Earth is our home and the only astronomical object where life exists. When compared to the whole universe, the Earth is not more than a speck but within it, such wonder of life exists that is found nowhere in the universe. We have gathered a complete collection of Earth Facts For Kids that will help you in learning all the facts about the Earth that you want to know. You are going to learn its definition, description, other names, meaning, characteristics, physical properties, its size, history, rotation, surface, composition, seven layers, statistics, and many other interesting facts about the Earth.
Earth Facts For Kids – Facts About The Earth
1. What Is Earth – Planet Earth Definition – Introduction Of Earth
- Earth is the third planet in the solar system from the sun and our home planet in which we live.
- Earth is at an average distance of about 93 million miles from the sun.
- Scientists believe that earth was formed about 4.5 billion years ago, nearly at the same time as the rest of the solar system was formed.
- Moon is the only natural and permanent satellite of the planet earth.
- In space, Earth revolves around the sun.
- It completes one orbit in 365.26 days and this time is known as the Earth year.
- During one year, Earth rotates about 366.26 times around its axis.

2. Describe Earth As A Planet – Description Of Earth
- Earth is the third planet of the solar system orbiting the sun.
- With a diameter of about 8,000 miles, it is the fifth-largest planet in the solar system.
- It is the only known planet in the solar system that contains free atmospheric oxygen, the largest amount of liquid water, and life.
- Earth is one of the four rocky or terrestrial planets of the solar system (the other three are Mercury, Venus, and Mars), in which Earth is the largest one.
- In the solar system, Earth is the densest of all the other planets.
3. Why Is Earth A Planet
- An astronomical object in the solar system is considered as a planet if:
- It orbits the sun
- Enough massive to be round from its gravity
- Has cleared the neighborhood region of its orbit of planetesimals
- Earth fulfill all the criteria and therefore is a planet.
4. Other Names For Earth – Scientific Name For Planet Earth
- There is no special scientific name for planet Earth because it is the only planet of its type.
- The word “Globe” is also often used to refer to the planet Earth.
- While “World” means the planet Earth and all life exists on it.
5. Who Named Our Planet Earth
- It is unknown who named our planet Earth.
6. What Is The Meaning Of Earth Planet
- The word “Earth” is derived from the old English words “eor(th)e” and “ertha” and from the German word “erde”.
- All three words have the same meaning as “ground”.
7. Why Do We Call Our Planet Earth
- The origin of the word “Earth” is the eighth-century Anglo-Saxon word “erda” the meaning of which is “soil” or “ground”.
- This word later became “eorthe”, which then became “erthe” in Middle English.
- In the early years of the 15th century, the word “Earth” was used for the first time as the name of the planet Earth.
- Since after that time, our planet is called by the name of “Earth”.
8. Characteristics Of Planet Earth – Features Of Earth Planet
- Earth is the only special planet of the Solar system that contains life due to the presence of liquid water in abundance and free atmospheric oxygen.
- Earth has an oblate spheroidal shape.
- The mass of Earth is approximately 5.97x10²⁴.
- Earth revolves around the sun and completes its one round in 365.26 days.
- The axis of rotation of the Earth is at a constant tilt to its orbital plane, which results in the changing of seasons on the Earth.
- Earth also revolves about its own axis and complete one rotation in 24 hours.
- The orientation of Earth on its axis is stabilized by the oceanic tides (the rise and fall of sea level), which are caused by the gravitational interaction between Earth, Moon, and the Sun.

9. Physical Properties Of Planet Earth
- The following are the physical properties of the planet Earth:
Shape
- Earth’s shape is spherical, but approximately of the oblate spheroidal type, due to its rotation.
- At the equator, it is slightly bulging while flattened at the poles.
- The equatorial diameter of Earth is 27 miles (43 km) larger than its diameter from pole to pole.
Chemical Composition
- Earth is chemically composed mostly of iron, oxygen, silicon, magnesium, sulphur, nickel, calcium, aluminum, and other elements.
Heat
- There are two sources of the internal heat of the Earth; residual heat from planetary accretion (approximately 20%) and radioactive decay (80%).
- The temperature may be up to 10,830°F (6,000°C) at the central point, while the pressure could be 52 million psi.
Force Fields
- There are two major force fields of the Earth;
- Gravitational Field is the force at a distance that attracts objects towards the center of the Earth, or toward any other objects having mass.
- The gravitational force holds down the oceans, atmosphere, etc.
- Magnetic Field of the Earth is mainly generated in the core.
- Earth’s rotation and the presence of iron in the Earth’s core are the main factors that create a magnetic field.
10. Is The Earth A Globe
- Yes, the Earth is a globe.
11. How Big Is Planet Earth – What Is The Size Of Planet Earth
- The radius of the Earth is 6,371 km.
- Its total surface area is 510.1 million km².
- Its equatorial circumference is 40,075 km while its axial (from pole to pole) circumference is 40,008 km.
- Its mass is 5.97 x 10²⁴ kg.
12. What Is The Diameter Of The Earth – Diameter Of Planet Earth
- The diameter of Earth is 12,742 km.
13. Where Is Earth
- As there is no edge or center of the Universe, so a particular reference point does not exist to plot a comprehensive location of Earth in the Universe.
- However, our planet Earth and the entire solar system are located in the “Orion”.
- Orion is one of the four spiral arms of the Milky Way Galaxy.
14. History Of Earth – History Of Planet Earth
- Our planet Earth came into being approximately 4.54 billion years ago.
- It was formed from the solar nebula (a collection of gas and dust clouds in outer space) through accretion (particles accumulation into a massive object through the gravitational attraction of more matter).
- The early atmosphere of the Earth and then the oceans were probably created by the release of volcanic gases.
- It is believed that there was no oxygen in the early atmosphere of the Earth.
- At that time, much of the Earth was in molten form due to the frequent collision with other bodies, which resulted in the highest volcanism.
- Moon is thought to be formed by the collision of the early Earth with a giant body named “Theia”, which had the size of a planet.
- The Earth then cooled over time, as a result of which a solid crust formed that allowed liquid water on the surface.
- The earliest accepted evidence of life on Earth dates back approximately 3.5 billion years ago.
- Between 3.2 and 2.4 billion years ago, the photosynthetic organisms appeared that started the atmosphere to be enriched with oxygen.
15. Is The Earth 6000 Years Old
- No, Earth is much older than 6,000 years.
- Scientific research reveals that Earth is about 4.54 billion years old.
16. Earth 4.5 Billion Years Ago
- It is believed that the planet Earth has formed 4.5 billion years ago.
- It is thought that Earth at that time was so hot that it was in molten form.
- There was no oxygen or life.
- The moon was formed approximately at that time.
17. Earth 50 Million Years Ago
- 50 million years ago, there was an initial Eocene Epoch (which began 56 million and ended 34 million years ago) on Earth.
- At that time, the continents of the Earth continued to move towards their present-day positions, however, Antarctica and Australia were still together.
- There was an exceptionally low concentration of the Carbon-13 (¹³C) isotope in the atmosphere as compared to the most common Carbon-12 (¹²C) isotope.
- The dinosaurs had become extinct 15 million years ago (dinosaurs became extinct around 65 million years ago from the present day).
- The prehistoric mammals continuously adapted to the climate and spread.
18. Earth’s Rotation
- Earth’s rotation means the rotational motion of the Earth around its axis.
- Earth rotates eastward and turns in the counterclockwise direction in prograde motion (the rotational motion of a body in the same direction of its primary).
- At the North Pole, the axis of rotation of Earth meets its surface.
- While at the South Pole (in Antarctica), the axis of rotation of Earth intersects its surface.
- Earth completes its one rotation to the sun in about 24 hours.
- With time, the rotation of the earth is slightly slowing with about 2.3 milliseconds per century.
19. The Earth And The Solar System
- The solar system is consists of the sun and all the objects bound to it by gravity and orbit it.
- The eight planets are the largest of all the objects that orbit the sun.
- After Mercury and Venus, Earth is the third planet that rotates around the sun.
- Of the four closest planets to the sun, Earth is the biggest one.
- The entire solar system (including the planet Earth) is situated in the Orion Spur or Orion Arm of the Milky Way.
20. Where Is Earth In The Solar System
- After Mercury and Venus, Earth is the third closest planet to sun in the solar system.
- After the Earth are Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, which are respectively further away from the sun.
21. What Number Planet Is Earth
- Earth is the 3rd number planet that rotates around the sun.

22. Closest Star To Earth
- Other than the sun, the Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to Earth.
- Alpha Centauri is consists of three stars; Alpha Centauri A (Rigil Kentaurus), Alpha Centauri B (Toliman), and Alpha Centauri C (Proxima Centauri).
- The Proxima Centauri is the closest one to Earth, which is at the distance of about 4.22 light-years from the Earth.
- The other two, Alpha Centauri A and Alpha Centauri B, are at the average distance of 4.3 light-years from Earth.
23. Distance From Earth To Sun
- 93 million miles is the average distance from Earth to the sun.
24. Meteor Close To Earth
- A meteor is informally known as a shooting star or falling star.
- A meteor is a small body of matter in space that becomes incandescent when entering into the atmosphere of Earth.
- The incandescence is due to its collision with air molecules in the upper atmosphere of Earth.
- A meteor looks like a streak of light in the sky, due to its rapid motion and sometimes due to shedding glowing material in its emergence.
- Usually, meteors occur at elevations from 250,000 to 330,000 feet (76 to 100 km), in the mesosphere.
- Every day, millions of meteors occur in the atmosphere of Earth.
25. Earth Map
27. Surface Of Earth – Surface Description Of Earth
- Planet Earth has a total surface area of approximately 197 million square miles (510 million km²).
- Of this, 139.43 million sq miles (361.13 million km²), which is about 70.8%, is covered by the oceans.
- The remaining 57.51 million square miles (148.94 million km²), which is about 29.2%, is not covered by water and is consists of landforms including mountains, hills, plateaus, valleys, plains, and deserts.
- The lowest elevation point of the land surface is -418 meter (-1,371 feet), the shores and surface of the Dead Sea.
- The highest elevation point is 8,848 meters (29,029 feet), the top of Mount Everest.
- 10.9% of the total land surface is arable land (land used to grow crops), out of which 1.3% is permanent cropland.
28. What Is In The Earth – What Is Planet Earth Made Of
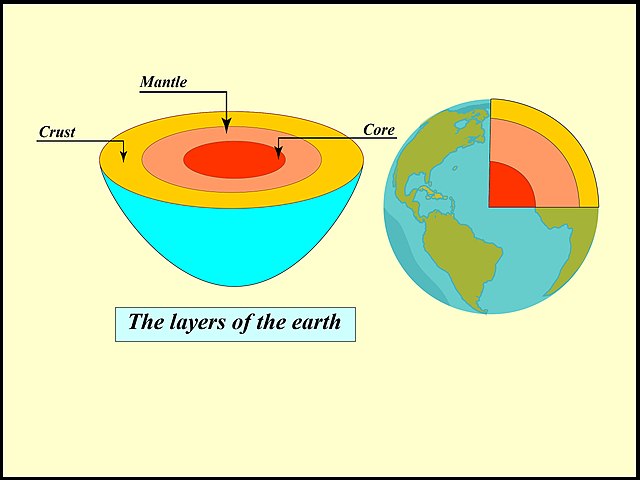
The planetary body of Earth is generally divided into four basic layers;
The Inner Core
- It is the innermost part of the Earth in its middle and is believed to be made up of an iron-nickel alloy. It may have a temperature like that of the sun’s surface (approximately 5505°C).
The Outer Core
- It is the part just above the inner core and below the mantle. This part is liquid and is made up of iron and nickel. It is approximately 2,260 km thick. Its temperature ranges from 6100°C (near the inner core) and 4,400°C in the outer region near the mantle.
The Mantle
- It is a layer above the outer cover and below the crust. It is the most massive and largest layer of the Earth’s planetary body and has about 67% of the total Earth-mass while 84% of the total Earth’s volume. It is 2,900 km (1,800 miles) thick. This layer is made up of silicate rocks.
The Crust
- It is the outermost, rocky surface layer of the Earth. It is made up of silicon, aluminum, iron, calcium, sodium, potassium, and magnesium. About 70% of the crust is covered by liquid water. The atmosphere mainly consists of nitrogen and oxygen with a little amount of carbon dioxide, water vapors, and other gases.
29. 7 Layers Of The Earth
- Mechanically, the structure of the Earth can be divided into 7 layers, which are:
The Lithosphere
- It is the outermost rigid layer, which includes the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle. It is approximately 60 km (37 miles) deep.
The Asthenosphere
- It is the second region of the upper mantle that lies below the lithosphere. It is a highly viscous zone. It is about 80 to 200 km (50 to 120 miles) deep below the surface. The Lithosphere and Asthenosphere are collectively known as the Upper Mantle.
Transition Zone
- It lies at the depth of 410 to 660 km (255 to 410 miles) below the Earth’s surface. In this region, rocks undergo a radical transformation.
Lower Mantle
- It lies at the depth of 660 to 2,700 km (410 to 1,678 miles).
D Double-Prime (D”)
- It is another layer. This layer is about 200 km thick. It lies beneath the Mantle. In some regions, it lies as a thin boundary with the outer core, while in other regions it lies like a thick iron and silicates accumulation.
The Outer Core
- It lies above the inner core. The outer boundary of the outer core lies about 2,890 km (1,800 miles) below the surface of the Earth.
The Inner Core
- It is the innermost central region the outer boundary of which lies at about 5,150 km (3,200 miles) beneath the Earth’s surface.
31. Composition Of Planet Earth – Chemical Composition Of Earth
- The following table shows the percent chemical composition of the oceanic (liquid part) and continental (solid or dry part) Earth parts.
| Compound | Formula | Oceanic Composition | Continental Composition |
| Silica | SiO₂ | 48.6% | 60.6% |
| Alumina | Al₂O₃ | 16.5% | 15.9% |
| Lime | CaO | 12.3% | 6.41% |
| Magnesia | MgO | 6.8% | 4.66% |
| Iron Oxide | FeOT | 6.2% | 6.71% |
| Sodium Oxide | Na₂O | 2.6% | 3.07% |
| Potassium Oxide | K₂O | 0.4% | 1.81% |
| Titanium Dioxide | TiO₂ | 1.4% | 0.72% |
| Phosphorus Pentoxide | P₂O₅ | 0.3% | 0.13% |
| Manganese Oxide | MnO | 1.4% | 0.10% |
| Total | 99.9% | 100.1% |
- The composition of a dry atmosphere is 78.084% (Nitrogen), 20.946% (Oxygen), 0.934% (Argon), and the remaining little amount is other gases and Carbon dioxide.
32. Planet Earth Statistics
- The following is a brief statistic of the planet Earth:
| Mass | 5.98x10²⁴ kg |
| Diameter | 12,753 km (7,926 miles) |
| Density | 5.51 g/cm³ |
| Surface gravity | 9.807 m/s² |
| Surface temperature | -89°C to 56.9°C |
| Surface pressure | 101.325 kPa |
| Surface area | 510.1 million km² |
| Circumference | 40,075.017 km |
| Orbital semimajor axis | 1.000 001 02 AU |
| Tilt of axis | 23.5° |
| Rotation period with respect to the sun | 24 hours |
| Rotation period with respect to stars | 23 hours 56 minutes |
| Minimum distance from the sun | 91 million miles (146 million kilometers) |
| Maximum distance from the sun | 94.5 million miles (152 million kilometers) |
33. Proof The Earth Is Round
- The most common and easy proof of the round shape of the Earth is the observation of the sunset.
- On the ground floor of our homes, the sun set quickly, however, at the same time, it is visible on the upper floor.
- If the Earth had a flattened shape, there would be no sun visibility at any altitude once it had set.
- Photos of the Earth taken from the International Space Station are the biggest proof.
34. Life On Planet Earth
- Microfossils evidence reveals that life on the planet Earth began about 3.465 billion years ago.
35. Special Features Of Earth Planet – Earth Is A Unique Planet
- The existence of liquid water and life makes the planet Earth unique from the other planets.
36. Other Planets Like Earth
- According to scientists, there may be billions of Earth-sized planets, even alone in the Milky Way Galaxy.
- The recently confirmed planet (on 23 July 2015) that has the most similar size and temperature to the Earth is Kepler-438b.
37. When Is Earth Day – World Earth Day
- 22 April is celebrated as Earth Day all around the world to demonstrate support for environmental protection.
38. Earth Hour
- Earth Hour is an annual movement organized by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) all over the world.
- The event is held at the end of March on a specific day as a symbol of dedication to the planet.
- People, communities, and businesses are encouraged to turn off non-essential electric lights from 8:30 to 9:30 pm, for one hour.
39. Amazing Facts About Earth
- Earth is approximately 4.5 billion years old.
- Earth is the only known planet in the Universe to have life.
- Earth completes one rotation around its axis in 23 hours, 58 minutes, and 4 seconds not exactly in 24 hours.
- Moon is the only natural satellite of the Earth.
40. Interesting Facts About Earth – Fun Facts About Earth – Interesting Facts About Earth For Kids
- Earth is the only planet of the solar system the name of which was not came after the Roman and Greek gods and goddesses.
- According to many scientists, the presence of human beings is the most special feature of the planet Earth.
- The rotation of the earth is slightly slowing with time (2.3 milliseconds per century) and thus days in the past were slightly shorter.
- The presence of iron in the molten outer core of the Earth causes the generation of a magnetic field that protects life on the Earth from being harmed.
- The atmosphere of the Earth extends up to 10,000 km.
- Earth completes one rotation around the sun in 365.256 days, not exactly in 365 days. The .256 part is adjusted as an extra day in the Leap year.
- The axial tilt of the Earth (23.439°) causes seasonal climate changes.
- The gravitational interaction between Earth, Moon, and the sun causes the ocean tides (the rise and fall of sea level).