Our solar system is an important topic in astronomy when teaching kids. With so many planets to study, kids are mostly interested in the biggest planet. Jupiter is the biggest planet in the solar system. We have gathered complete Jupiter Facts For Kids that will provide you with all the Jupiter Information For Kids that you need. You are going to learn all about Jupiter, its description, about its name, type, characteristics, special features, physical properties, appearance, color, surface, location, size, diameter, mass, comparison with earth, gravity, temperature, composition, layers, history, atmosphere, distances, climate, atmosphere, rotations, revolution, great red spot, Jupiter space missions, moons and many other interesting facts about Jupiter.
Jupiter Facts For Kids
1. What Is Jupiter – What Is Jupiter Planet
- Jupiter is a planet in the Solar System that exists at the 5th number from the sun.
- The mass of Jupiter is 1.898 x 10^27 kg and its surface area is 61.42 billion km², which makes it the largest planet in the Solar System.
- The mass of Jupiter is 0.001 times that of the sun while more than twice the combined mass of all planets in the solar system.
- Jupiter is known to astronomers since the ancient past or antiquity.
- Currently, the spacecraft of NASA, Juno Orbiter, is exploring Jupiter.

2. What Is Jupiter Named After – Jupiter Origin Of Name
- Except for Earth, all the planets in the Solar System are named after the ancient Roman or Greek gods.
- The origin of the name Jupiter is the Roman god “Jupiter”, who was also known as “Jove”.
- In the ancient Roman religion and myths, Jupiter was the god of the sky and thunder.
3. What Type Of Planet Is Jupiter
- Jupiter is a “Gas Giant” type of planet.
- Like the sun, its atmosphere comprises mostly hydrogen and helium gases.
4. What Is Jupiter Known For
- Jupiter is known for:
- Being the largest planet in the Solar System
- Being the fastest spinning planet in the Solar System
- Having the largest number of moons (79)
- Having a system of rings
- Its iconic Great Red Spot
5. Characteristics Of Jupiter – Jupiter Features
- The following are the major characteristics of Jupiter Planet:
- Jupiter is a large and massive planet of all the planets of the solar system.
- The density of Jupiter is relatively low.
- It rotates rapidly as compared to any other planet in the solar system.
- The atmosphere of Jupiter is opaque and thick.
- Its diameter is 142,984 km, which is 11 times greater than the diameter of Earth.
6. Special Features Of Jupiter – Unique Features Of Jupiter
- The following are some of the unique and special features of Jupiter:
- The most unique feature of Jupiter is its iconic Great Red Spot. It is a storm like a giant hurricane. It continues to exist for more than 300 years.
- Jupiter is 2.5 times heavier than the combined mass of all the other planets in the Solar System.
- Its spinning speed is higher than all the planets in the Solar System.
- It has 79 moons.
- The magnetic field of Jupiter is 14 times stronger than the magnetic field of the Earth.
7. Jupiter Physical Properties
- The following are some of the main physical properties of Jupiter:
| Property | Value |
| Composition | Liquid and gaseous matter |
| Diameter (at its equator) | 142,984 km (88,846 mi) |
| Average density | 1.326 g/cm³ |
| Mass | 1.8982×1027 kg (4.1848×1027 lb) |
| Surface area | 6.1419×1010 km2 (2.3714×1010 sq mi) |
| Volume | 1.4313×1015 km3(3.434×1014 cu mi) |
| Rotation period | 9.925 hours (9 hours 55 minutes 30 seconds) |
| Mean surface temperature | 165 K (-108℃) |
| Mean surface pressure | 20 – 200 kPa |
8. Is There Water On Jupiter
- Yes, water is found in the cloud tops of Jupiter in the form of vapors.
- Some moons of Jupiter also have water or water ice.
- The Europa moon is believed to have a surface ocean of salty water.
- A recent study by Gordon Bjoraker, who is an astrophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provides hints that water found in the Great Red Spot of Jupiter.
9. What Does Jupiter Look Like – Jupiter Appearance
- Jupiter looks like a ball with a pattern of many color strips and the Great Red Spot.
- The pattern of stripes is clouds of brown, orange, red, and white colors.
10. What Color Is Jupiter – Jupiter Planet Color
- The outer atmosphere of Jupiter is mostly composed of hydrogen and helium gases with a little amount of water vapor and ice crystals, crystals of ammonia, and other elements.
- The clouds of all these elements make the colors white, red, orange, and brown.
11. What Does Jupiter Look Like From Earth – Jupiter From Earth
- When Earth and Jupiter come to their closest point, the distance between them remains only about 365 million miles (588 million kilometers).
- Jupiter looks brightly glowing from the Earth at night.
- After the Moon and Venus, it is the third brightest natural object in the sky at night.
12. What Does Jupiter’s Surface Look Like
- There is no true surface of Jupiter as it is a gas giant.
- Due to thick gaseous clouds of brown, orange, red, yellow, and white colors, the surface of Jupiter looks like a ball with colored stripes.
13. Where Is Jupiter Located – Jupiter Location
- Jupiter is located at the fifth number from the sun in the solar system.
- Its Right Ascension (RA) is 17 hours, 35 minutes, and 25 seconds.
- While its Declination is -23° 7′ 57″
- It spins at a distance of about 778 million kilometers (484 million miles) from the Sun.
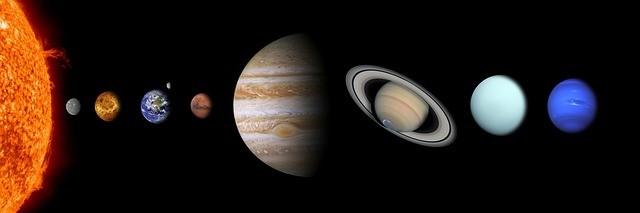
14. Where Is Jupiter Located In The Solar System
- In the Solar System, Jupiter is located at the fifth position from the Sun.
- It orbits between Mars and Saturn.
- Jupiter is also located near the Asteroid Belt, which spins between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
15. Where Is Jupiter In The Sky – Jupiter Location In Sky
- Jupiter comes to the opposition (become aligned with earth and sun) once after every 399 days.
- It is observable throughout the year, however, more easily and brighter when coming to the opposition.
- Currently, Jupiter appears in the early evening. In the Northern Hemisphere, Jupiter appears in the southwest sky at mid-northern latitudes.
16. What Is The Size Of Jupiter – Jupiter Size
- The radius of Jupiter is 69,911 km (43,440.7 miles).
- While the surface area is 6.1419×1010 km2 (2.3714×1010 sq mi).
- No other planet in the Solar System has such a big size.
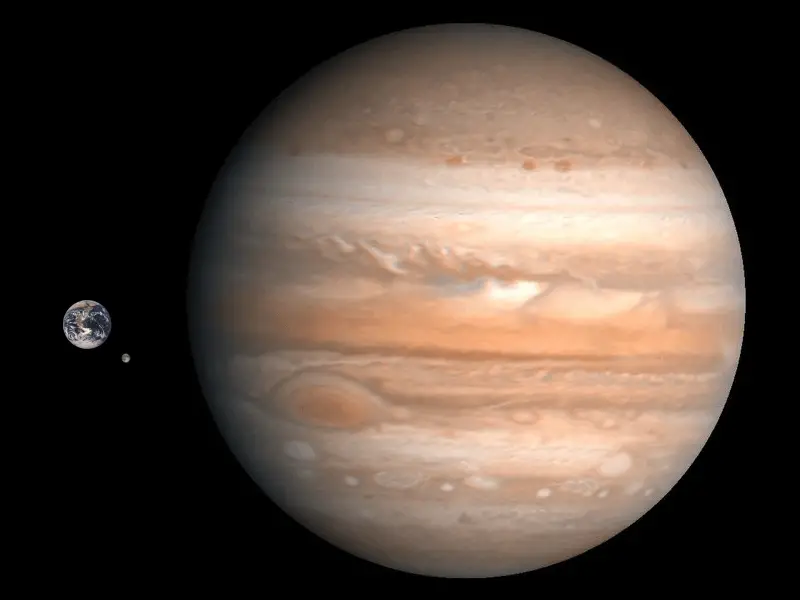
17. How Large Is Jupiter Compared To Earth – Jupiter Vs Earth Size
- The radius of Jupiter is 69,911 km (43,440.7 miles), while the radius of Earth is 6,371 km (3,958.8 miles).
- The surface area of Jupiter is 6.1419×1010 km2 (2.3714×1010 sq mi), while Earth’s surface area is 5.1×10⁸ km2 (1.969×10⁸ square miles).
- So Jupiter is 11 times bigger than earth.
- If compared simply, we can say that Earth would have a size of a nickel while Jupiter would have the size of a basketball.
18. What Is The Diameter Of Jupiter – Jupiter Diameter
- The diameter of Jupiter is 139,829 km (86,881 miles).
19. What Is The Mass Of Jupiter – Mass Of Jupiter (Mass Of Jupiter)
- The mass of Jupiter is 1.898 × 1027kg (317.8 M⊕).
Jupiter Mass Compared To Earth
- If we compare the sizes of Earth and Jupiter, we will know that Jupiter is 11 times bigger than Earth.
- Despite its bigger size, Jupiter is only 318 times more massive than Earth.
- This is due to the difference between the densities of both planets.
- The density of Jupiter is 1.33 g/cm³, which is extremely low as compared to the density of Earth (5.51 g/cm³).
Mass of Jupiter Compared To Sun
- The radius of Jupiter is approximately 1/10 the radius of the Sun.
- While the mass of Jupiter is 0.001 times the mass of the Sun.
- It means that both Sun and Jupiter have similar densities.
22. What Is The Gravity On Jupiter – Jupiter Gravity
- Gravity on Jupiter is 2.528 g (24.70 m/s).
Jupiter’s Surface Gravity
- The surface gravity of Jupiter is defined as the gravitational force at its cloud tops.
- Jupiter’s surface gravity is 2.528 g (24.70 m/s).
Jupiter Gravity Compared To Earth
- Jupiter is a massive planet as compared to Earth, so its gravitational pull is also stronger than Earth.
- Earth’s gravity is 1 g (9.807 m/s), while Jupiter’s gravity is 2.528 g (24.79 m/s), which is 2.4 times greater than Earth.
- So an object or human being of 100 kg would weigh 240 kg on Jupiter.
Gravitational Pull Of Jupiter
- Gravity or gravitational force is the attraction force of two bodies towards each other.
- Everything having mass also has a gravitational pull.
- The gravitational pull of massive objects is stronger than less massive objects.
- Jupiter’s gravitational pull is 25.79 m/s, which is 2.4 times stronger than Earth’s gravitational pull.
23. What Is The Temperature Of Jupiter – Jupiter Temperature
- On Jupiter’s clouds, the temperature is approximately -145 °C (-234 °F).
- The temperature of Jupiter is driven by its inner part, not by Sun.
- So unlike Earth (where the temperature changes when one moves far away or closer to the equator), the temperature on Jupiter mostly depends on the height from the surface.
What Is The Average Temperature On Jupiter – Jupiter Average Temperature
- The average temperature on Jupiter is -145 °C (-234 °F).
What Is The Surface Temperature Of Jupiter – Jupiter Surface Temperature
- Scientists identify the Jupiter surface as the region where the surface pressure is equal to the Earth’s surface pressure (1 bar).
- However, nothing can stand on Jupiter’s surface as it is gas.
- The surface temperature of Jupiter is -145 °C (-234 °F).
What Is The Temperature Range On Jupiter – Jupiter Temperature Range
- In the clouds of Jupiter, the temperature is about -145 °C (-234 °F).
- In the atmosphere of Jupiter, the temperature changes in the layers of the gas region.
- About 50 km (30 miles) above the surface, the temperature decreases and ranges from -100 °C (-150 °F) to -160 °C (-260 °F).
- The source of temperature is not Sun, but the inner region of Jupiter.
- So inside the clouds, the temperature increases to 67 °C (-152 °F) at a 10 bar pressure level.
- At the transition phase (where the hydrogen is in the metallic form), the temperature is 9.700 °C (17,500 °F).
- Near the center of the planet, the temperature is extremely high and may be approximately 24,000 °C (43,000 °F) at the core region, which is hotter than the Sun’s surface.
24. What Is Jupiter Made Of – What Is Inside Jupiter
- Jupiter is a gas giant planet and is mostly composed of hydrogen and helium.
- It is believed that there is a dense innermost layer or Core.
- The Core is thought to consist of a mixture of elements.
- Liquid metallic hydrogen and some helium surround the Core.
- The outer cloudy part of Jupiter is composed of molecular hydrogen with traces of some other elements like helium, ammonia, methane, and water vapor.
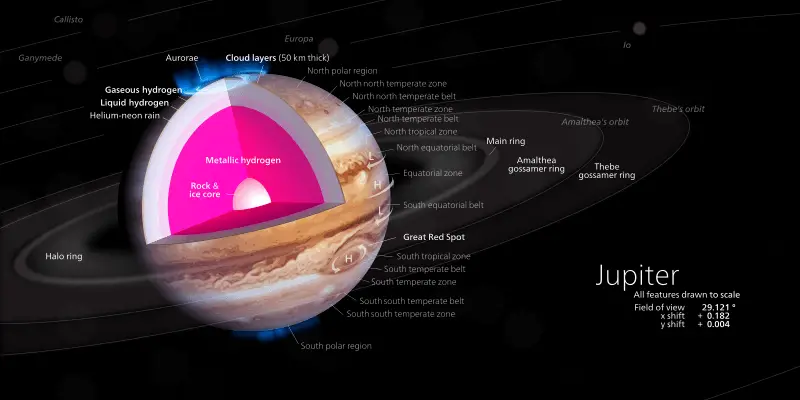
25. Layers Of Jupiter
- Scientists believe that Jupiter is composed of :
- The Core or innermost layer
- Liquid metallic hydrogen layer
- Liquid molecular hydrogen layer
- 50 km thick cloudy layer
26. History Of Jupiter – History Of Jupiter Planet
- Since the ancient past, Jupiter is known to astronomers as it is so big and can be observed with the naked eye.
- On 7 January 1610, Galileo Galilei discovered the moons of Jupiter with the help of a telescope.
- In 1831, the Great Red Spot of Jupiter was discovered. Samuel Heinrich Schwabe was the first person who observed the Great Red Spot.
- In 1944, two astronomers (Barnard Burke and Kenneth Franklin) discovered the rotating speed of Jupiter around its axis with the help of radio transmissions. They found with their calculations that the length of Jupiter’s day is only about 10 hours.
- In 1979, the NASA spacecraft Voyager 1 and 2 approached Jupiter and sent important photographs and information through which scientists discovered the Ring System around Jupiter.
- In 1995, Galileo Orbiter was the first successful spacecraft to orbit around Jupiter. This spacecraft discovered the volcanic activity and its strength on the moon Io. It also found the presence of ammonia clouds in the atmosphere of Jupiter, which was its major discovery. Other findings of the Galileo Orbiter was the evidence about the presence of saltwater below the ice surface of the moons Europa, Callisto, and Ganymede. The mission of Galileo Orbiter was ended in 2003.
- On 4 July 2016, the space probe “Juno” was sent by NASA to explore Jupiter.
27. Chemical Composition Of Jupiter – Jupiter Composition
- Jupiter is a gas giant type of planet and is mostly composed of hydrogen and helium.
- The atmosphere of Jupiter, which makes up the whole planet is mainly composed of molecular hydrogen (H2) and helium. Relative to the solar atmosphere, argon, krypton, and xenon noble gases are found in abundance while neon is found in scarce amounts. Other simple compounds are also found in the atmosphere, such as water vapor, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and phosphine (PH3). A trace amount of other chemical compounds are also present such as arsine (AsH3), and germane (GeH4). Simple hydrocarbons such as ethane, acetylene, and diacetylene are also found in small amounts. Other chemical compounds are carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.
- The composition of the core region is unknown, however, it is often described as rocky.
28. What Is Jupiter’s Surface Made Of – Jupiter Surface Composition
- Jupiter is a gas giant and there is no solid surface to touch down on.
- Scientists identify the region as the surface of Jupiter where the pressure is equal to the surface pressure of the Earth (1 bar).
- This region is known as the “troposphere” and has a complicated cloudy structure.
- The upper clouds of the troposphere, where pressure ranges between 0.6 and 0.9 bar, are composed of ammonia ice.
- Below the clouds of ammonia ice are denser clouds where the pressure ranges between 1 and 2 bar. It is made of ammonium hydrosulfide ((NH4)SH) or ammonium sulfide ((NH4)2S.
29. Jupiter Core Composition
- Scientists are not sure about the existence of a solid core inside Jupiter.
- So the composition of the core is unknown, however, it is often described as solid and rocky.
30. What Is The Atmosphere Of Jupiter
- The atmosphere of Jupiter makes up the whole planet and is the largest planetary atmosphere in the Solar System.
- There is no clear lower boundary in the atmosphere of Jupiter and it gradually changes into the planet’s liquid interior.
- Jupiter’s atmosphere is divided into the following 4 layers from lowest to highest:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere
- Each layer has a specific temperature gradient.
- To study the atmosphere of Jupiter is a major science target for the Juno mission of NASA, which is currently exploring Jupiter.
What Is Jupiter’s Atmosphere Made Of – Jupiter’s Atmosphere Composition
- The atmosphere of Jupiter is mainly composed of molecular hydrogen and helium in roughly similar solar proportions.
- A small amount of other chemical compounds are also found in Jupiter’s atmosphere, such as ammonia, methane, hydrogen sulfide, and water vapor.
- It is believed that water is found in the deep atmosphere, however, its directly measured concentration is extremely low.
- Sulfur and nitrogen as well as noble gases argon, krypton, and xenon are in abundance in the atmosphere of Jupiter and surpass the solar proportions by a factor of approximately 3.
- Other compounds found in small amounts in Jupiter’s atmosphere are arsine (AsH3), germane (GeH4), phosphine (PH3), carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, acetylene, and diacetylene.
What Is The Atmosphere Like On Jupiter
- The atmosphere of Jupiter is thick and cloudy.
- There are storms in some regions, particularly on the Great Red Spot where the pressure is constantly high.
31. What Is Jupiter’s Distance From The Sun – Jupiter Distance From The Sun
- Jupiter’s distance from the sun is 778.5 million kilometers (484 million miles).
- More exactly, it is 778,547,200 km.
- In other words, the distance of Jupiter from the sun is 5.2 AU (Astronomical Units).
- One Astronomical Unit means, the distance of Earth from the Sun.
32. Distance From Earth To Jupiter
- The distance from Earth to Jupiter is 628,743,036 km when both planets are at their closest positions to each other.
- At their most far away position, the distance is 928,081,020 km, as all the planets in the Solar System follow an elliptical orbit.
- This distance in Astronomical Units is 4.2 AU at the closest position and 6.2 AU at the most distant position.
33. Jupiter Climate
- The climate of Jupiter is cold.
- In the cloudy region, the climate is colder than Antarctica with a temperature of about -145 °C (-243 °F).
- Near the planet’s center, the temperature becomes extremely hot.
34. What Is The Weather On Jupiter – Jupiter Weather
- Jupiter experience extreme patterns of weather.
- There are storms in some regions that grow only in a few hours to up to a thousand kilometers in diameter.
- Wind storms, auroras, and lightning also happen in some regions of the planet.
- The Galileo Orbiter had made images of lightning on the night side of Jupiter. The extreme weather of Jupiter can be observed from space.
35. Is Jupiter Habitable – Is Jupiter Livable – Life On Jupiter
- Jupiter is an unlikely place for living things as the environment is not supportive of life.
- No organism can adopt the temperature, pressure, and all the materials Jupiter is made of.
- However, the moon of Jupiter Europa is one of the places elsewhere on Earth in the Universe where life could be possible.
- There is evidence of a vast saltwater ocean beneath the icy crust of Europa.
- Jupiter is not habitable because:
- The gravity of Jupiter is double Earth’s gravity
- There is no oxygen in Jupiter’s atmosphere
- The temperature is extremely cold at 1 bar pressure level
- There are clouds and no firm surface to touch down
- So Jupiter is not livable as its overall environment is not supportive and habitable for any kind of life.
36. What Is Jupiter’s Great Red Spot – Jupiter Red Spot
- The Great Red Spot is an extremely high-pressure region in Jupiter’s atmosphere.
- It is the largest anti-cyclonic storm of the Solar System.
- It is located in the south of the equator of Jupiter.
- The diameter of the Great Red Spot is approximately 24,000 km, while its height is about 12 to 14,000 km.
- Its size is 2 to 3 times greater than the size of Earth.
- It has been existing for at least 350 years.
- It is believed that Italian astronomer Giovanni Cassini was the first person who observed and identified the Great Red Spot in 1665.
- During the 20th century, astronomers started to theorize that what Cassini observed was a storm that Jupiter’s fast-moving and turbulent atmosphere created.
- The theory was confirmed true when the Voyager-1 spacecraft closely approached Jupiter in 1979 and observed the Great Red Spot from a very near position.
- Based on Cassini’s observations, astronomers estimate the 17th-century size of the Great Red Spot about double its current size.
- So the Great Red Spot has been appeared to be reduced in size since that time.
- According to astronomers, it is unknown when will be it completely disappear. However, they are relatively sure that at the end of it, another would appear somewhere else in the Jupiter atmosphere.
Where Is The Great Red Spot Located
- The Great Red Spot is located 22 degrees south at the equator of Jupiter.
37. What Is The Rotation Of Jupiter – Jupiter Rotation
- The rotation of Jupiter means its rotation around its axis.
- Like many other planets of the Solar System, Jupiter also rotates in a counter-clockwise direction from west to east.
- All planets in the solar system orbit around the Sun in the same direction.
Jupiter Rotation Period – Jupiter Rotation Time
- The rotation period of Jupiter around its axis is 9.9 hours.
- As Jupiter is the fastest rotating planet of the Solar System, it has the shortest day of all the planets in the Solar System.
38. What Is The Revolution Of Jupiter – Jupiter Revolution
- The revolution of Jupiter means the rotation of Jupiter around the sun in its orbit.
- Jupiter is at an average distance of 480 million miles (788 million km) from the Sun.
- So it takes about 12 Earth years to complete its one revolution around the Sun.
Jupiter Period Of Revolution – Jupiter Revolution Time
- Jupiter’s period of revolution is nearly 12 years.
- So one year of Jupiter is equal to the 11.86 years of the Earth.
39. Jupiter Missions
- Jupiter’s exploration was included in the nine space missions that were visiting outer space.
- The missions were:
Pioneer 10
- NASA Ames Research Center in California conducts this American space exploration project.
- It was launched in 1972 and fly by Jupiter in 1973.
Pioneer 11
- Pioneer 11 or Pioneer G is a robotic space probe.
- NASA launched it in 1973 to study the environments around Jupiter and Saturn, the asteroid belt, cosmic rays, and solar winds.
Voyager 1
- NASA launched Voyager 1 space probe on 5 September 1977.
- The main objective of Voyager 1 were flybys of Jupiter, Saturn, and Titan (the largest moon of Saturn).
- This space probe is still effective and communicates with the Deep Space Network of NASA.
Voyager 2
- NASA launched this space probe on August 20, 1977.
- Voyager 2 flyby Jupiter in 1979, Saturn in 1981, Uranus in 1986, and Neptune in 1989.
Galileo
- Galileo’s spacecraft was launched to study Jupiter, its moons, and other bodies in the Solar System.
- Space Shuttle Atlantis launched on October 18, 1989, from Earth and it reached near Jupiter on December 7, 1995.
Ulysses
- Ulysses was a collaborated venture of NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and the National Research Council of Canada.
- The major mission of Ulysses was to orbit and study the sun, however, it also encountered Jupiter for a gravity-assist maneuver.
Cassini-Huygens
- It is commonly known as just “Cassini” and was launched in 1997.
- It was jointly conducted by NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and ASI (Italian Space Agency).
- Its major purpose was to study Saturn, its rings, and moons.
- However, flybys of Venus, Earth, Jupiter, and the asteroid 2685 Masursky were also included in this mission.
New Horizons
- New Horizon was an interplanetary space probe.
- NASA launched it in 2006 as part of its New Frontier Program.
- The main mission of the spacecraft was a flyby study of Pluto.
- It also closely approached Jupiter in 2007 and sent information about its atmosphere, magnetosphere, and moons.
Juno
- Juno is the space probe of NASA orbiting around Jupiter.
- The probe was launched in 2011 and reached the polar orbit of Jupiter in 2016.
- Juno is a special mission for Jupiter to study its composition, gravitational and magnetic fields, and polar magnetosphere.
40. How Many Spacecrafts Have Visited Jupiter
- Nine spacecraft have been launched to explore Jupiter.
- However, 4 of the spacecraft have been also visited Saturn, while one, Voyager 2, also visited Uranus and Neptune.
41. What Are The Moons Of Jupiter – Jupiter Moons
- Moons of Jupiter are the natural satellites orbiting around Jupiter.
- Scientists think that Jupiter has 79 moons.
- Out of 79, 53 moons are officially named while the other 26 are waiting to be named officially.
- Of all the Jupiter moons, the Gelalian moons are the largest and are of the most scientific interest.
- Many of the moons rotate in the opposite direction of Jupiter’s spin around its axis.
- The revolution period of moons around Jupiter ranged between 7 hours and three Earth years.
How Many Moons Does Jupiter Have – Jupiter Number Of Moons
- The number of known moons of Jupiter is 79.
What Is Jupiter’s Largest Moon – What Is Jupiter’s Biggest Moon
- The largest moon of Jupiter is Ganymede.
- It is bigger than the planet Mercury.
42. Titan Moon Facts
- Titan is the largest moon of Saturn.
- After Ganymede, it is the 2nd largest moon in the Solar System.
- It is the only known moon in the Solar System to have a substantial atmosphere.
- After Earth, Titan is the only known body in the Solar System to have surface liquid in the form of lakes, rivers, and seas.
- Titan is a planet-like moon, which is about 50% larger and 80% more massive than the moon of Earth.
What Is Titan Made Of
- The primary composition of Titan is ice and rocky material.
- The core region of Titan is rocky. Various layers of ice surround the core.
- The subsurface layer is made of ammonia-rich liquid water.
- Like Earth, the atmosphere of Titan is mostly made up of nitrogen, however, the surface pressure is extremely high (about 50% higher than Earth’s surface pressure).
- According to the information the 2004 Cassini-Huygens mission provided, there are lakes, rivers, seas, clouds, and rain of liquid hydrocarbons in Titan.
What Does Titan Look Like
- In photos from space, Titan looks yellowish-brown due to its thick atmosphere.
- According to scientists, the surface and other conditions on Titan are mostly similar to that of early Earth.
43. What Is Europa – Jupiter’s Moon Europa
- Europa is one of the four Galilean moons of Jupiter, and the 6th largest moon in the Solar System.
- It is also the smallest Galilean moon orbiting Jupiter.
- Of all the known 79 moons of Jupiter, Europa is the 6th closest moon to the planet.
- Galileo Galili discovered it in 1610.
- The surface of Europa is mostly made up of silicate rocks and has a crust of ice-water.
- There is evidence that an ocean of salty water exists beneath the ice crust.
- The moon was named “Europa” after the mother of King Minos.
- In Greek mythology, Minos was the first king of Crete and the son of Zeus (Greek god of thunder and sky, and an equivalent of the Roman god Jupiter).
Life On Europa
- There is no evidence about the existence of any kind of life in Europa.
- However, scientists say that there is a probability that the deep ice-ocean has a similar environment to hydrothermal vents of the Earth’s deep-ocean where life could exist.
Is Europa Habitable
- It is thought that Europa has double the amount of water as does Earth.
- This moon has the potential for having a habitable zone, so it always fascinates astrobiologists.
44. What Are The Galilean Moons – Galilean Moons Facts
- Galilean moons are the four moons of Jupiter, which Galileo Galili discovered in 1610.
- German astronomer Simon Marius also claimed that he observed the moons around the same time. However, he did not publish his work and so Galileo is credited for the discovery.
- Galilean moons are Jupiter’s largest moons and are also known as the Galilean Satellites.
- Galileo called it Cosmica Sidera (Cosimo’s stars) at the start of his discovery.
- Simon Marius gave them the names Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto after the lovers of the Greek god Zeus.
- After the Sun and eight planets, Galilean moons are among the largest bodies in the Solar System.
45. What Is Ganymede
- Ganymede is a Galilean moon of Jupiter.
- It is the most massive and largest moon in the Solar System.
- Ganymede is the 9th largest body in the Solar System and is ever bigger than the planet Mercury.
- Its diameter is 5,268 km, which is 1.08 times that of Mercury and 0.41 times that of Earth.
- It is the only known moon in the Solar System to have a magnetic field.
- It completes one orbit around Jupiter in roughly seven days
Life On Ganymede
- There is no evidence of life on Ganymede.
- Its atmosphere and overall environment are unlikely to inhabit any kind of living organism.
Ganymede Mass
- The mass of Ganymede is 1.4819×1023.
Ganymede Gravity
- The surface gravity of Ganymede is 1.428 m/s² (0.146 g).
Ganymede Temperature
- The average surface temperature of Ganymede is -163 °C (-325 °F).
- The minimum temperature is -203 °C (-397 °F), while the maximum is -121 °C (249 °F).
46. Fun Facts About Jupiter For Kids
- After the Moon and Venus, Jupiter is the 3rd brightest natural body in the sky at night.
- Jupiter was named after the god of sky and thunder in ancient Roman mythology.
- The volume of Jupiter is so big that 1,300 planets of our Earth’s size can be easily fit in it.
- On Jupiter, there is no solid or firm surface for an object to touch down.
- The gravitational field of Jupiter is 2.4 times that of the Earth. So a man of 100 kg would have a bodyweight of 240 kg on Jupiter.
47. Interesting Facts About Jupiter For Kids
- In the Solar System, Jupiter is the fastest spinning planet around the sun, which means it has the shortest days of all planets.
- Jupiter takes approximately 12 Earth years to complete one rotation around the sun.
- The temperature at the core region of Jupiter is hotter than the sun’s surface.
- After the sun and 8 planets, Jupiter’s moon Ganymede is the 9th largest body in the Solar System.
- The magnetic field of Jupiter is 14 times stronger than that of the Earth.
- It is believed that Jupiter’s magnetic field is one of the contributing factors, which protect our planet Earth from the worst fall of meteoroids.
- Jupiter was the representation of the Marduk god for Babylonians. They used to define their zodiac constellations along with the 12-year orbit of Jupiter.
48. FAQs About Jupiter:
Where To Find Jupiter In The Night Sky
- In different countries, Jupiter appears at different times.
- In the Northern Hemisphere, Jupiter appears in the southwest sky at mid-northern latitudes at the time of dusk.
Could We Live On Jupiter – Living On Jupiter – Does Jupiter Support Life
- Living on Jupiter is impossible as it is a gas giant and has no solid surface.
- There is no oxygen and the overall environment is uninhabitable for any kind of life.
What Is The Distance Between Earth And Jupiter
- The distance between Earth and Jupiter at their closest positions is 628,743,036 km (4.2 AU).
- The distance when both planets are far away from each other is about 928,081,020 km (6.2 AU).
Is It Hot Or Cold In Jupiter
- Jupiter is much cooler.
- At the outer region of the atmosphere, the temperature is about -145°C.
- Even the warmest weather in Jupiter is colder than Antarctica.
Is There Water On Europa
- Astronomers thought that there is a saltwater ocean beneath the icy crust of Europa.
- There is no evidence of life on Jupiter.
- The overall environment of Jupiter can not support any kind of life.
