Koala is one of the cutest animals that are only found in Australia. They are marsupials just like Kangaroos and have a pouch to carry their babies. We have gathered complete sets of Koala Facts For Kids that will provide you with all the Koala Information For Kids you need. You are going to learn all about Koalas, their definition, scientific name, taxonomy, meaning, appearance, description, types, evolution, size, weight, color, lifespan, habitat, diet, lifecycle, reproduction, baby facts, predators, endangerment, adaptations and many other interesting facts about Koalas.
Koala Facts For Kids
1. What Is A Koala – Koala Definition
- Koala is a marsupial or pouched mammal indigenous to Australia.
- It is the only living species of the Phascolarctidae family.
- It is also the living closest relative of the wombat.
- Koalas are herbivores in nature and mostly eat the leaves of eucalyptus.
- They are arboreal and live in the eucalyptus trees in the open woodlands.
- It is a 2 to 2.7 feet long animal with a stocky body, a large head with fluffy ears, and a spoon-like nose.
- Koala is one of the most iconic animals in the world and distinguished as a symbol of Australia throughout the world.
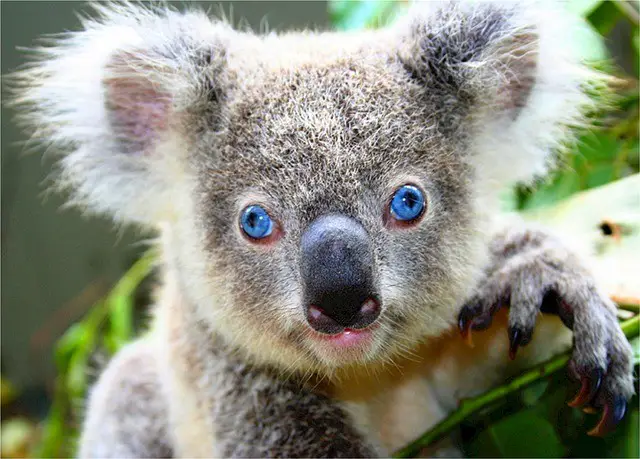

2. Koala Scientific Name – Koala Bear Scientific Name
- The scientific name of koala is Phascolarctos cinereus.
3. What Does Koala Mean – Koala Meaning – Koala Meaning In English
- The origin of the word koala is the Darugh (Sydney language) word ‘gula’, which means ‘no water.
- It was believed once that these animals can survive without drinking water, as they were not often observed coming down from the trees.
- In English orthography, the ‘u’ in the word gula was originally written as ‘oo’, which was possibly changed to ‘oa’ due to an error.
4. What Do Koalas Look Like – Koala Appearance
- A koala is a beautiful animal that looks cuddly and innocent.
- It is a medium-sized animal with a stocky body that lacks a tail.
- Koalas have big round ears covered with fur from both inside and outside.
- They have big, spoon-shaped noses.
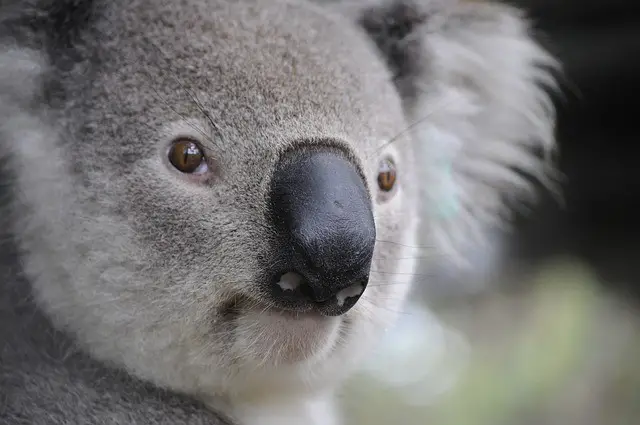

5. Are Koalas Dangerous
- Koalas are generally not dangerous until they are threatened.
- If humans threaten them, they are observed chasing humans with a long distance and then scratching and biting them with their sharp claws and front teeth.
6. Are Koala Bears Bears
- No, koalas are not bears.
- People, especially the early settlers in Australia, wrongly called them the koala bears because of their supposed resemblance to bears.
7. Koala Classification – Koala Taxonomy
- The following is the scientific classification or taxonomy of koala:
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Sub-phylum | Vertebrata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Infraclass | Marsupialia |
| Order | Diprotodontia |
| Family | Phascolarctidae |
| Genus | Phascolarctos |
| Species | Phascolarctos cinereus |
8. What Are Koalas Related To
- Koalas are closely related to kangaroos and wombats.
9. What Type Of Animal Is A Koala
- Koala is a “Marsupial” or pouched type of animal, the females of which have a special pouch to raise their young ones.
10. Where Do Koalas Come From – Koala Evolution
- Koala-like animals probably evolved on the continent of Australia around 45 million years ago.
- The discovered fossil remains of koala-like animals date back to 25 million years ago.
- Koalas lived in the rainforests during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs, where they had no specialized diet.
- The continent of Australia started drying out during the Miocene, the rainforests declined and the open eucalyptus woodlands spread out.
- During the late Miocene, the genus Phascolarctos (the current genus of koala) split from the genus Litokoala (an extinct genus of marsupials that was closely related to modern koala).
- Several physical adaptations occurred in their body that allowed them to survive on a specialized eucalyptus diet, such as; their palate (roof of the mouth) shifted towards the front of their skull, the molars and premolars grow larger, pterygoid fossa became smaller, and the gap between the incisors and molar teeth became larger.
- When Australia experienced climate and vegetation changes during the Pliocene and Pliestocene, the species of koalas grew larger.
- The existing koala species (P. cinereus) probably emerged as a dwarf form of a giant koala.
11. Koala Species – Types Of Koalas
- Koala is the only species of its kind.
- However, koalas are divided into three types based on fur color, fur thickness, and the habitat region:
- Brown Koalas are the biggest of all koalas. They have brown color fur, which is also the thickest of all koalas fur. They are found in the Southern region of Australia.
- Grey Koalas have fur of grey color. They have the smallest size of all koalas. They are found in the Queensland region of Australia.
- Grey-brown Koalas have a mixed grey and brown fur color. They are found in the New South Wales region of Australia.
12. Koala Characteristics – Koala Features
- Koalas are marsupials and the females have a special pouch-like structure in which they raise their younger ones.
- Their bodies are covered with thick fur which acts like a raincoat.
- They are arboreal and live in the trees.
- They eat a specialized diet mainly composed of eucalyptus leaves.
- Koalas have the smallest brain of any mammals relative to their body weight.
- They have highly developed senses of smell and hearing. However, they do not have sharp vision.
- Koala is a sexually dimorphic species. The males have a 50% larger body size than females. Males also have more curved noses and special scent glands on their chests.
13. How Big Is A Koala Bear – Koala Bear Size
- The body size of koalas ranges from 60 to 85 cm (24 to 33 inches).
- Males usually have a 50% larger body size than females.
- Koala is among the biggest arboreal species of marsupials.
- An adult koala has 24 to 33 inches body length and 4 to 15 kg body weight.
How Tall Are Koalas – Koala Height
- Adult fully grown koalas have 2 to 3 feet in height.
How Heavy Is A Koala – Koala Weight
- Koala has 4 to 15 kg (9 to 33 pounds) body weight.
- Koalas found in the Victoria region have double bodyweight than those found in the Queensland region.
14. What Color Is A Koala Bear – Koala Color
- Koalas usually have a light-grey to the chocolate-brown color of fur.
- Their chest, bottom, and inner-sides of the arms and ears have whitish fur, the rump has dapple-whitish fur, while their backs and outside region of the ears have dark fur.
15. Koala Physical Description
- A koala is a sturdy animal with a large round head.
- It has no actual tail and has only a vestigial tail or non-existing tail.
- An adult koala has an average body size of 24 to 33 inches and 4 to 15 kg body weight.
- Koala is a sexually dimorphic species and males usually have a 50% larger body size than females.
- Males have special chest glands, while they also have more curved noses than females.
- As koala is a marsupial species, the females have pouches with mammary glands where they raise their babies.
- Koalas have longer and thicker fur on the backside and shorter on the belly.
- Their ears have long and thick fur both outside and inside.
- Koalas have large forepaws with sharp, curved claws and two opposable digits, which allows them a strong grasp on small tree branches.
- They also have friction ridges on their paws, just like humans and other primates.
- Koalas have hard bottoms like wombats, which allows them to comfortably wedge on tree forks for long intervals.
16. Koala Jump
- Koalas are observed jumping from branch to branch and even tree to tree.
- For koalas, jumping is a secure option to swap trees and avoid predators.
- However, koalas can jump only a few meters, and they can not cover long distances through jumping.
- Young koalas are commonly observed practicing their jumping between small branches.
17. Koala Speed
- On the ground, the running speed of a koala is around 32 km/h.
18. Koala Swimming
- Koalas can swim if they fall in a river or swimming pool in the search of water.
19. Koala Climbing
- Koalas have amazing climbing abilities.
- Their sturdy skeleton, short and muscular upper body, and long upper limbs enhance their grasping and climbing abilities.
- They climb through bounding, in which their two forelimbs reach forward as one while their hindlimbs push off.
20. Where Do Koala Bears Live – Koala Habitat
- Koalas are indigenous to the continent of Australia.
- They are found in mainland eastern Australia and some islands off the eastern and southern coasts.
- They live in a variety of habitats, including coastal islands, tall eucalypt forests, and low inland woodlands.
- The presence of koalas’ favorite tree species along with fertile soil and proper rainfall and the presence of other koalas are the factors that make a habitat suitable for koalas.
- It is thought that koalas once lived in rainforests millions of years ago when much of Australia was covered with rainforests.
- However, the present koalas do not inhabit desert or rainforest regions.
Where Do Koalas Live Map – Koala Habitat Map
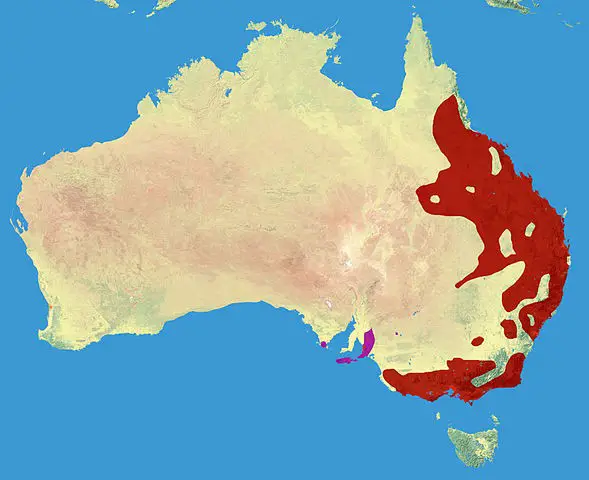
Koala Natural Habitat
- The eucalyptus forests in Australia are the natural habitat of koalas.
What Trees Do Koalas Live In
- Koalas mostly prefer to live in the eucalyptus trees.
- However, they may also live in other tree species.
Where Do Koalas Live In The Wild
- Koalas are naturally found in the wild only in Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, and South Australia.
- There, they mostly live in the eucalyptus woodlands.
What Country Do Koalas Live In
- Koala lives only in Australia.
21. What Do Koalas Do
- In the 24 hours of the day, koalas eat for 2 to 6 hours.
- While they spend much of their time sleeping and dozing; 18 to 22 hours per day.
22. How Long Do Koalas Sleep – Koalas Sleep Facts
- Koalas get 18 to 22 hours of sleep per day.
- To sleep, they tucked in tree nooks or forks to stay protected.
- Koalas get such a huge amount of sleep in 24 hours because of their diet, which has a very low amount of nutrition. So they mostly sleep and stay inactive to conserve energy.
- On hot days, koalas climb down to rest on the coolest part of the tree. They lie on their stomach or with their back against a branch and with their limbs hanging.
- For losing heat without panting, koalas usually hug the tree branches while sleeping.
- During cold and wet days, they curl their body while sleeping to conserve heat.
- Koalas are commonly nocturnal, however, they also get sleep in parts of the night and sometimes move around during the daytime.
Koala Sleep Time – Koala Sleep Hours
- The daily sleep time of a koala is 18 to 22 hours.
- They sleep during both daytime and night.
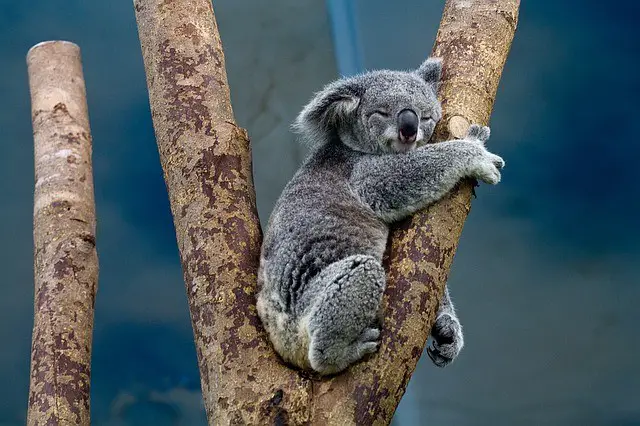

23. How Long Do Koalas Live – Koala Lifespan – Koala Life Expectancy
- The lifespan or life expectancy of koalas in the wild is 13 to 20 years.
- In captivity, they live longer than 20 years.
Average Lifespan Of A Koala
- According to National Geographic, the average lifespan of koalas in the wild is 20 years.
- Another source (Australian Koala Foundation) describes its average lifespan in the wild as 10 years.
Koala Lifespan In Captivity
- In captivity, koalas live longer than their wild relatives because of a good diet, care, and protection from diseases and predators.
- They are known for living more than 18 to 20 years in captivity.
24. Koala Life Cycle Facts
- The lifecycle of a koala starts when it is born after a gestation period of 33 to 35 days.
- It continuously stays and feeds in the mother’s pouch for about six months.
- After six months, a baby starts coming out from the pouch and gradually transforms into a leafy diet.
- A baby is completely weaned at the age of one year.
- Females become sexually mature at the age of 3 years while males mature at the age of 4 years.
- They start breeding in the middle of spring to summer or early autumn.
- Females usually reproduce in alternate years probably because of the high dependency of the babies.
- Koalas live for an average of 12 years of life in the wild.
25. What Do Koalas Eat – Koala Bear Diet
- Koalas are herbivores in nature and they fulfill most of their nutritional requirements by eating plant matter.
- They mostly consume the leaves of eucalyptus, however, they can be also found in the trees of other species.
- The daily consumption of leaves for adult koalas is from 200 to 500 grams.
What Leaves Do Koalas Eat
- Koalas mostly eat the leaves of eucalyptus trees.
- They choose fresh, juicy, and newly emerged leaves with high water content.
What Trees Do Koalas Eat
- Koalas usually consume the leaves of eucalyptus trees.
- However, they are also observed consuming leaves of other tree genera, such as Acacia, Callitris, Leptospermum, Allocasuarina, and Melaleuca.
- Their favorite tree species are Eucalyptus microcorys, Eucalyptus camaldulensis, Eucalyptus teriticornis.
What Do Koalas Eat In The Wild
- In the wild, koalas eat the foliages of eucalyptus trees.
What Do Koalas Eat-In Captivity
- In captivity, koalas are fed with eucalyptus foliages.
- According to the San Diego Zoo, fresh branches from several eucalyptus tree species are offered to koalas every day, from which they choose their favorite varieties. The daily consumption of koalas there is 454 to 680 grams of leaves.
26. Koala Diet And Eating Habits
- Koalas mostly eat the foliages of eucalyptus.
- There are more than 600 species of eucalyptus, however, only around 30 of them are the favorite of koalas.
- Koalas are choosy and select only those species, which have a high content of proteins and low amounts of fiber and lignin.
- Because of the high water content in eucalyptus leaves, koalas usually do not often need to drink water.
- During feeding, koalas usually hold onto a tree branch with their two hind paws and one forepaw while the other forepaw is used for grasping leaves.
- Large koalas stay near the thick bases of tree branches when feeding while younger koalas go to the end of branches.
- They take four to six feeding sessions to fulfill their daily food requirement of 200 to 500 grams of leaves.
27. How Do Koalas Reproduce – Koala Reproduction
- Koalas reproduce through sexual reproduction.
- They are seasonal breeders and the middle spring to summer or early autumn is their breeding season.
- The females usually mate only once a year.
- To find mates, females experience oestrus during the breeding season.
- Males usually do not recognize the oestrus signs of the females and often mount with non-estrous females.
- Males attract the females by screams, vocal calls, and marking trees with their scents.
- Several males usually fight for a single female mate.
- After finding suitable mates, koalas mate, and the females become pregnant.
- A single baby (sometimes twins) is born after a gestation period of 33 to 35 days.
Koala Reproductive System
- Koala is a marsupial mammal (pouched mammal) and has a much different reproductive system than placental mammals.
- Like most other marsupial species, male koalas have bifurcated penises that have two separated columns with two ends. Their penis is not associated with the urinary tract and is used only for copulation. Their penis also has a covering of foreskin (known as the penile sheet) which has naturally occurring bacteria that play a vital role in fertilization.
- Similarly, the female koalas have two lateral vaginas and two separate uteri.
- The females have pouches that contain a circular muscle known as a sphincter at its opening point that keeps the raising youngsters from falling out.
28. Baby Koala Facts – Koala Bear Baby Facts
- A baby koala (known as a joey) is born after a gestation period of 33 to 35 days.
- Like other marsupial species, baby koalas are also born in an underdeveloped form or during the embryonic stage.
- A baby koala has only 0.5-gram weight at birth.
- Even born immature, baby koalas have well-developed fore-limbs, shoulders, and lips as well as functioning digestive, urinary, and respiratory systems.
- After birth, the baby koalas crawl to their mothers’ pouches where their further development continues.
- Within the pouch of a female koala is two teats. The baby attaches itself to one and suckles throughout its pouch life.
- At the seven-week of a baby’s life, its head becomes bigger, pigmentation starts to develop, and its sex can be determined with the appearance of the scrotum in males and the start of pouch development in females.
- At the age of 13 weeks, the weight of joey reaches around 50 g, and its head size becomes double. Fine hairs grow on their forehead, nape, arms, and shoulders. They also start to open their eyes.
- At the age of 26 weeks, a joey’s body became fully covered with fur. It resembles the adults and starts poking its head out of the pouch.
- At the age of 9 months, the bodyweight of joey reaches over 1 kg. They develop adult fur coloring. At this age, they permanently leave the pouch and depend on their mothers’ backs for transportation.
- They are completely weaned at the age of 12 months when their body weight becomes 2.5 kg.
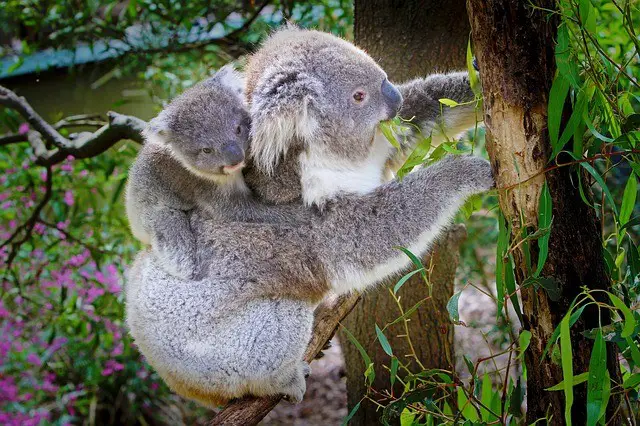

What Is A Baby Koala Called
- A baby koala is called a joey.
What Do Baby Koalas Eat
- Baby koalas suckle milk from one of their mothers’ two teats in the pouch.
- When they reach around six months of age, the mothers start to prepare them for the eucalyptus diet.
- The mothers start producing faecal pap through pre-digesting the eucalyptus leaves, which the joeys eat from her cloaca.
- The pap has a completely different composition than the regular feces of koalas. It has a high concentration of bacteria and has a similar composition to the content of the caecum.
- Baby koalas eat pap at the time of their transition from milk to leaf diet. They eat it for about a month as a supplementary source of proteins.
- They are fully weaned at the age of 12 months and they start eating a complete leafy diet.
29. Do Koalas Have Predators – What Are Koala Predators
- Yes, koalas have predators.
- Their predators are the carnivore animals found in their habitat.
- However, natural predators have no significant impact on their wild population.
- Carnivore animals of 6 species are the regular predators of koalas.
- They are:
- Wild dogs
- Dingoes
- Wedge-tailed eagle or Bunjil
- Pythons
- Owls
- Goannas
30. Koala Adaptations
Koala Physical Adaptations – Koala Structural Adaptations
- The following are the physical or structural adaptations of koalas:
a. Dental system
- The dental system of koalas consists of incisors and cheek teeth that have a single premolar and four molar teeth on each jaw.
- Like herbivore mammals, a large gap separates their incisors and cheek teeth.
- They grasp leaves through incisors which are then passed to the premolars for snipping at the petiole and then to the molars for crushing and chewing.
- They also can store food in their cheek pouches before chewing.
- Koalas sometimes also regurgitate the food into the mouth to chew it for the second time and extract more nutrients and energy.
b. Thick fur
- The thick and wooly fur of koalas provides them insulation and protection.
- It acts as a protective raincoat on their bodies, which repels moisture and keeps their bodies warm and dry.
c. Paw structure
- The paw structure of koalas along with sharp and curved claws is a special adaptation for arboreal life.
- They have spread fingers that look like two thumbs, which allows them a stronger and better grip on the tree branches.
- Both fore and hind limbs have similar toes which provide them the same grip and so one of their forelimbs is free for grasping leaves.
d. Hard and cushioned bottom
- Koalas have hard cartilage at the end of their curved spine, which makes their bottoms hard.
- The hard and cushioned bottoms of koalas allow them to easily and comfortably poke in the tree branches.
- It also protects them from harm when they accidentally fall from the trees.
e. Scent glands
- Male koalas have strong scent glands through which they attract their mates.
Koala Behavioral Adaptations
- Koalas sleep for 18 to 22 hours a day to conserve energy.
- Koalas are choosy eaters and prefer to eat the leaves of only around 30 out of 600 eucalyptus tree species.
- They live in societies that consist of residents (mostly adult females) and transients (mostly adult males).
- When an adult male enters a new tree, he marks it by rubbing his scent gland against the trunk or branches. This scent-marking behavior is probably for communication, as the koalas are known for sniffing the tree bases before climbing.
- Adult male koalas make loud bellow sounds to communicate. Their bellows have low frequency and travel long distances along with air. The bellow of a male indicates its size that attracts females. The bellows of the females are soft and associated with screams, wails, and snarls.
- Koalas are social and live in the form of communities. When one community dies, the other does not take over for about a year until their scent fades.
Koala Adaptations For Survival
- All the above adaptations of koalas are for their survival. However, there are some other special adaptations of koalas to survive on the highly toxic and low nutrition value of the eucalyptus diet.
- Koalas are hindgut fermenters and have a single-chambered simple stomach.
- In the wild, their digestive retention lasts for about 100 hours and about 200 hours in captivity.
- Their caecum has an extraordinary size of up to 80 inches long and 4 inches in diameter.
- Their digestive system can select which particles would be retained for long fermentation and which ones would be gone.
- Koalas produce Cytochrome P450 enzyme, which enables their digestive system to break down the toxins present in the eucalyptus leaves. They digest the toxins in the liver.
- Their caecum also stores water by passing dry feces in the form of pellets that have a high amount of undigested fibers.
31. Are Koalas Going Extinct – Why Are Koalas Going Extinct
- No, koalas are not going extinct.
- Koala is included in the list of vulnerable species of the IUCN Red List.
Koala Extinction Status – Koala Conservation Status
- Koala is not extinct.
- Its conservation status on the IUCN Red List is as a Vulnerable Species.
32. Are Koalas Endangered – Why Are Koalas Endangered
- No, koalas are not endangered.
- However, some factors are causing threats to their survival in the wild.
- The major threats are:
- The loss of habitat because of deforestation and construction of the cities in their natural habitat.
- Injuries and deaths from the increased traffic
- Diseases like the koala’s retrovirus (KoRV) and koala immune deficiency syndrome (KIDS) which is similar to human AIDS as well as other severe bacterial and viral infections.
- Koalas are also extremely vulnerable to bushfires in the forests of Australia because of their slow movement and high flammability of eucalyptus trees.
- Climate change is also a serious threat to their survival.
33. How Many Koalas Are Left In The World – Koala Population – Koala Numbers
- According to the Australian Koala Foundation, the estimated population of koalas in the wild is less than 100,000 or as few as 43,000 individuals.
- It is unknown how many koalas are found in zoos or the private captivity of people.
How Many Koalas Are Left In The Wild
- The estimated number of koalas left in the wild is as greater as 100,000 and as fewer as 43,000 individuals.
34. Koala Conservation Centre
- Koala Conservation Center is a nature preserve located in the Phillip Island nature park, Victoria, Australia.
- There, koalas can be viewed while walking on boardwalk trails.
35. Why Are Koalas Important
- Koalas are important because they play an important role in the ecosystem of their habitat.
- The leaves of eucalyptus have oil that can easily catch fire.
- Koalas consume the leaves of eucalyptus and reduce the risk of intense fires in the forests.
- They also serve as food for large carnivore animals found in their habitats, such as marsupial lions, a giant python, and a giant goanna.
- Their presence and thriving in the forests is an indicator of a healthy ecosystem.
36. Koala Books
- The following are some of the famous books about koalas for kids:
- ‘Koala’ by Claire Saxby
- ‘The Koala Book’ by Ann Sharp
- ‘The Koala Who Could by Rachel Bright
- ‘Koala Lou’ by Mem Fox
- ‘Explore My World Koalas’ by Jill Esbaum
37. Interesting Facts About Koalas
- Koalas are sometimes wrongly called koala bears, however, these animals are marsupials, not bears, and have no close relationship with bears.
- Koalas eat eucalyptus leaves as their diet that has less nutritional value and energy. That is why they mostly stay inactive and spend most of their time sleeping to conserve energy.
- Koalas have a specially adapted fiber-digesting organ known as the caecum, which detoxifies toxins found in the eucalyptus leaves.
- Koalas have five digits on their paws just like humans. Their forepaws have two opposing digits that can move in different directions from the others. It provides them a strong grip on branches and helps in climbing.
- The hind paws of koalas have 2nd and 3rd digits in fused form, which they use for grooming.
- Loss of habitat is the biggest threat to the survival of koalas. About 80% of their habitat has been lost by humans, bushfires, and drought.
38. Fun Facts About Koalas For Kids
- Koalas are found only in the continent of Australia and nowhere else in the world.
- It is one of the national symbols of Australia.
- In the Aboriginal language of Australia, the word “koala” means ‘no drink’. It was given such a name because its diet has enough moisture and it is not often observed for drinking water.
- Koalas spend much of their time resting and sleeping for 18 to 22 hours a day.
- A baby koala stays for six months in the mother’s pouch. It then rides on the mother’s back for another six months.
