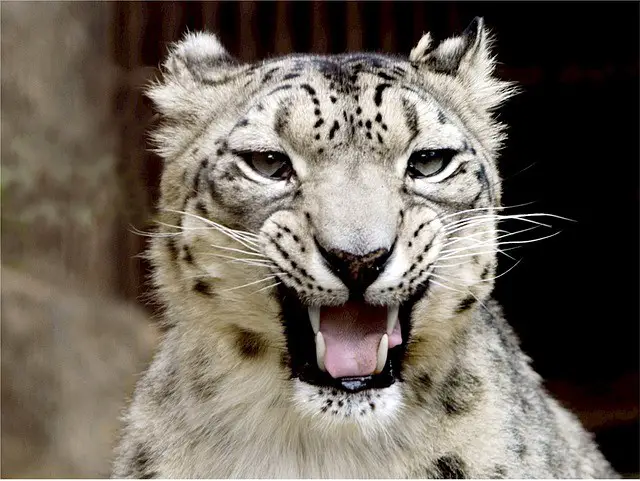

12. Snow Leopard Teeth
- Like other big cat species, an adult snow leopard has 30 teeth.
- Its canine teeth are 1.13 inches (2.8 cm) long and more sharp and slender as compared to any other Panthera species.
13. Snow Leopard Tail
- A snow leopard has a long bushy tail covered with thick fur like the rest of its body.
- Its tail also has a rosette pattern usually of bigger size than those of the body and black stripes at the ending point.
- Of all the big cat species, the snow leopard has the longest tail.
- The tail length ranges from 31 to 41 inches (80 to 105 cm).
- The unusual long tail helps a snow leopard to maintain its balance in the rocky habitat.
- During snowstorms and blizzards, the snow leopard wraps its long tail around its face just like a muffler to stay warm.
How Long Is A Snow Leopard’s Tail
- The average length of a snow leopard’s tail is up to 91.5 cm (36 inches).
- Its maximum length reaches about 105 cm (41 inches), which makes about 70% of its whole body length.
14. Why Are Snow Leopards Called Ghost Cats
- Snow leopards are called “ghost cats”, “grey ghosts” or “ghosts of mountains” because of their extremely elusive nature.
- When seeing people or other animals they frequently hide. That is why a snow leopard is not a well-studied big cat.
15. How Fast Can A Snow Leopard Run – Snow Leopard Speed
- The usual running speed of a snow leopard is about 48 km/h (30 mph).
- Their fastest speed is 64 km/h (40 mph).
- Like other big cats, a snow leopard also can not sustain its fastest speed for long distances.
16. Snow leopard jumping
- Snow leopards are tremendous jumpers.
- Their powerful short, stocky limbs allow them to jump as high as 6 meters (20 feet) in the air while covering a distance of 15 meters (50 feet).
How Far Can A Snow Leopard Jump – Snow Leopard Jump Distance
- In one leap, a snow leopard can cover up to 15 meters (50 feet) horizontal distance.
How High Can A Snow Leopard Jump – Snow Leopard Jump Height
- A snow leopard is an excellent vertical leaper and can jump as high as 20 feet (6 meters) in the air.
17. Do Snow Leopards Swim
- Yes, snow leopards can swim.
Snow Leopards Swimming
- According to research studies, snow leopards are good swimmers.
- The GPS collaring data and camera traps reveal the swimming of snow leopards across streams and deep rivers considered as impossible to cross.
- Researchers of the Nature Conservation Foundation (NCF) found a dripping-wet snow leopard in their camera traps during a recent snow leopards’ population study in the Pin Valley National Park of India. The camera was placed near the Pin River, which is a fast-flowing tributary and was 15 to 30 meters wide at that time when the snow leopard was crossing.
- Another snow leopard swimming was observed in Kyrgyzstan by a snow leopard scientist, Kuban Jumabai uulu.
- The Kuban observed a snow leopard (he named Fighter) in camera traps crossing frequently the Sarychat river during spring as well as autumn.
- Another snow leopard was observed in photos that had crossed the Tongtian River in Qinghai Province, China. The spot in the river the snow leopard swam across was at least 50 meters wide.
18. Where Do Snow Leopards Live – Snow Leopard Habitat
- Snow leopards live in the mountain ranges of South and Central Asia.
- They inhabit the alpine and subalpine zones at the altitude of 9,800 to 14,800 feet (3,000 to 4,500 meters).
- In the summer season, snow leopards usually live above the tree line in rocky regions and mountainous grasslands at an elevation from 8,900 to 19,700 feet (2,700 to 6,000 meters).
- In the winter season, they come down to the forest region found relatively at lower elevations of about 3,900 to 6,600 feet (1,200 to 2,000 meters).
- Snow leopards prefer to live in rocky and broken terrain.
- They have no problem traveling and walking in 33 inches of deep snow.
Snow Leopard Natural Habitat – Where Do Snow Leopards Live In The Wild
- In the wild, snow leopards live in the alpine and subalpine forest zones.
- Their natural habitat range covers up to 2 million km² areas.
- They live at high elevations from Western China and Mongolia to Eastern Afghanistan.
- However, the northern range of their habitat is at lower altitudes.
What Biome Do Snow Leopards Live In
- The biome where snow leopards live is known as “taiga”.
- Such biome is also known as the boreal forest biome.
- The vegetation of taiga is primarily composed of scale-leaved or needle-leaved cone-bearing evergreen trees.
- Such biomes are located in the far South or far North.
- The main characteristic of the taiga biome is long winters and moderate to high degree annual precipitation.
19. Snow Leopards In Captivity
- There are about 600 snow leopards in captivity living in accredited zoos throughout the world.
- Of this number, approximately 250 are found only in American Zoos.
20. Where Do Snow Leopards Live In The World
- In the world, snow leopards are found in South and Central Asia.
- They live in the following protected areas:
- In Pakistan; Khunjerab National Park and Central Karakoram National Park (Gilgit-Baltistan region), Chitral National Park (Khyber Puntukhwa region), Deosai National Park, Baltistan Wildlife Sanctuary, and Naltar Wildlife Sanctuary.
- In India; Kishtwar National Park, Dachigam National Park, and Hemis National Park (Ladakh region), Jammu and Kashmir, Great Himalayan National Park, Pin National Park, Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary (Himachal Pradesh region), Gangotri National Park, Valley of Flowers National Park, and Nanda Devi National Park (Uttarakhand), Khangchendzonga National Park (Sikkim), Dibang Wildlife Sanctuary (Arunachal Pradesh), Hirpora Wildlife Sanctuary (Kashmir).
- In Bhutan; Wangchuck Centennial National Park, Jigme Dorji National Park, Bumdeling Wildlife Sanctuary.
- In Nepal; Shey Phoksundo National Park, Langtang National Park, Makalu Barun National Park, Sagarmatha National Park, Api Nampa Conservation Area, Annapurna Conservation Area, Kanchenjunga Conservation Area, Manaslu Conservation Area, Dhorpatan Hunting Reserve.
- In China; Sanjiangyuan National Nature Reserve and Qomolangma National Nature Preserve (the Tibetan Plateau region), the western Tianshan Mountains’ Tomur National Conservation Zone, Qilianshan National Nature Reserve (Qilian Mountains).
- In Mongolia; Gobi Gurvansaikhan National Park, and Ubsunur Hollow (located at the international border of Mongolia and the Tuva Republic, a Republic of Russian Federation).
- In Russia; Katun Nature Reserve (located in South Siberia).
- In Uzbekistan; Zamin National Park, Ugam-Chatkal National Park, Chatkalskiy State Nature Preserve, Hissar National Reserve.
- In Tajikistan; Pamir National Park.
- In Kazakhstan; Aksu-Zhabagly National Reserve (Central Asian oldest nature reserve).
- In Kyrgyzstan; Sarychat-Ertash State National Reserve, Besh-Tash State Nature National Park, Sary-Chelek Nature Reserve, Karakol National Park, Kyrgyz-Ata National Park, Chychkan Wildlife Refuge.
What Country Do Snow Leopards Live In
- The habitat of snow leopards covers the following countries:
- Russia
- Kazakhstan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Uzbekistan
- Tajikistan
- Afghanistan
- Mongolia
- China
- Pakistan
- India
- Nepal
- Bhutan
21. Where Do Snow Leopards Live Map – Snow Leopard Habitat Map
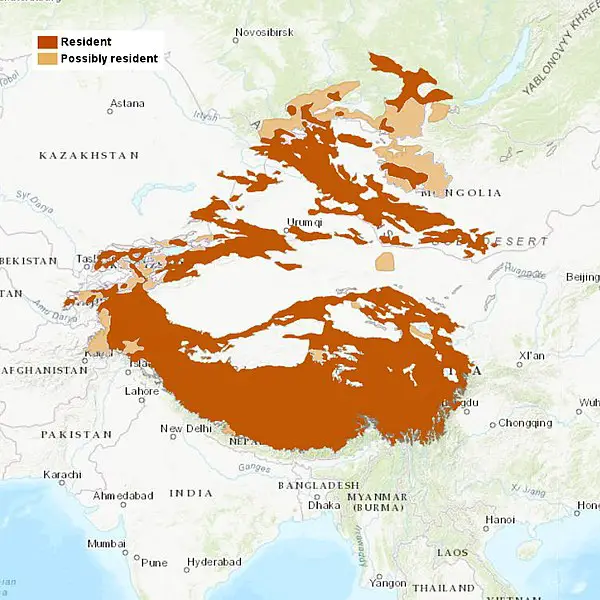
22. How Do Snow Leopards Survive
- Snow leopards have many adaptations that help them to survive in harsh mountainous habitats.
- Their well-adapted respiratory features, such as large nasal cavities and robust chest muscles, allow them to draw enough oxygen from the thin air at high altitudes.
- Their overall body structure is well-adapted to survive in the rocky habitat with a cold and snowy climate.
23. How Long Do Snow Leopards Live – Snow Leopard Lifespan – Snow Leopard Life Expectancy
- The estimated lifespan of a snow leopard in the wild is 15 to 18 years.
- In captivity, they live longer due to good care, proper and abundant food availability, and being secure from natural threats and diseases.
- They live normally for up to 20 to 22 years in captivity.
- Their known maximum age in captivity is up to 25 years.
Snow Leopard Average Lifespan – Snow Leopard Age
- The average lifespan of snow leopards in the wild is about 15 to 18 years.
- In captivity, their average age is up to 20 years.
24. What Do Snow Leopards Eat – Snow Leopard Diet Facts
- The snow leopard is a carnivore in nature and fulfills most of its nutritional requirements by eating the flesh or meat of other animals.
- Animals of weight range from 79 to 186 pounds (36 to 76 kg) are its favorite prey.
- It is capable of hunting animals three times bigger than its size.
- However, it also preys some small animals such as pika, vole, and marmot species.
- A snow leopard eats several kilograms of meat at a time.
- Their diet changes across its habitat range and in the time of year with an abundant and reduced prey availability.
- In the Himalayas, the diet of a snow leopard is mostly composed of Himalayan blue sheep and Siberian ibex (Capra sibirica).
- In the Karakoram range, Tian Shan, Altai, and Tost Mountains of Mongolia, their major diet is Thorold’s deer (Cervus albirostris), Siberian ibex (Capra sibirica), argali (Ovis ammon), and Siberian roe deer (Capreolus pygargus).
- They also sometimes eat carrion.
- A snow leopard survives on a blue sheep for about two weeks and consumes all the edible parts of the carcass.
- Annually, a snow leopard eats approximately 20 to 30 adult blue sheep.
- Unlike other big cats, snow leopards are also known for eating a significant amount of vegetation.

What Animals Do Snow Leopards Eat – Snow Leopard Prey
- The following animal species are the favorite prey of snow leopards:
- Himalayan blue sheep (Pseudois nayaur)
- Himalayan tahr (Hemitragus jemlahicus)
- Markhor (Capra falconeri)
- Argali
- Wild goat (C. aegagrus)
- Other animal species a snow leopard hunt if available are:
- Red panda
- Langur monkey
- Wild boar
- Snow cock
- Chukar partridge
- Sometimes, a snow leopard also hunts small mammal species, such as; pika, marmot, hare, and vole.
- Due to habitat loss and reduced availability of natural prey, snow leopards sometimes attack domestic livestock.
Snow Leopard Eating Habits
- A snow leopard drags the carcass to a safe location before eating.
- It is a slow eater and consumes all the edible parts of the prey.
- It usually takes 3 to 4 days to eat its prey.
- When threatened, a snow leopard readily abandoned its hunt and flee.
25. How Do Snow Leopards Hunt – Snow Leopard Hunting
- A snow leopard chases its prey and usually uses the broken terrain for its conceal approach.
- It chases its prey across icy surfaces, snow, and stones. Its broad paws provide traction on the icy surface just like snowshoes.
- It uses the momentum of its first jump to chase prey for up to 980 feet (300 meters).
- It ambushes from above and kills the prey usually with a single bite on the neck.
- Successful hunts have been recorded when snow leopards are in pairs, specifically the mating pairs.
26. Snow Leopard Life Cycle
- The life cycle of a snow leopard starts when it becomes sexually mature at the age of 2 to 3 years.
- They mate in the late winter season and give birth to cubs from April to June.
- Mothers have total responsibility for parenting their cubs.
- At the age of 18 to 22 months, the cubs become independent.
- The generation time of snow leopards is 8 years.
- They live for 15 to 18 years in the wild and 20 to 25 years in captivity.
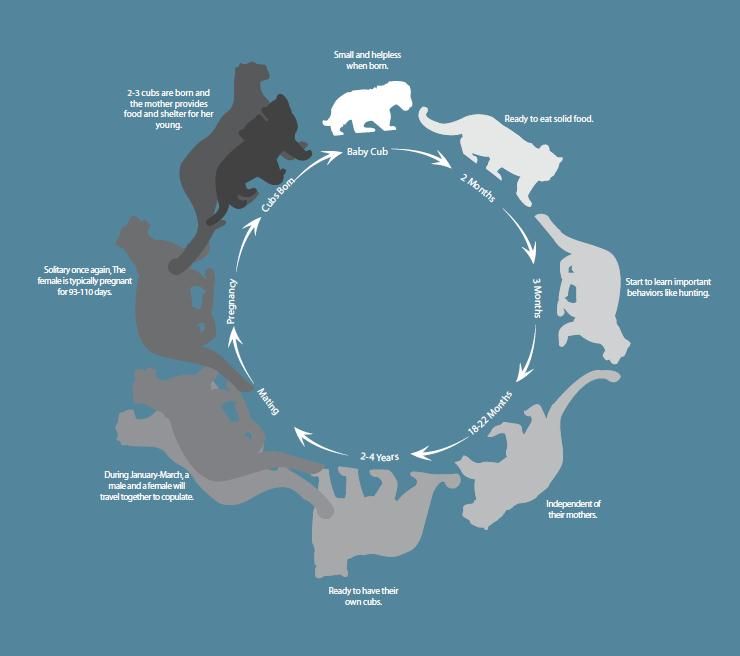
27. How Do Snow Leopards Reproduce – Snow Leopard Reproduction
- Like other mammals and big cats, a snow leopard gives birth to living offspring.
- Their Estrus or Oestrus (a phase of increased sexual receptivity) lasts usually for 7 to 8 days.
- Unlike other big cats, snow leopards have a well-defined birth peak.
- Late winter is their mating season.
- Females give birth to cubs between April and June after a gestation period of 90 to 100 days.
- The average number of cubs born is 2.2, however, it could be from 1 to 5.
- The cubs are born in a rocky crevice or den, which has a lining of fur shed from the mother’s underside.
- Mothers feed the cubs for about 10 weeks.
- The cubs become fully independent at the age of 18 to 22 months.
How Often Do Snow Leopards Reproduce
- Female snow leopards reproduce about once every two years.
- A female reproduced in one spring will be teaching the hunting skills to her year-old cubs in the next spring.
28. Baby Snow Leopard Facts – Snow Leopard Cubs Facts
- Baby snow leopards are called cubs.
- They are born after a gestation period of 12 to 13 weeks.
- They are born blind but still have a thick coat of fur.
- They have solid black spots on their fur which turn into rosettes as they grow to adulthood.
- At the time of birth, the cubs weigh from 11.3 to 20.0 oz (320 to 567 g).
- Their eyes open after about one week.
- They are fed with the mother’s milk and become able to walk at the age of 5 weeks.
- A two-month-old cub can eat and digest solid food.
- They are completely weaned after 10 weeks.
- The cubs leave the den after about 2 to 4 months of age.
- They start following their mothers and learning hunting skills at the age of only 3 months.
- The cubs become completely independent at the age of 18 to 22 months.
- Upon independence, the cubs disperse over wide areas and cross considerable expenses to seek out new hunting regions and territories.
What Do You Call A Baby Snow Leopard
- A baby snow leopard is known as a “cub”.
How Long Do Snow Leopards Stay With Their Mother
- The baby snow leopards stay with their mothers for about 18 to 22 weeks.
29. What Is A Female Snow Leopard Called
- A female snow leopard is called “leopardess”.
30. What Are Snow Leopards Predators – Snow Leopard Predators
- The snow leopard is itself an apex predator and has no predators in its natural habitat.
- Human beings are the biggest threat to their survival and their only predators.
What Eats Snow Leopards
- The snow leopard is itself the top predator of its habitat and no animal can dare to attack or eat it.
- Humans are the only predators of snow leopards and kill them for their bushmeat, fur, and organs.
- Many of its organs are used in Chinese medicine.
31. Snow Leopard Predators And Threats
- Humans are the sole predators of snow leopards.
- Illegal hunting of snow leopards for their fur and body parts is a major threat to its population.
- Other threats to its survival are habitat loss and less availability of prey, climate change, and infrastructure development.
32. Snow Leopard Adaptations
- Snow leopards have many adaptations to survive in the high-altitude mountain habitat. The major adaptations are:
Chest and Respiratory System
- The overall respiratory system of the snow leopards is well-adapted to survive in the thin air at high altitudes.
- They have extra-large nasal cavities to inhale more air, as the air at high altitudes has less oxygen. They also have a unique capability to warm the cold air they inhale before it gets into the lungs. This ability protects them from the problems of lungs’ coldness and all body coldness, as their thick fur would be useless if their body gets cold from inside.
- Their well-developed robust chest muscles provide them excellent stamina so that they can approach the prey for a long distance with a good running speed.
Coat or Fur
- They have a coat color that resembles the grey mountains and snowy habitat, which provides them camouflage. Their fur is about 4 to 5 inches long and thick that grows extra thicker in the winter to keep their body warm and insulated.
Powerful Limbs
- Snow leopards have short and extremely powerful limbs, especially their hind limbs. It allows them to cover a large distance (up to 45 feet) with a single leap. They are the masters of vertical spaces and their short forelimbs allow them to keep balance after the jump and easy landing.
Broad Paws
- A snow leopard has broad paws. If we compare a snow leopard’s paw with an average human hand, it would be about 2 to 3 times wider. The paws also have extremely thick skin and are covered with fur. It provides them a good grip and balance and they have no problem while walking on rocky terrain and deep snow.
Long and Thick Tail
- Snow leopards have a long and thick tail with an average length of 36 inches. Their tail has a key role in balance. Their tail also has up to 5 inches long and extremely thick and dense fur. They wrap their tails around its head and body and use it as a muffler in the freezing mountain nights and blizzards.
Snow Leopard Behavioral Adaptations
- A snow leopard is extremely shy and elusive and is active only at dawn and dusk.
- They are nocturnal in areas inhabited by many humans. However, if there are no or few humans around, they might be active during the daytime.
- A snow leopard is the least aggressive big cat towards humans.
- If threatened, a snow leopard usually escapes. However, if the cubs of a female are threatened, she will fight and do not even care about her life.
- Because of its elusive nature, the snow leopard is the least studied species of big cats. Scientists are trying to understand more about snow leopards’ behavior.
Snow Leopard Structural Adaptations – Snow Leopard Physical Adaptations
- The following are the structural or physical adaptations of snow leopard:
- Powerful limbs
- Large nasal cavities
- Robust chest and a good respiratory system
- Wider paws
- Sharp claws
- A long and thick tail
- Whitish-grey fur with rosette
Snow Leopard Adaptations For Hunting
- All the adaptations of snow leopards provide help in hunting. However, some of the adaptations are especially for hunting, such as:
- Their short and powerful legs are so nimble that they can go up to 20 feet high in the air and can cover more than 40 feet distance with a single leap to catch their prey.
- The shoulders of a snow leopard are extremely powerful and specially adapted for; taking down prey bigger than their size, and the proper landing and take off when it jumps.
- Their broader paws act like snowshoes and allow them to keep balance on deep snow and rocky terrain when approaching prey.
- They have extremely sharp claws which they use for taking down large prey, about 3 times larger than their size.
- A snow leopard also has night vision and extremely sharp eye-sight, approximately 6 times better than an average human. It makes them capable of hunting at night.
- Snow leopards have a good sense of hearing and small round-shape ears, which is an important adaptation for hunting. A snow leopard can flatten its ears along with its head to conceal its presence while stalking prey.
33. Are Snow Leopards Extinct
- No, snow leopards are not extinct.
34. Are Snow Leopards Endangered – Why Are Snow Leopards Endangered
- No, snow leopards are not endangered now.
- They are listed as vulnerable.
Snow Leopard Reason For Endangerment
- The following are the major reasons for the snow leopard’s endangerment:
Poaching
- Poaching or illegal hunting of snow leopards is the biggest reason why snow leopards are endangered.
- Snow leopards are killed for their body parts and fur.
- The white and thick fur of the snow leopard is much in demand to make fur clothing.
- Its organs, skin, and bones are used in traditional Chinese and Asian medicine.
Loss of habitat
- Another main reason for the endangerment of snow leopards is habitat loss.
- Human beings are stealing the food of snow leopards indirectly.
- People living in the region pushed their livestock into the habitat of snow leopards.
- It causes overgrazing of vegetation and food scarcity for the wild herbivore animal species such as wild goats and sheep, which are the main prey of snow leopards.
- With reduced vegetation, wild herbivore animals are going to become fewer and the snow leopards have no other choice but to prey on domestic livestock for their survival.
Retaliatory killing
- The livestock owners and farmers either kill the snow leopards to retaliate and revenge or to secure its remaining domestic animals.
35. Snow Leopard Endangered Species – Endangered Snow Leopard Facts
- In 1972, the snow leopard was listed as an endangered species by the IUCN Red List because of the extreme decline in population and many other threats to its survival.
- In 2003, their estimated worldwide population was 4,080 to 6,800 individuals.
- In 2016, their estimated population slightly increased and was from 4,678 to 8,7454 individuals.
- So its status was changed from “Endangered” to “Vulnerable”.
How Are Snow Leopards Endangered
- Snow leopards are endangered as their estimated worldwide population is less than 10,000 mature individuals.
- About 40% decline is expected in their population by 2040.
How Long Have Snow Leopards Been Endangered
- The snow leopard was on the list of IUCN Endangered species for about 45 years.
When Did Snow Leopards Become Endangered
- The IUCN Red List included snow leopards in Endangered species in 1972.
36. What Is Being Done To Save Snow Leopards
- The following are some of the efforts that have been done to save the snow leopards:
Global Snow Leopard Forum and Bishkek Declaration
- The government leaders and officials from 12 countries (encompassing the habitat range of snow leopards) gathered in 2013 at the Global Snow Leopards Forum (GSLF).
- President of the Kyrgyz Republic, Almazbek Atambayev, and the State Agency on Environmental Protection and Forestry initiated GSLF under the government of the Kyrgyz Republic.
- In the meeting, all the countries agreed on the need for transboundary support for the snow leopards and their high-altitude habitat.
- All 12 countries signed the Bishkek Declaration at the meeting of GSLF.
- The declaration was to
“acknowledge that the snow leopard is an irreplaceable symbol of our nations’ natural and cultural heritage and an indicator of the health and sustainability of mountain ecosystems; and we recognize that mountain ecosystems inhabited by snow leopards provide essential ecosystem services, including storing and releasing water from the origins of river systems benefitting one-third of the world’s human population; sustaining the pastoral and agricultural livelihoods of local communities which depend on biodiversity for food, fuel, fodder, and medicine; and offering inspiration, recreation, and economic opportunities.”
Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection Program
- The Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection Program is a joint initiative of the country governments that encompasses the habitat range of snow leopards, international agencies, the private sector, and civil society.
- The goal of this program is the snow leopard’s long-term protection in its natural habitat.
Designation of 2015 As the Year of the Snow Leopard
- Government authorities and conservation groups designated 2015 as the International Year of the Snow Leopard.
- The main purpose of this effort was to make people aware of snow leopards’ endangerment and save the cat and its natural ecosystem.
- The governments of the range countries, inter-governmental and non-governmental organizations, local communities, and many private sector businesses undertook to take the year as an opportunity to work more for the conservation of snow leopards and their high-mountain habitat.
37. Why Are Snow Leopards Important
- Snow leopards are important because they are vital in the ecological balance of the region where they live.
- The presence and flourishing of snow leopards is an indicator of the overall health of their high-elevation habitat.
- They are the top or apex predators of their environment and mostly eat herbivore animals like wild mountain goats and sheep.
- In the absence of snow leopards, the population of herbivore animals would increase, which would cause a change to the vegetation and would influence the other wildlife living in the region.
- The habitat landscape of the snow leopards is also a source of food and other important resources for many people living there.
- These people rely on the vegetation to obtain medicines and wood for fuel and shelter.
- So snow leopards are extremely important to keep the natural environment of the region in balance and to benefit the people who depend on it.
38. How Can We Help Snow Leopards
- We can do many things if we want to help snow leopards. Such as;
- We can symbolically adopt a snow leopard at WWF. The symbolic adoption helps to save real snow leopards in the wild.
- We can take action against snow leopards in case of seeing something unlawful. We can visit our Wildlife Action Center to inform the government leaders.
- Become a wildlife defender and speak up for wildlife. For this purpose, we should stay informed and learn how to be powerful wildlife advocates.
39. Snow Leopard Conservation
- A lot of organizations, agencies, and NGOs are working for the conservation of snow leopards and the ecosystem of their threatened habitat.
- These includes:
- The Snow Leopard Trust
- The Snow Leopard Conservancy
- TRAFFIC (the Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network)
- The Cat Specialist Group
- The Panthera Corporation
- The Snow Leopard Network
- The above groups and many national governments encompassing the snow leopard’s habitat, donors, and nonprofits from throughout the world collectively worked at the 10th International Snow Leopard Conference held in Beijing.
- Their research focus was:
- Arranging community programs in the snow leopard regions
- Education programs aiming to understand the needs of the cat
- Needs of the herder communities and villagers sharing habitat of snow leopards The above groups and many national governments encompassing the snow leopard’s habitat, donors, and nonprofits from throughout the world collectively worked at the 10th International Snow Leopard Conference held in Beijing.
Snow Leopard Conservation Status
- The snow leopard was included in the Endangered species of the IUCN Red List till 2017.
- The current conservation status of the snow leopard at the IUCN Red List is as a “Vulnerable” species.
40. What Is The Population Of Snow Leopards – Snow Leopard Population
How Many Snow Leopards Are Left In The World
- The 2016 estimated population of snow leopards is from 4,678 to 8,745 individuals.
- While approximately 600 snow leopards are found in captivity throughout the world.
- In the following table, the country-wise estimated population of snow leopards is shown:
| S.No | Country | Habitat Area (Km²) | Estimated Population |
| 1 | China | 1,100,000 | 4,500 |
| 2 | Mongolia | 101,000 | 1000 |
| 3 | Kyrgyzstan | 105,000 | 300 – 400 |
| 4 | Kazakhstan | 50,000 | 100 – 120 |
| 5 | Tajikistan | 100,000 | 250 – 280 |
| 6 | Uzbekistan | 10,000 | 30 – 120 |
| 7 | Afghanistan | 50,000 | 50 – 200 |
| 8 | Pakistan | 80,000 | 250 |
| 9 | India | 75,000 | 516 – 524 |
| 10 | Nepal | 30,000 | 300 – 400 |
| 11 | Bhutan | 15,000 | 100 – 200 |
| 12 | Altai-Sayan region | 20,000 | 70 – 90 |
How Many Snow Leopards Are Left In The Wild
- The estimated number of snow leopards left in the wild is from 4,678 to 8,745 individuals.
Snow Leopard Population Graph
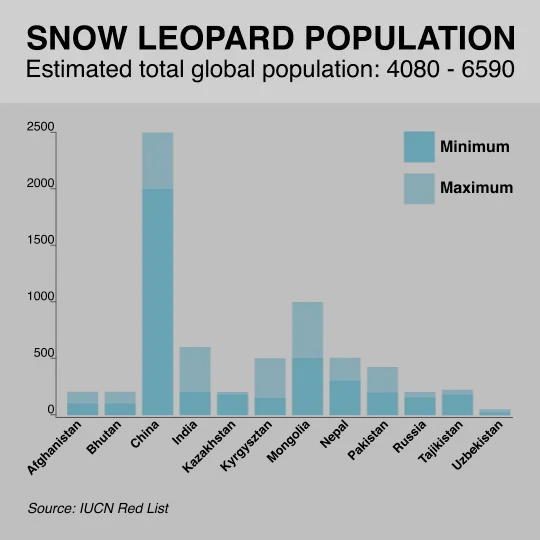
41. Snow Leopard Book
The Snow Leopard Project
- The Snow Leopard Project is a book written by Alex Dehgan.
- It is an astonishing account of the heroic efforts made to conserve and save wildlife in Afghanistan.
42. Are Snow Leopards Leopards
- No, the snow leopard is not a leopard.
- It has many similarities with leopard, however, both are separate species of the genus Panthera.
Difference Between Leopard And Snow Leopard
- The following are some of the major differences between leopard and snow leopard:
| Characteristic | Snow Leopard | Leopard |
| Scientific name | Panthera uncia | Panthera pardus |
| Bodyweight | 77 to 120 pounds | 51 to 86 pounds |
| Body length | 6 to 7.5 feet | 5 to 8.5 feet |
| Fur color | Whitish-grey with black rosettes | Brownish-yellow with black rosettes |
| Rosette shape | Large square-like enclosing small spots | Circular ring-like without any spots |
| Lifestyle | Active at dawn and dusk | Active at night |
| Vocalization | Do not roar.
Make other sounds to communicate, such as loud hisses, noisy chuffs, and growls | Roaring, grunting, meowing, and purring |
| Lifespan | Unknown in the wild
21 years in captivity | 12 to 17 years in the wild
Up to 24 years in captivity |
| Estimated population in the wild | 7,000 | 69,000 |
| Conservation status | Vulnerable | Near Threatened |
43. Interesting Facts About Snow Leopards
- Snow leopards are also called the ghost of mountains because of their elusive nature.
- Because of their extremely solitary nature, there is no term for a group of snow leopards. Even two snow leopards are rarely seen together.
- The broad and furred paws of snow leopards act like a pair of natural snowshoes.
- Of all the big cat species, the snow leopard has the thickest fur, which grows extra thicker and denser during the winter season to provide more insulation and keep its body warm.
- Unlike other big cats, snow leopards also eat a significant amount of vegetation.
- Of all the big cats, the snow leopards have appeared to be the least aggressive towards humans.
- Unlike other big cat species, snow leopards have amazing stamina because of their well-developed and robust chest. They have an incredible ability to travel about 27 miles distance across the open desert in only a single night.
- A snow leopard has about 6 times better eye-sight than an average human. They also have night-vision.
44. Fun Facts About Snow Leopards
- The snow leopard is the only big cat species that inhabit the cold desert of Asia.
- Unlike other species of the genus Panthera, the snow leopard can not roar.
- A snow leopard uses its tail for balance in the way we use our arms in balancing.
- Known for its high skill of jumping vertical spaces, a snow leopard can go up to 6 meters high and can cover about 15 meters distance in a single jump.
- It can take down prey 3 times bigger than its size.

