Among all the bears species, Polar Bears are very unique and interesting to study. Their adaptations to their environment in the cold arctic and their survival instincts have always fascinated researchers. Most recent studies have suggested a significant impact of global warming on the life of polar bears and have revealed alarming situations regarding their survival. We have gathered a complete set of Polar Bear Facts for Kids that will enable you to learn all about this amazing animal. Please do share this information with your friends and family to create awareness about polar bears.
Polar Bear Facts for Kids
1. What are polar bears?
- The Polar Bear is a carnivorous bear that is found in the Arctic Circle i.e. the Arctic Ocean, Seas, and surrounding Land Masses.
- It is the sister species of the Brown Bear.
- It is born on land but spends most of its time on sea ice in the Arctic Circle.
- It is one of the largest mammals living on land.
- It is a marine mammal because it is mostly found near ice and water.
- Polar bears are on the top of the food chain in the Arctic region and feed primarily on the seals’ fat.
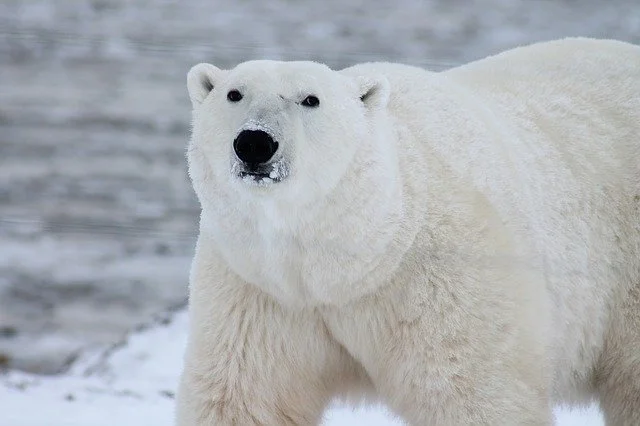

2. Polar Bear Scientific Name
- The polar bear is scientifically named Ursus maritimus, meaning “Sea Bear”.
3. Polar Bear Classification
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Ursidae |
| Genus: | Ursus |
| Scientific Name: | Ursus maritimus |
| Common Name: | Polar Bear |
| Other Name(s): | Nanuuq |
4. Polar Bear Description
- The Polar Bear is one of the largest carnivorous mammals living on land.
- It adopted its name – Polar Bear from the fact that it is mostly found at the North Pole of the earth.
- A Polar Bear’s body is covered in white fur generally. However, its fur color can range from white to creamy yellow and even light brown during summer.
- Its fur is very thick, which keeps it warm in the extremely cold climate of the Arctic Circle.
- The length of a male Polar Bear is 240-260 cm. And the length of a female polar bear is 190-210 cm.
5. Types of Polar Bears – Polar Bear Species
- There are NO other types or species of Polar Bears.
6. Characteristics of a Polar Bear
- The Polar Bear is made for the cold climate of the Arctic Circle.
- Its fur is made up of dense and insulating underfur which has guard hair on top. This fur prevents any heat loss. It can overheat an adult male if he runs.
- Its skin below the fur is black, which surrounds an 11.4 cm thick layer of fat. Only this fat keeps the bear warm in water because the bear’s fur is a bad insulator when wet.
- Bear cubs can’t swim in the water because their fat layer isn’t thick enough to prevent heat loss.
- The polar bear’s tail is short and ears are small and round, which further minimizes the heat loss.
- The paws of the Polar Bears are ideal for walking in the Arctic.
- In water, the front paws act as large paddles, and the rear paws act as rudders for swimming.
- Polar bears have a remarkable sense of smell as they can detect a seal 3 feet beneath the ice from a distance of one kilometer.
- Adults polar bears are great swimmers as they can swim for hours in search of food.
Learn more: Do Polar Bears Have Tails

7. Polar Bear Speed
- A polar bear can run at a speed of about 40 kph (25 mph).
8. Polar Bear Eyes
- The eyes of the Polar Bear are dark brown which is quite close together.
- Polar Bears’ eyesight is similar to that of humans.
- Its eyes have a protective membrane that protects them from ultraviolet light.
9. Polar Bear Paw
- The Polar Bear has large paws with five toes each. Their diameters are 30 cm (12 inches).
- These paws act like snowshoes, carrying the bear’s weight as it travels over ice and snow.
- The Polar Bear has round and partially webbed forepaws and elongated hind paws.
- The sole of Polar Bear’s feet has black thick pads which are covered with soft, small dermal bumps scientifically known as “papillae”.
- These papillae help the Polar Bear in walking without slipping because it produces friction between the foot and ice.
- Each toe of the Polar Bear has round, thick, and non-retractile claws. These claws are used for grasping prey and for adhesion during climbing and running on ice.
10. Polar Bear Skin – Polar Bear Skin Color
- A Polar Bear has 11.4 cm of thick fat which is covered by its skin.
- The polar bear’s skin color is black. It absorbs the heat from the sun and keeps the bear warm.
- The skin is covered with fur, made up of two layers:
1. The outer layer of the fur is clear, having long ‘guard’ hair. Their length is 5-15 cm.
2. The inner layer is a thick undercoat having shorter hair. - Some of the unusual characteristics of the guard hair are:
1. They are tapered and have a hollow core filled with air.
2. They have light-scattering particles inside them.
3. They are made of keratin which is a protein.
4. They also have small salt particles which are present in every hair. - The white fur is a very good insulator and prevents almost any heat loss.
- However, the fur is a poor insulator when it becomes wet.
11. Why do Polar Bears have Black Skin
- Polar bears have evolved to have black skin.
- Black objects don’t reflect any light. Hence, they absorb the most heat energy from the sun among all the other colors.
- The temperature in countries around the Arctic Circle like Alaska, Russia, Greenland, Norway, and Canada is very low. So, sunlight is an important source of energy for Polar Bears in the Arctic Circle.
- The black skin of the Polar Bear absorbs the maximum heat from the sunlight to keep the bear warm.
- The clear fur covering the skin allows this sunlight to pass through and be absorbed by the skin, but the fur still looks white due to luminescence.
12. Are Polar Bears White – Why do Polar Bears have White Fur
- A polar bear’s fur has no color. It looks white because of luminescence.
- When the sun’s rays bounce off the clear “guard hair” some of the light energy enters the hair and is trapped.
- The energy inside the hollow part of the hair bounces around which causes the emission of light, called luminescence.
13. What Color are Polar Bears
- Polar Bears generally appear white due to luminescence in their colorless fur.
- However, the colors of the Polar Bears range from White to Creamy Yellow to Light Brown.
14. Why do Polar Bears have thick Fur
- Polar Bears are found mostly in the Arctic climates where it is extremely cold during winters.
- They have thick fur which keeps them safe from freezing to death.
- The thick fur is a poor conductor of heat, so it minimizes heat loss from the body after trapping air from surroundings.
- So, the basic purpose of the thick fur on Polar Bears is to keep them warm.
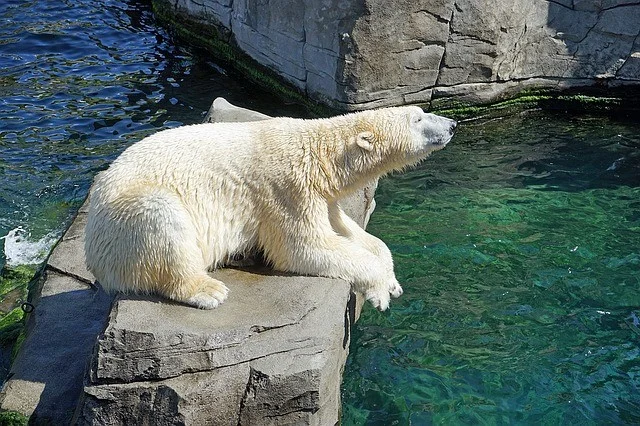

15. How Big is a Polar Bear – Polar Bear Size
Among all the bear species polar bear is the biggest bear.
How Tall are Polar Bears – Polar Bear Height
- The average height of polar bears when standing on all of its fours legs is 1 to 1.5 meters i.e. 3.5 to 5 feet.
- The average height of polar bears when standing on their hind legs is more than 3 meters i.e. 10 feet.
- The average length of a polar is around 2.2 to 2.5 meters i.e. 7.25 to 8 feet from head to rump while the tail only adds another 3 to 5 inches.
Learn more: How Tall is a Polar Bear
How Heavy is a Polar Bear – Polar Bear Weight
- Adult Female – 150 to 250 kg
- Adult Male – More than 800 kg
Learn more: How Much Does A Polar Bear Weigh
16. How long do Polar Bears Live – Polar Bear Life span
- The average life span of Polar Bears is:
1. Wild Polar Bear – 15 to 18 years
2. Captive Polar Bear – 20 to 30 years - The oldest that a Polar Bear ever lived was 42 years.
17. How do Polar Bears Adapt to their Environment- Adaptation of Polar Bear
- Polar Bears have evolved to adapt to their habitat to survive.
- The adaptations developed by Polar Bears are:
1. Small Ears – Reducing heat loss
2. Small Tail – Reducing heat loss
3. Thick layer of Fat – Insulation and Energy storage
4. Thick fur – Insulation and Camouflage
5. Fur on soles – Better grip and Insulation
6. Large feet – Better load management on ice
7. Sharp Teeth and Claws – Help in Hunting and Eating
18. Polar Bear Life Cycle
The Polar Bear life cycle includes 3 major steps:
- Mating (Spring)
1. The Polar Bears start looking for mates as the snow starts to melt.
2. After mating, the eggs don’t implant until fall. This phenomenon is called delayed implantation.
3. The male takes off on his own after staying with the female for a few days. - Denning (Fall & Winter)
1. After feeding in summer, a pregnant female Polar Bear starts looking for a den, where the cubs will be born and nursed till Spring.
2. It builds a den by digging up a snow cave, big enough for him to turn around in. And then waits for the snow to block the entrance to the cave. - Birthing (Winter)
1. The cubs are born in December. One, two, or three cubs are born.
2. They stay with their mother in the den. During this time, the mother doesn’t eat or drink anything. She nurses her children all the time.
Learn more: Polar Bear Life Cycle
19. Polar Bear Reproduction
- A male Polar Bear becomes capable of breeding at the age of 6 to 10 years.
- A female Polar Bear becomes capable of breeding at the age of 5 to 6 years.
- It breeds once every three years.
- Its breeding season lasts from late March to mid-July.
- After mating, the fertilized egg converts into a blastocyst, which floats in the uterus for about four months without any growth.
- The growth starts when the blastocyst implants in the uterine wall.
- The physical embryo takes four months to develop.
- The cubs are born in December due to delayed implantation. This provides time for the female to improve her physical condition, so she can nurse her cubs better.
- These cubs are guarded against cold in a den resembling an igloo.
- They feed on their mother’s milk until late March or April.
20. Polar Bear Gestation
- The average Polar Bear gestation period is 8 months.
- The delayed implantation occurs during this period.
- After mating, the fertilized egg converts into a blastocyst, which floats in the uterus for about four months without any growth.
- The growth starts after the implantation of the blastocyst in the uterine wall.
- The physical embryo takes four months to develop.
- The cubs are born in December due to delayed implantation. This provides time for the female to improve her physical condition, so she can nurse her cubs better.
21. Polar Bear Baby – Polar Bear Cub
- After birth, the weight of a polar bear cub is about 454 to 680 grams (16-24 oz.). They are approximately 30 cm (12 in.) long.
- Females cubs are slightly smaller than males.
- Polar Bear cubs are born little and impotent.
- Their eyes are closed when they are born.
- After birth, their fur is very fine due to which they look hairless.
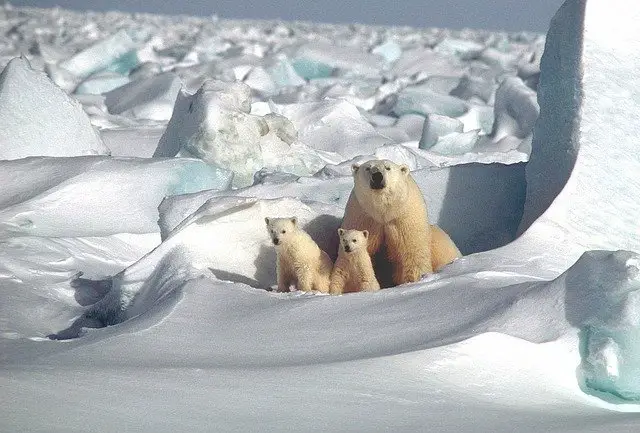

22. Polar Bear Cubs Facts
- Polar Bear cubs spend their early childhood days in the den to stay safe and warm. The mother nurses them for 12 to 18 weeks.
- The cubs grow quickly in size and weight by feeding on their mother’s milk. Within a few months, the newborn cubs are ready to eat food. Their new fur grows in 8 to 10 weeks, but sometimes it takes 14 weeks.
- The Polar Bear cubs move out of the den with their mother after 3 or 4 months. Because of their inborn abilities, they quickly learn hunting and survival skills from their mother.
- The cubs stay close to “mom” wherever she goes. Once they take their first dip in the ocean, they become acclimated to the water quickly and become good swimmers.
- The baby polar bears keenly observe their mother during the hunt and learn all the hunting and survival techniques they will use once they are adults.
23. Do Polar Bears Hibernate – Polar Bear Hibernation
- Polar Bears don’t hibernate like the brown and black bears.
- Female bears hibernate only when they are pregnant.
- The pregnant female polar bears dig snow dens when they are about to give birth to their babies.
- The female Polar Bears stay readily active inside their dens as they have to nurse their cubs.
- They hibernate for three months in these dens and when the cubs are strong enough they come out.
24. Polar Bear Swim
- Polar bears are well adapted to swimming.
- They can swim throughout the ocean at 10 kph (6 mph) because of their huge webbed paws.
- The Polar Bears can usually swim for 160 km (100 miles) continuously.

25. Polar Bear Strength
- The Polar Bear is a very strong and courageous mammal.
- Its bite force is very large at 1200 pounds per square inch.
- It can kill any animal with a single swipe of its paw.
26. Polar Bear Distribution
- The natural habitat of the Polar Bear is very cold areas.
- The areas where it has been spotted in the Northern Hemisphere are:
1. the North Pole
2. Ice over the Continental Shelf
3. Archipelagos at the edge of the Polar Basin
4. Arctic Sea Ice
5. Throughout the circumpolar Arctic - The areas where it has been spotted in the Northern Hemisphere are:
1. Southern Labrador
2. Norway
3. Newfoundland
4. Gulf of St. Lawrence (Winter)
5. Bering Sea (Winter)
6. James Bay, Canada (Southern-most)
27. Polar Bear Habitat Map
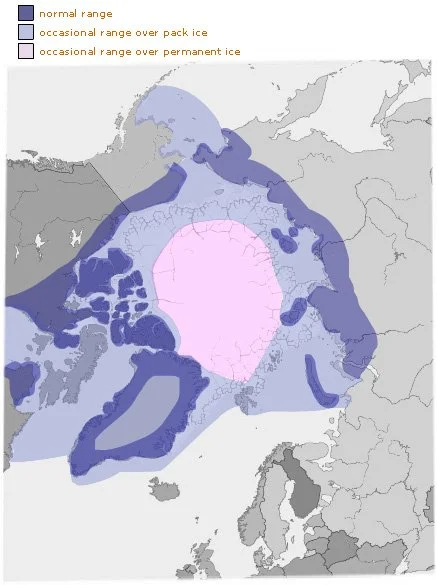
28. Where do Polar Bears Live – Polar Bear Habitat
- The Polar Bears’ main habitat is along with costs, shoreside pack ice, and the island of the Arctic region.
- Today, over 40 percent of Polar Bears live on pack ice and along the shores of the various island of Northern Canada.
- There are many ice packs in the Arctic Ocean and Sea.
- There are many organisms and plankton in the sea which is a rich food source for the Seals.
- These Seals live on ice packs and look for food in the sea.
- Ultimately, Polar Bears are mostly found near ice packs because they hunt Seals for food.
- Polar Bears may stay in the ice pack’s habitat throughout the year. They prefer the sea ice over all other places.
- Sea ice is very important to polar bears. It acts as a platform for them to live, breed, hunt, and create maternal dens.
- The sea ice is declining at a rate of 4.6% per decade which is threatening a food source for the Polar Bears.
- At the southern end, some Polar Bears spend 5 to 6 months on land with no Seals to eat.
- This shortage of food has forced the Polar Bears to look for other food sources like:
1. Garbage dumps
2. Human food storage
3. Sled dog yards - However, they are also threatening human life by moving to human communities.

29. What do Polar Bears eat – Polar Bear Diet
- Polar Bears are the largest land carnivores in the world.
- They feed on:
1. Ringed Seals
2. Bearded Seals
3. Walrus
4. Beluga Whale carcass
5. Bowhead Whale carcass
6. Birds’ eggs
7. Vegetation (rare) - They travel very long distances in search of prey.
Learn more:
30. What do Polar Bears Drink
- The freshwater reserves in the Arctic Region are frozen and a Polar Bear can’t drink seawater due to health problems it will cause.
- It has evolved so it doesn’t need to drink water at all.
- It gets water from the chemical reactions that break down its body fat.
- This is why most of the diet of a Polar Bear comprises fats.
31. How do Polar Bears Hunt
- A Polar Bear exclusively hunts Seals.
- It waits for the Seal to come to the water surface to breathe.
- When the Seal comes to the surface, it attacks the Seal by biting and bringing it to land before eating.
- Sometimes, when prey isn’t available, the Polar Bear eats whale carcasses.
32. Polar Bear Predators – What eats Polar Bears
- The only predators a Polar Bear has are other Polar Bears and humans.
- However, Polar Bear cubs are likely to fall prey to wolves or other carnivores.
- Sometimes, newborn cubs are eaten by their mothers or other Polar Bears. This phenomenon is called Cannibalization.
Learn more: What Eats Polar Bear

33. Are Polar Bears Endangered – Polar Bear Population
- Polar Bears are currently marked as Vulnerable and their number is decreasing continuously.
- The total number of Polar Bears left in the world is 20,000 to 25,000.
34. Are Polar Bears dangerous
- Yes, Polar Bears are dangerous animals.
- They are natural hunters, as they get their food by hunting Seals and Walruses.
- They have been reported to attack humans too.
- In 2011, a boy was killed and some other people were injured in Norway.
- In the past 20 years, six people have been killed by Polar Bears in Canada.
35. International Polar Bear Day
- The International Polar Bear day is celebrated on February 27th of every year.
Are you fascinated by cute and special polar bears? Then come and design a polar bear pin!
Custom Enamel Pins Canada can be printed with cute polar bear patterns. They can walk on ice or gently and quietly when holding ice. Pin them on your schoolbag to turn it into a polar bear paradise; pin them on your clothes, and you will be the “little expert” who understands polar bears the most in the crowd.
Wearing a customized polar bear pin is not only a decoration but also a super cool symbol of your love for polar bears. Come and have a customized polar bear pin of your own, and have a different kind of “intimate contact” with polar bears!

