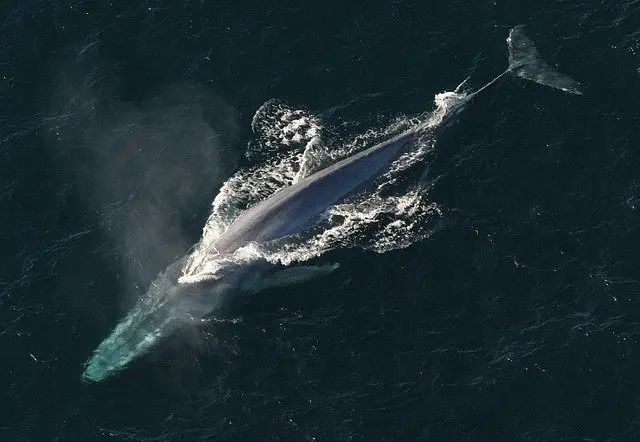
Blue Whale is well known around the world for being the largest living animal on earth. It looks like a fish and lives in water but it is a mammal, this makes it even more interesting for kids. We have gathered a complete set of Blue Whale Facts For Kids that includes all the Blue Whale Information that kids would want to know. Kids are going to learn about its appearance, classification, size, weight, height, sound, diet, habitat, life cycle, breeding, its body parts, adaptations, baby whale, hunting, and many Blue Whale Fun Facts.
Blue Whale Facts For Kids
1. What Is Blue Whale
- Blue Whale is the largest known animal that has ever lived on the planet earth.
- It is a marine mammal and survives in oceanic and marine ecosystems.
- Blue Whale belongs to the “Mysticeti” pervader of baleen whales, which are also known as Whalebone Whales.

2. Blue Whale Scientific Name
- The scientific name for Blue Whale is “Balaenoptera musculus”.
3. What Does A Blue Whale Look Like – Blue Whale Appearance
- A Blue Whale has a giant tapered body with a wide flat head and a broad triangular tail fluke.
- It looks blue underwater, however, on the water surface, its color ranges from mottled grey to blue.

4. Blue Whale Classification
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Subphylum | Vertebrata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Cetacea |
| Suborder | Mysticeti |
| Family | Balaenopteridae |
| Genus | Balaenoptera |
| Species | Balaenoptera musculus |
5. Blue Whale Description – Blue Whale Characteristics
- Unlike other whales that have the thickest body, Blue Whales have a tapered body structure.
- They have a U-shaped head and a protruding ridge that goes in the direction from blowhole to upper lip.
- They have a wide mouth with baleen (a special system inside the mouth of filter-feeders) plates at the front region.
- They have small dorsal fins with an average height of 11 inches and different shapes in every individual.
- They have a pair of blowholes, which are protected by a wide and large structure resembling a splash guard.
- They have 10 to 13 feet (3 to 4 meters) long flippers.
- Their body color ranges from slate-grey to dark blue and is usually densely mottled.
6. What Color Is A Blue Whale – Blue Whale Color
- The color of the upper body sides of a Blue Whale is generally grey with a narrow white border, while the lower body parts are white.
- The tail fluke and the head usually have consistent grey colors.
- Blue Whales have usually mottled flippers on the upper body sides and every individual has a different mottling degree.
- All Blue Whales demonstrate a consistently mottled body color that ranges between uniform slate-grey, grey, dark blue, and black.
7. What Sound Does A Blue Whale Make – Blue Whale Sounds – Blue Whale Noise
- A Blue Whale can create sounds with fundamental frequencies between 10 to 40 Hz.
- Mainly, Blue Whales make three types of sounds; pulsed calls, clicks, and whistles.
- A sound produced by a Blue Whale may last between 10 to 30 seconds.
- According to researchers, recognition of physical surroundings, navigation, and social communication are the possible reasons for making these sounds.
- In the ocean near Sri Lanka, Blue Whales’ “songs” of four sound notes have been recorded, each one of which lasted for approximately 2 minutes.
8. Blue Whale Echolocation Facts for Kids
- Echolocation, also called Biosonar, is the utilization of echoes and sound waves to visualize the orientation of objects in their surroundings.
- Echolocating animals produce sounds in the environment and then listen to the reverberations of those sounds that return from different objects in their surroundings.
- Blue Whale is one of the animals that echolocate by producing several kinds of sounds, which are commonly known as “songs”, to communicate and navigate underwater.
- They also detect their prey and predators by echolocation.
9. Is The Blue Whale The Biggest Animal Ever- Blue Whale Largest Animal Ever
- Yes, Blue Whale is the biggest animal ever known on the earth.
- A Blue Whale has a body length of up to 98 feet (29.9 meters) and a maximum bodyweight of 173 tonnes.
- No other animal of such size has been found on earth.
10. How Big Is A Blue Whale – Blue Whale Size Facts for Kids
- Generally, female Blue Whales have a longer body length than male individuals.
- While male individuals of the same length often have a heavier body weight than females due to heavier bones and muscles.
- The average size of a Blue Whale is 98 feet (29.9 meters) with a bodyweight of approximately 176.5 tonnes.
11. Biggest Blue Whale Ever – Largest Blue Whale In The World – Largest Recorded Blue Whale
- The recorded largest Blue Whale were two females with body lengths of 109 feet (33.3 meters) and 110 feet (33.6 meters).
- The recorded largest male Blue Whale was 104 feet (31.7 meters) long that was caught in 1926 near the South Shetland Islands.
12. Blue Whale Size Comparison – Blue Whale Size Chart
- The following is the size comparison chart of Blue Whale with other Whale species.
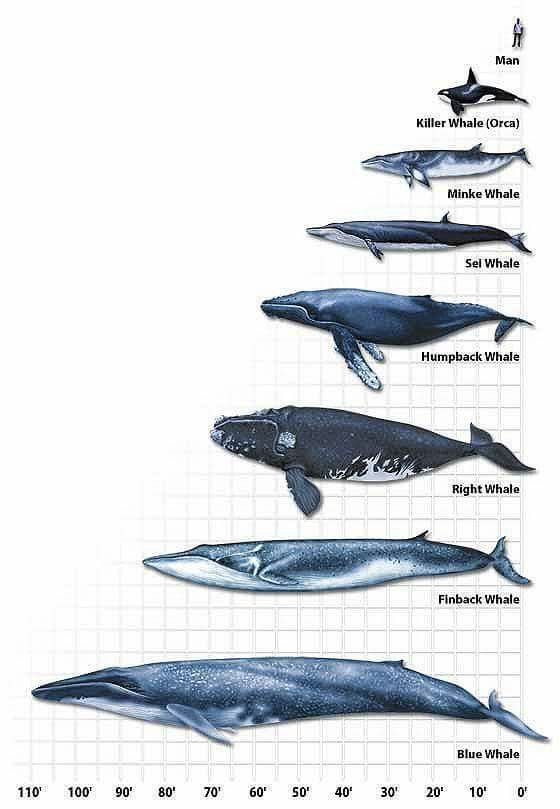
13. Blue Whale Compared To Elephant
- A Blue Whale is extremely large as compared to an elephant.
- Only the tongue of a Blue Whale (2.7 tones or 2,700 kg) is equal to the weight and size of an African forest elephant (2,700 kg).
- A Blue Whale with a weight of 173 tonnes is approximately 28.8 times greater than an African bush elephant (6 tonnes body mass), 32 times bigger than an Asian elephant (5.4 tonnes), and 64 times bigger than an African forest elephant (2.7 tonnes).
Recommended for Reading: Elephant Facts For Kids
14. How Long Is A Blue Whale – Blue Whale Length
- The average verified body length of a Blue Whale is 98 feet (29.9 meters).
How Many Feet Is A Blue Whale – Blue Whale Length In Feet
- The average body length of a Blue Whale in feet is 98 feet.
15. How Much Does A Blue Whale Weigh – Blue Whale Weight – Blue Whale Mass Facts for Kids
- The recorded average body weight of a Blue Whale is 173 tonnes.
How Heavy Is A Blue Whale
- Male Blue Whales are slightly heavier than female individuals with a maximum body weight of 140,000 kg.
Blue Whale Weight In Pounds
- The maximum bodyweight of a Blue Whale in pounds is 381,400 pounds.
How Much Does A Blue Whale Weigh In Tons – Blue Whale Weight In Tons
- The maximum verified weight of Blue Whale in tons is 190 tons.
16. How Do They Weigh A Blue Whale
- Due to its huge size, weighing a Blue Whale is extremely difficult.
- It is impossible to weigh a Blue Whale as a whole, so it is cut into pieces of 1.6 to 2 feet (0.5 to 0.6 meters) and then each piece is weighed separately.
- During this process, a sizable amount of body fluids and blood is lost which is considered to be approximately 6% of the entire body weight.
- The total body weight is then evaluated by the addition of all the estimated values.
17. How Tall Is A Blue Whale – Blue Whale Height Facts for Kids
- The tallest Blue Whale verified by scientists was 98 feet (29.9 meters) tall.
- Female Blue Whales have usually bigger body lengths or heights as compared to male individuals.
- In 1947-48, a Japanese scientist verified the body length of a male Blue Whale to be 88 feet (26.8 meters).
- The reported tallest female Blue Whale was 92 feet (28 meters) long captured in the Davis Strait of Labrador Sea.
18. Blue Whale Diagram
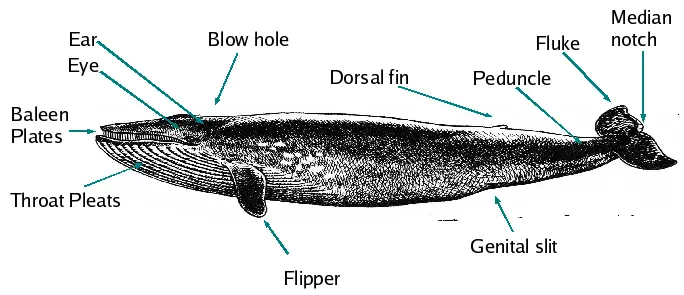
19. Blue Whale Brain
- The brain of a Blue Whale weighs 15.26 pounds (6.92 kg), which is very small when compared to its body size.
- The brain has an extremely convoluted cerebral cortex and makes only 0.007% of the whole body weight.
20. Blue Whale Eye
- Blue Whales have proportionally small eyes of approximately 6 inches in size.
- Their eyes don’t have any eyelashes or tear glands.
- Their eyesight is considered to be very weak.
21. Blue Whale Mouth
- Blue Whales have such a big mouth that they can hold up to 100 people at once.
- Their mouths have baleen plates at the front section which go in about 20 inches in the back direction of the mouth.
- The number of baleen plates is about 300 and each one is approximately 3.3 feet (1 meter) long.
- The amount of food and water they intake with one gulp is about 90 tonnes, however, their throat dimension does not allow things of the size more than grapefruit to pass.
- Blue Whale is a filter feeder and an adult individual can eat up to 40 million zooplankton and krill per day.
22. Blue Whale Mouth Open
- The fully open mouth of Blue Whale is wide enough to hold up to 100 people at a time.
- They ingest up to 90 tonnes of water and food with one gulp.
23. How Many Teeth Does A Blue Whale Have
- Blue Whales do not have real teeth, but rather they have about one meter long teeth-like structures called baleen plates.
- The average number of baleen plates is up to 300 that are hanging in the front section of their mouth.
- These baleen plates work as a filter and only allow plankton and other small animals to pass through the throat.
24. Blue Whale Tongue – Blue Whale Tongue Weight
- The tongue of a Blue Whale weighs about 2.7 tonnes (2,700 kg), which is equivalent in weight and size to an African forest elephant.
25. Blue Whale Heart Facts for Kids
- The heart of a Blue Whale is the largest among all animals on the earth.
- It is about 5 feet long and 4 feet wide with a weight of approximately 180 kg (400 pounds), which makes only 1% of its whole body weight.
- The heart of a Blue Whale is so big that an adult human being can crawl through the aorta.
- It beats once after every 10 seconds and pumps 220 liters of blood in one beat.
- The heartbeats of a Blue Whale are so loud that they can be heard from a distance of 3 km using a sonar apparatus.
How Big Is A Blue Whale Heart – Blue Whale Heart Size
- The heart of a Blue Whale is about 5 feet long, 4 feet wide, and 4 feet tall in size.
Blue Whale Heart Weight
- The heart of a Blue Whale weighs about 180 kg (400 pounds).
26. Blue Whale Lungs – Blue Whale Breathing Facts for Kids
- Blue Whales use their lungs to breathe as Blue Whale is a marine mammal and doesn’t have gills to extract oxygen from water.
- They inhale oxygen through their blowholes and for this reason they come to the water surface every once in a while.
- Blue Whale is a species of baleen whale that have two blowholes while other toothed whales have only one blowhole.
- Blue Whales discharge a single-column vertical stream of water during breathing, usually 30 feet high.
- They breathe for 15 to 60 minutes and their lungs capacity is approximately 5,000 liters.
- Blue Whales can store much of the inhaled oxygen (about 75%) in their blood circulatory system.
27. Blue Whale Tail
- The tail of a Blue Whale divides into two flukes of the size of a professional soccer net.
- Some of the Blue Whales in the North Pacific and North Atlantic oceans have been observed raising their tail flukes while diving.
28. How Long Can A Blue Whale Live – Blue Whale Lifespan – Blue Whale Life Expectancy
- According to the estimation of scientists, the lifespan of a Blue Whale is up to 80 years.
- Their estimated average lifespan is 70 to 90 years.
- The lifespan of an individual in the eastern North Pacific Ocean was recorded as 34 years.
29. What Do Blue Whales Eat – Blue Whale Diet – Blue Whale Eating
- Blue Whale is a filter-feeder and almost exclusively consumes krill.
- However, they also consume some small fish, squids, copepod, and other crustaceans caught up along with krill.
- The average number of krill an adult Blue Whale eats in one day is up to 40 million.
- In the areas of higher krill concentration, Blue Whales sometimes consume 3,600 kg (7,900 pounds) of krill in one day.
- As different species of krill are found in different oceans, the diet of a Blue Whale varies from ocean to ocean.
- The krill species Meganyctiphanes norvegica, Thysanoessa inermis, Thysanoessa raschii, and Thysanoessa longicaudata are their usual diet in the North Atlantic ocean.
- In the North Pacific ocean, Thysanoessa inermis, Thysanoessa spinifera, Thysanoessa longipes, Euphausia pacifica, Nematoscelis megalops, and Nyctiphanes simplex make a major part of a Blue Whale’s diet.
- In the Southern Hemisphere, they eat most of the Euphausia crystallorophias, Euphausia superba, Nyctiphanes australis, and Euphausia valentini species of krill.
30. How Much Does A Blue Whale Eat
- An adult Blue Whale consumes up to 40 million krill per day.
- A Blue Whale needs approximately 997 kg (2,200 pounds) of krill to fill its stomach.
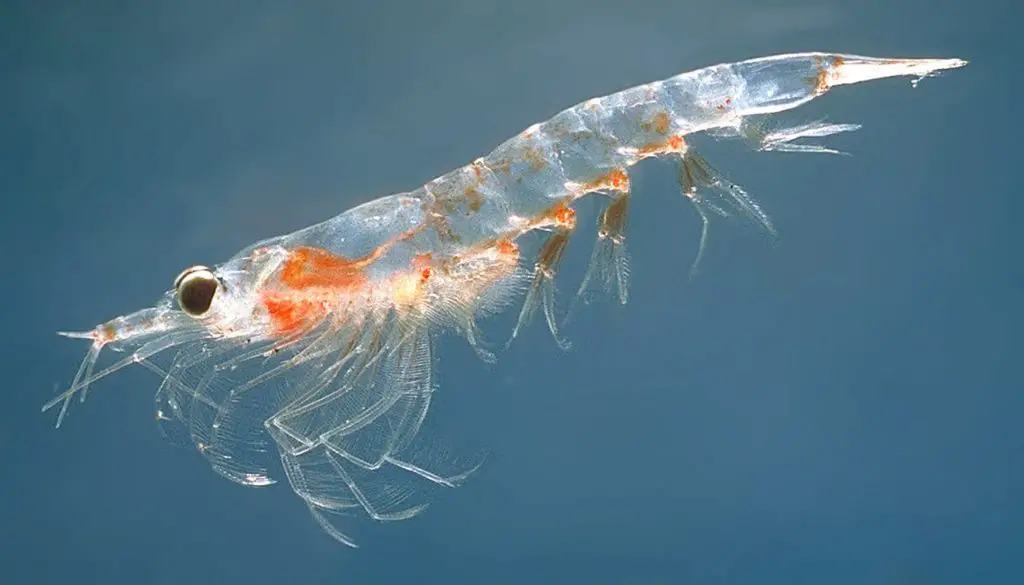

31. Blue Whale Eating Krill
- When feeding, a Blue Whale thrusts forward in waters of higher krill concentration.
- Along with krill they also intake a large amount of water.
- The tongue and ventral pouch then apply pressure and cause the water to squeeze out via the baleen plates, and the remaining stuff is then swallowed.
32. Blue Whale Where Do They Live – Blue Whale Habitat – Blue Whale Location
- Blue Whales are inhabitants of the cold and temperate waters of all oceans.
- Blue Whales are divided into four distinct subspecies, which are found in different oceans.
- Individuals of the subspecies
- Balaenoptera musculus musculus are the inhabitants of the North Pacific and North Atlantic oceans.
- Balaenoptera musculus brevicauda (Pygmy Blue Whale) are inhabitants of the Southern Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean.
- Balaenoptera musculus intermedia inhabit the Antarctic Ocean.
- Balaenoptera musculus indica inhabit the Indian Ocean.
33. Blue Whale Range
- The Blue Whales have vast ranges and are found in oceans all over the world.
- They usually spend summers in the cold waters of the Southern Ocean (Antarctic Ocean) and winters in the temperate waters of Oceans near the equator.
34. Blue Whale California
- Blue Whales are found and can be seen off the coasts of California between May to October.
- During this time, krill is abundantly found there which attracts Blue Whales and other whale species.
35. Antarctic Blue Whale
- Balaenoptera musculus intermedia subspecies of Blue Whale is called the Antarctic Blue Whale.
- The Antarctic Blue Whale is a close relative of both the Balaenoptera musculus brevicauda and Balaenoptera musculus musculus subspecies of the Blue Whale found in the Pacific, North Atlantic, and Indian oceans.
- The Antarctic Ocean is their feeding ground in summer whereas they are found in the cold water around Antarctica.
- The Antarctic Blue Whale was a critically endangered subspecies, however, in 1966 the International Whaling Commission prohibited its commercial hunting and now their population is about 2,200.
36. Blue Whale Population – Blue Whale Number
- According to the estimation of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the worldwide population of Blue Whales is between 10,000 and 25,000.
37. How Fast Is A Blue Whale – Blue Whale Speed
- The top speed of a Blue Whale is up to 31 miles per hour (50 km/h), however, it can retain this speed only for short bursts.
- Its usual speed is 12 miles per hour (19.3 km).
- It swims slowly at a speed of only 3.1 miles per hour (5 km/h) while feeding.
38. How Deep Can A Blue Whale Dive- Blue Whale Diving
- The verified deepest dive of a Blue Whale is 1,660 feet (506 meters).
- When they are migrating, they usually swim at a depth of approximately 43 feet (13 meters).
39. Blue Whale Jumping – How High Can A Blue Whale Jump
- It might be possible for Blue Whales to jump out of the water, however, the height of their jump is unknown.
40. Blue Whale Family
- Blue Whale belongs to the baleen whales family Balaenopteridae, which are also known as “Rorquals”.
- There are two genera in this family with nine extant (living) species.
- Blue Whale is the largest species of this family and even the largest animal on the earth, while the Northern Minke Whale is the smallest species (with a weight of 9 tonnes).
- All the members of this family have special “Pleated throat grooves” called baleen through which they filter their food from the water.
41. Blue Whale Life Cycle
- Blue Whales usually mate in late autumn and winter.
- The calves are born after a gestation period of 10 to 12 months and weigh up to 2.5 tonnes.
- For the initial six months of life, the calves are fed by their mother’s milk with a daily quantity of 380 to 570 liters.
- The calves become sexually mature at the age of 5 to 10 years.
- A Blue Whale lives for 80 to 110 years.
42. Blue Whale Breeding – Blue Whale Reproduction
- Female Blue Whales usually reproduce once after two to three years.
- Their breeding grounds are still unknown, however, they migrate to the temperate waters of the Atlantic, South Pacific, and Indian Oceans.
- As the Blue Whales are dioecious (bi-parental), they reproduce via sexual reproduction.
- The haploid gametes of both male and female (sperm and egg) fertilize internally, which causes the female to become pregnant and she undergoes a gestation period of 10 to 12 months.
- As the Blue Whale is a mammal, the newborns are fed by their mother’s milk for about six months.
- The mother protects and takes care of the calves for about one year.
43. Blue Whale Pregnancy
- The pregnancy of female Blue Whales lasts for about 10 to 12 months.
44. Baby Blue Whale – Blue Whale Calf
- A Baby Blue Whale or calf is born after a gestation period of 10 to 12 months.
- The newborns weigh up to 2.5 tonnes and have a body length of 23 feet (7 meters).
- A calf begins swimming just after 30 minutes of his birth.
- The calves are fed with the milk of high energy content (18,300 kJ/kg) with a quantity of 380 to 570 liter/day.
- Calves are usually weaned at the age of six months.
What Is A Baby Blue Whale Called
- A baby Blue Whale is called a Calf.
How Big Is A Baby Blue Whale- Blue Whale Baby Size
- A baby Blue Whale has a length of up to 23 feet (7 meters) and weighs approximately 2,700 kg (2.7 tonnes).
How Much Does A Baby Blue Whale Weigh – Baby Blue Whale Weight
- A baby Blue Whale weighs approximately 2.5 tonnes (2,500 kg).
45. Blue Whale Milk
- Blue Whales have approximately 1.5 meter long mammary glands, which are the largest mammary glands on the earth.
- The calves are fed milk with an average amount of 380 to 570 liters per day.
- Their milk has a 35% to 50% fat composition that enables the calf to gain up to 90 kg of weight per day.
- The energy content of a Blue Whale’s milk is about 4,370 kcal/kg (18,300 kJ/Kg).
46. Blue Whale Adaptations Facts for Kids
- Being a warm-blooded (the animals that can maintain constant body temperature through the regulation of metabolism) mammal, Blue Whales have several physiological adaptations, which enable them to survive in the cold waters of the ocean. That is:
Blubber
- Blubber is a thick layer of fat tissue beneath the skin of whales and other cetaceans. Blubber makes about 27% of the entire body mass of a Blue Whale. It provides them protection and thermal insulation as the heat loss in water is about 27 times greater than the heat loss on dry land. Through blubber, a Blue Whale can maintain its body temperature, which is necessary for the normal functioning of metabolic activities.
Heart And Circulatory System
- Like other mammals, the heart of a Blue Whale is four-chambered and possesses a closed circulatory system. Such a system enables them to maintain constant body temperature.
Blowhole And Lungs
- Rather than having gills like fishes, Blue Whales have a pair of blowholes for the inhalation and exhalation of oxygen. Their lungs are also highly efficient and have 80 to 90% oxygen exchanging capacity (humans have only 10 to 15%). It helps them to stay within water for a long time.
Tail Fluke And Fins
- Blue Whales have a wider tail fluke and dorsal fins. Unlike fish, the tail fluke of a Blue Whale can only move in up and down directions. Wider fluke helps them to keep their balance in water as their spine can not bend too much horizontally and is flexible only in the vertical direction.
Ears
- Blue Whales lack external ears and only have internal ears as well as bones and sinuses that act like sensors, through which they communicate and navigate within the water.
Eyes
- The eyes of a Blue Whale are complex that do not have any lashes or tear glands. They also have very weak eyesight as they do not rely on their eyes for navigation or communication.
Spin
- The spine of a Blue Whale can bend only in a vertical direction like humans. So for making quick and precise turns, they utilize the rolling type of motion.
47. Blue Whale Behavior
- Blue Whales usually live alone, however, they occasionally gather in groups called pods or games in the feeding grounds.
- The voice of Blue Whales is the loudest in the kingdom Animalia. Even their low-frequency sounds can travel thousands of kilometers in the deep waters of the ocean.
- So alone Blue Whale is not considered to be alone but rather in constant contact with other Blue Whales through its powerful voice and echolocation.
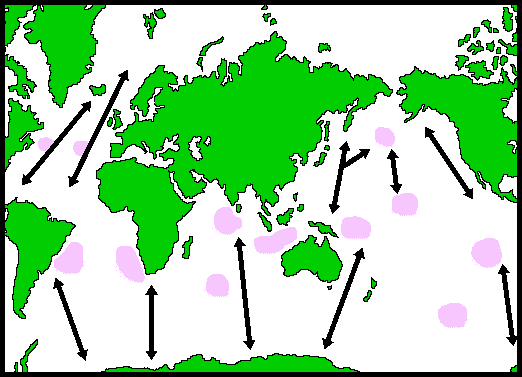
48. Blue Whale Migration
- Blue Whales seasonally migrate and travel thousands of kilometers in the vast expanses of sea.
- The temperature of water directs their course of migration during summer and winter.
- In summer, they travel towards their feeding ground, the cold Antarctic or the Arctic Ocean that has food in abundance.
- In winter, they migrate towards the tropical waters of the oceans near the equator that are the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. The temperate waters are not rich in food, however, it is their breeding ground where they reproduce.
49. Blue Whale Migration Map
50. Blue Whale Sleeping
- A Blue Whale can’t become unconscious and sleep like humans and other land mammals because if they did, they would drown and die.
- However, their brain takes rest in parts, which means one part of the brain sleeps while the other parts still function.
51. White Blue Whale
- White Blue Whale does not exist.
- In 1991, a white humpback whale (another species of baleen whales) was observed for the first time off the coast of Australia that was named Migaloo.
- When the other one was seen, it was named Migaloo Junior and now it is believed that there are three white humpback whales in the region.
- According to scientific speculation, hypopigmentation or genetic mutation (like albinism) are the possible reasons for their white color.
52. Blue Fin Whale
- The Fin Whale is another species of baleen whale, which is the world’s second-largest mammal after the Blue Whale.
- Hybrids of Blue Whale and Fin Whale have been recorded in at least 11 cases.
- Scientists describe that the genetic distance between a Blue Whale and a fin whale is similar to that of humans and gorillas.
53. Blue Whale Humpback Whale
- Researchers believe that they photographed a hybrid “Blue Whale – Humpback Whale” off Fiji.
- This statement is reinforced by discovery via the DNA analysis of a meat sample obtained from a market in Japan.
54. Where Can I See A Blue Whale – Blue Whale Spotting – Blue Whale Watching
The following are the best places in the world to see Blue Whales:
- Saguenay – St. Lawrence Marine Park in Quebec
- Mirissa in Sri Lanka
- Pico Island of Azores Archipelago in Portugal
- San Diego in California, USA
- Husavik and Reykjavik in Iceland
- Baja California Sur in Mexico
- Monterey Bay in California, USA
55. Blue Whale Breaching
- Blue Whales also breach like other whales, however, the extent of their breaching height is unknown.
56. Blue Whale Vs Humpback Whale
| Blue Whale | Humpback Whale | |
| Family | Balaenopteridae | Balaenopteridae |
| Size | Bigger, even the biggest animal on the earth | Smaller than Blue Whale |
| Feeding Ground | The cold polar waters of the Antarctic Ocean | Same |
| Breeding Ground | The tropical temperate water of oceans near the equator | Same |
| Feeding Method | A filter-feeder that has a special filter-feeder system known as baleen | Other than baleen, they also feed through a special technique known as bubble net |

57. Killer Whale Vs Blue Whale
- Killer whale belongs to the family of oceanic dolphins and is the only natural predator of Blue Whale.
- There are some recorded cases of killer whales attacking the Blue Whales. In some of these cases, the Blue Whales succeeded to escape while in others they were killed.
58. Blue Whale Predators
- The killer whale or Orca is the only natural predator of the Blue whale.
- Research revealed that about 25% of adult Blue Whales have marks on their skin which are a result of attacks from killer whales.
- Humans are also the primary predators of Blue Whales and hunt them usually for meat. However, Blue Whale hunting is now banned in many countries.
59. Blue Whale Conservation Status
- Blue Whale is listed as an endangered species on the IUCN Red List.
- The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), a federal agency of the USA that takes care of the national marine resources, also listed the Blue Whale as endangered species and protected them not only under the Endangered Species Act of 1973 but also under the Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972.
60. Blue Whale Endangered Animals – Blue Whale Endangered Species
- Blue Whale is an endangered species, however, its population is increasing as several countries made its hunting illegal through laws.
61. Blue Whale Threats
- Other than hunting and attacking killer whales, there are several threats to the survival of Blue Whales.
- Sometimes, Blue Whales are wounded after colliding with ships and rocks.
- The increasing amount of noise in oceans due to sonars and other human activities affects the vocalization of Blue Whales and creates difficulties in their communication.
- Global warming is also a major threat for Blue Whales as it is causing the glaciers to melt and an increase of freshwater in oceans. In such situations, there will be an interruption in the thermohaline circulation and it would directly affect the migratory patterns of Blue Whales.
- Global warming is also causing a change in the temperature of the ocean, which directly affects the food supply of Blue Whales.
62. Blue Whale Hunting
- Hunting Blue Whales was not an easy task for earlier Whalers due to their giant body, speed, and power.
- A Norwegian whaler Svend Foyn first hunted a Blue Whale in 1864 with the help of a steamboat equipped with harpoons.
- Later, Blue Whales were hunted in other parts of the world like Iceland in 1883, off the Faroe Island in 1894, and Newfoundland in 1898.
- In 1966, the International Whaling Commission banned illegal whaling and hunting of Blue Whales due to the critical decline in their population.
63. Blue Whale Extinct
- Blue Whales were going to become extinct as their population had been reduced to only about 0.15% of the initial in the Antarctic region, which was their most populous zone.
- However, in 1966 the International Whaling Commission protected the species by banning its hunting.
64. Amazing Facts About Blue Whale – Blue Whale Fun Facts for Kids
- Blue Whale is the largest animal that lives on the planet earth.
- It has such a big mouth that it can hold up to 90 tonnes of water and food when fully opened.
- Despite its huge size, a Blue Whale is a filter-feeder and can only swallow things the size of a grapefruit.
- An adult Blue Whale consumes up to 3,600 kg (7,900 pounds) of krill in one day.
- The daily energy requirement of an adult Blue Whale is approximately 1.5 million kcal.
- As Blue Whale is a marine mammals, they feed their babies (calves) with milk. The daily amount of milk that a calf drinks ranges from 380 to 570 liters.
- The milk of Blue Whales has a higher fat content and provides about 4,370 kcal/kg (18,000 kJ/kg) energy. By feeding on such milk, a calf gains approximately 90 kg of weight per day.
- The penis of a Blue Whale is the largest of any existing animal, with an average length of 8 to 10 feet (2.4 to 3 meters).
- The heart of a Blue Whale beats so loudly that it can be heard from a distance of 3 km via sonar apparatus.
- Blue Whales navigate and communicate under the dark depths of the ocean by producing several types of sounds, which are usually called “songs”.











