The brain is an integral part of the human body that not only controls our body but also enables us to think, store memories, have feelings, learn new things, and many other important functions. When studying the human body, the human brain is an important topic. We have gathered a complete set of Brain Facts For Kids that will help you in learning all the brain information you need along with pictures, diagrams, and videos. You are going to learn all about the brain including its definition, what it is made of, its size, weight, capacity, types, its regions, layers, parts, structure, functions, brain cells, memory, and many other interesting brain facts.
Brain Facts For Kids
1. What Is Brain
- The brain is a central organ in all vertebrates and also in most invertebrates, that control all the functions of the body.
- In all vertebrates and particularly in human beings, it is the most complex organ.
- In vertebrates, the brain is usually located in the head near the sensory organs for senses like vision, hearing, smell, and test.
- A human brain is made up of over 100 billion nerve cells or units called neurons.
- The neurons are connected by connections called synapses. The approximated number of synapses is in trillions.
- Neurons communicate through long nerve fibers known as axons.
2. Scientific Name Of Human Brain
- There is no specified scientific name of the human brain.
- However, the human brain is identified by “Cerebrum” and “Encephalon” in Latin and Greek respectively.
3. What Does A Brain Look Like
- The brain looks like a mass of folded lobes.
- The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum which is divided into two hemispheres; the right and left cerebral hemispheres.
- Each hemisphere is consists of 4 lobes known as the frontal lobe, the temporal lobe, the parietal lobe, and the occipital lobe.
- All four lobes are separated by two deep grooves called the lateral sulcus and the central sulcus (a groove is technically known as a sulcus).
- Besides the cerebrum, the brainstem and cerebellum are the other parts of the brain, and all the parts collectively form a complete brain.
- All the regions and parts of the brain have different functions.
4. Is The Human Brain An Organ
- Yes, the human brain is an organ and the most complex one in the entire body of humans.
5. Where Is The Brain Located
- The brain is located in the head.

6. What Is Your Brain Made Of – What Is The Human Brain Made Of
- Barin is the fattiest organ in the entire human body and is composed of about 60% of fats.
- Mainly, the human brain is made of nerve cells (neurons), glial cells, neural stem cells (NSCs), and blood vessels.
7. What Is Inside Your Brain
- There are three main regions inside the brain; the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brain stem.
- Inside each region, there are different types of cells (nerve cells, glial cells, neural stem cells) and a huge network of blood vessels.
8. How Much Does A Human Brain Weigh – Weight Of Human Brain
- The average weight of an adult human’s brain is about 2.6 to 3.1 pounds (1.2 to 1.4 kg), which makes approximately 2% of the whole body weight.
9. What Is The Size Of Human Brain – Human Brain Size
 The human brain has an average size of about 140 mm (14 cm) in width and 167 mm (16.7 cm) in length.
The human brain has an average size of about 140 mm (14 cm) in width and 167 mm (16.7 cm) in length.- The average volume of a woman’s brain is about 1130 cm³ and that of a man’s brain is about 1260 cm³.
10. Human Brain Capacity
- The capacity of the human brain to store memory is nearly about 2.5 petabytes (2.5 million gigabytes).
11. Types Of Human Brain
- The human brain is divided into three main parts or units known as; the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
- Sometimes, these parts or units are also referred to as types of the human brain.
12. Regions Of The Human Brain
- The following are the anatomical regions of the human brain during early development:
Forebrain
- The forebrain which is also known as the prosencephalon is the most forward region of the brain.
- In later life, this region controls the functions of reproduction, body temperature, emotions, sleeping, and eating.
Midbrain
- Midbrain is also known as the mesencephalon.
- This region is part of the central nervous system.
- It is associated with the functions of motor control, regulation of body temperature, alertness, reflex actions, and senses of hearing and vision.
Hindbrain
- The hindbrain is also known as the rhombencephalon.
- This region develops to the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata.
- This region is associated with vital body functions like heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, and digestion.
13. Layers Of Human Brain Facts for Kids
- There are three layers of the human brain.
- All the layers are interconnected with each other and form an organized structure of the brain. They are:
The central core
- The central core is consists of five regions;
- The medulla
- The pons
- The reticular formation
- The thalamus
- The cerebellum
The limbic system
- The limbic system is consists of three regions;
- The hippocampus
- The amygdala
- The hypothalamus
The cerebral cortex
- This layer is divided into two halves known as the cerebral hemispheres.
- Each cerebral hemispheres is consists of four lobes;
- The frontal lobe
- The parietal lobe
- The occipital lobe
- The temporal lobe
14. How Many Parts Of Human Brain – Parts Of The Brain – Parts Of The Human Brain Facts for KIds
- There are 3 parts of the human brain:
The Cerebrum or the Forebrain
- In all parts of the human brain, the cerebrum is the largest one and performs functions like remembering, cognition or thinking, problem-solving.
- It is also associated with the senses of vision, hearing, and touch.
- This part also controls the emotions and movements of a person.
The brainstem or the midbrain
- This part is located just beneath the cerebrum and links the spinal cord and brain.
- This part controls the automatic functions of the body like heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, body temperature, digestion, swallowing, sneezing, and the cycles of sleeping and waking up.
The cerebellum or the hindbrain
- This part lies under the cerebrum and controls the functions of balance and coordination.
15. Biggest Part Of Brain
- The cerebrum is the biggest part of the brain, which makes up about two-thirds of the total mass of the brain.
16. Human Brain Lobes
- Every cerebral hemisphere of the cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes.
- All the lobes are named according to the bones of the skull that lies upon them.
- The lobes are;
- The frontal lobes
- The parietal lobes
- The temporal lobes
- The occipital lobes
- Each lobe has special functions, however, some of the functions are combinedly performed by the lobes.
17. Structure Of Human Brain – Human Brain Anatomy Facts for Kids
- There are three major parts of the human brain, which are:
The Cerebrum
- The cerebrum is the largest and wider region of the brain.
- A longitudinal deep groove known as the longitudinal fissure divides the cerebrum into two equal symmetrical halves; the left and right hemispheres.
- The outer extensively folded region of the cerebrum is called the cerebral cortex, which is consists of grey matter.
- The grey matter is made up of cortical layers, the neocortex, and the allocortex.
- The neocortex is consists of six layers of neurons while the allocortex is made up of three to four layers of neurons.
- Five commissures (commissure is an anatomical word for the linking or joining location of two objects) link both hemispheres.
- The brain has a folded surface with many grooves (sulci) and ridges (gyri), some of which are named due to their specific positions.
- Each cerebral hemisphere is further divided into four lobes; the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe, and the occipital lobe.
- Just below the grey matter is located the white matter, which is the inner and deeper region of the hemispheres.
The Cerebellum
- The cerebellum is located under the cerebrum at the back region of the cranial cavity.
- It is divided into three lobes; anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular lobes.
- A cerebral tentorium separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres.
The Brainstem
- The brainstem is located at the back region of the skull beneath the cerebrum and behind the cerebellum.
- It consists of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata.
- The spinal cord is the continuation of the brainstem beneath the skull.
- The meninges envelope and protects the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, and spinal cord.
- The meninges is made up of three membranes; an outer and hard dura mater, the arachnoid mater at the middle, and the innermost pia mater.
- A subarachnoid space exists between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater that have the cerebrospinal fluid.
- The cerebrospinal fluid not only provides mechanical protection to the brain but also immunological protection.
18. Brain Cells Facts for Kids
- The human brain is made up of two types of cells:
- The Neurons
- The Glial cells
The Neurons
- The neurons are the primary signaling cells that transmit, receive, and process information via chemical and electrical signals.
- The neurons are of four types, that are; the interneurons, the motor neurons, the pyramidal cells, and the Purkinje neurons.
- The estimated number of neurons in the brain of an adult human is 86±6 billion.
- Out of this number, about 80% (69 billion) neurons are located in the cerebellum while 19% (16 billion) are in the cerebral cortex.
The Glial cells
- The glial cells are the non-neuronal cells that protect neurons and support their function.
- The glial cells are of five types: the astrocytes, the oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia, and radial glial cell.
Other Cells
- The number of non-neuronal cells in the brain of an adult human is roughly estimated as 85±10 billion.
- Another type of cell known as the Neural Stem Cells (NSCs) also exists in the brain.
- Neural Stem Cells are the progenitor cells and are responsible for the production of all types of cells (neurons and glia) of the nervous system.
- Besides these basic types of cells, certain immune cells like Mast Cells (a type of White Blood Cells or WBCs) are also found in the brain, particularly in the meninges.
19. What Does The Brain Do – Human Brain Functions
- The human brain controls all the functions of the body.
- All the specialized areas of the brain work together.
- The outermost layer of the cerebrum, the cerebral cortex, is associated with the functions of cognition and voluntary movements.
- At the deep central region of the brain is a group of structures, known as the basal ganglia, that perform the function of coordination messages between areas of the brain.
- The cerebellum is associated with the functions of coordination and body balance.
- The brainstem is responsible for the most vital automatic functions of the body like breathing, heart rate, digestion, and blood pressure.
- Besides these functions, all the brain lobes perform their special functions.
- The frontal lobes control the motor functions, decision-making, and problem solution.
- The temporal lobes are associated with memory and sense of hearing.
- The parietal lobes control the body position (posture), sensations, and handwriting.
- The occipital lobes are the center of the visual processing system of the brain.
20. How The Human Brain Works
- All parts of the human brain work together, however, every part has its specialized function.
- The human brain consists of billions of interconnected nerve cells or neurons.
- The structure of neurons has a central part known as the cell body, while two types of branches extend from the cell body.
- Short branches are known as “dendrites” that receive information from the other neurons.
- While a long branch is known as an “axon” carries signals or nerve impulses from the cell body.
- When a neuron is stimulated, it communicates with other neurons via electrical impulses.
- The electrical impulse moves inside the neuron to the end of the axon where it causes the release of chemicals known as neurotransmitters.
- The neurotransmitters act as a messenger and pass through the junction between two neurons and bind with the receptors on the receiving cell.
- In this way, all the interconnected neurons work and provide extremely fast and efficient communication.
21. How Does The Brain Control The Body
- Every part of our body is connected with the nervous system, through which our brain controls our body.
- The nerves act like electrical cables and carry electrical impulses to the brain.
- The electrical impulses are produced upon stimulation.
- In this way, the brains control all the functions of our bodies.
22. Human Brain Facts On Memory for Kids
- Scientific research has proved that the human brain begins remembering from the womb, only 20 weeks after conception.
- The human brain has virtually unlimited storage capacity.
- The duration for which most of the short-term memory lasts is only 20 to 30 seconds.
- Good sleep improves the retrieval and storage of long-term memories.
- Caffeine only boosts alertness and does not have any role in the maintenance of memory performance.
- Memory loss is not associated with aging, rather it is associated with less exercise of the brain in old age.
- Exercise is extremely important for the brain just like for the body muscles.
- The human brain can associate the smell of ascent with a particular incident or event.
23. Human Brain Usage
- Most parts of the brain are almost always in use.
- Every time, most of our brain remains active even when we are sleeping or resting.
- It was a common myth that humans utilize only 10% of their brains.
- However, this myth was debunked by a research study published in the Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
24. Brain Stem Function
- The brain stem region of the brain controls the information flow between the brain and body.
- It also controls the basic automatic functions of the body like heart rate, breathing, blood pressure, consciousness, and digestion.
25. Brain Stem Facts for Kids
- The brain stem is comprised of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
- Our brainstem is responsible for the most basic functions our body needs to stay alive, like pulse rate, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
- The brain stem also controls the functions of alertness, awareness, pain sensitivity, and consciousness.
- Any damage to the brain stem can be life-threatening as it is responsible for vital body functions.
- The basic sensory and motor nerve supply to the neck and face also comes from the brain stem through the cranial nerves.
26. Human Brain Diagram
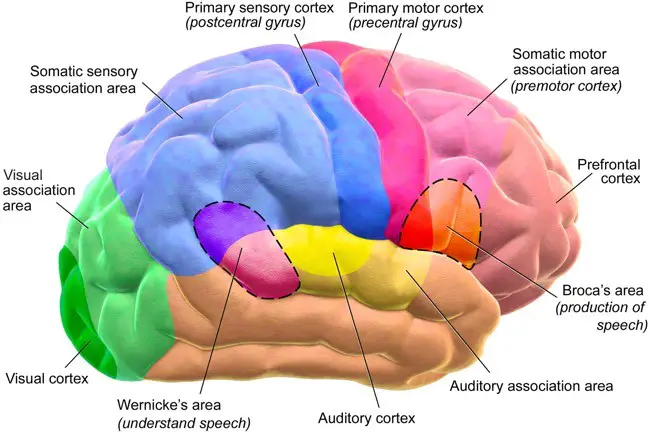
27. Human Brain Pictures With Labels

28. Brain Foods
- Brain foods are referred to the foods that keep our brain healthy and improve concentration and memory.
- Foods rich with Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals are considered foods that improve brain health.
- Some of such foods are:
- Fatty fishes
- Blueberries
- Coffee
- Pumpkin seeds
- Nuts
- Turmeric
- Broccoli
- Dark chocolate
- Eggs
- Oranges
29. Brain Exercises
- Some of the best brain exercises are:
- Testing your remembrance by making and memorizing a list of things and recalling it after one or two hours later.
- Learning a foreign language is also a good brain exercise, as it involves listening and cognition.
- Doing maths in your mind without any aid (like paper, pen, etc).
- Doing cooking, involves the senses of touch, smell, test, and sight that is controlled by the different parts of the brain.
30. Brain Diseases
- There are five main categories of brain diseases, which are:
- Infections of the brain include meningitis and encephalitis.
- Seizures include epilepsy as a major form, which is caused by immoderate and abnormal electrical activities within the brain.
- Trauma includes conditions like a concussion, intracerebral hemorrhage, and traumatic brain injury.
- Strokes include conditions like ischemic stroke and hemorrhagic stroke.
- Brain tumors may be cancerous or benign but exert excessive pressure on the brain.
31. Human Brain Development
- A neural tube is the precursor of the spinal cord and brain during the development of the human brain.
- At the sixth week of pregnancy, three major structures are formed that are; the prosencephalon, the mesencephalon, and the rhombencephalon.
- From these three structures, five secondary structures develop in the seventh week of pregnancy, which is; telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon, metencephalon, and telencephalon.
- Further, the telencephalon develops to the cerebrum and diencephalon to the thalamus and hypothalamus regions of the forebrain.
- The mesencephalon develops to the midbrain, while the metencephalon and telencephalon develop to the hindbrain (which include the brainstem, cerebellum, and reticular formation).
32. Early Childhood Brain Development Facts – Child Brain Development Facts
- The first three years of a child’s life are the fastest period of brain development.
- Due to the rapid development of the brain in early childhood, a baby’s brain took about 60% of the whole metabolic energy.
- At birth, children are capable to learn any language.
- Regular physical touch strengthens the neuronal connections within a baby’s brain.
- The unwillingness of a baby to leave his parent is a sign of the development of long-term memory.
- The executive functions of the brain of bilingual babies are much stronger than the brain of babies who speak one language.
- Social interaction improves the learning speed and accuracy of children.
33. Teenage Brain Facts
- The brain of teenagers does not have a completely developed prefrontal cortex.
- The prefrontal cortex is the brain region associated with the functions of decision making, complex thinking behavior, expression of personality, and social behavior.
- That is why teenagers are so emotional, often show dangerous behaviors, and take risks.
34. Interesting Facts About The Brain – Fun Facts About The Brain for Kids
- The most complex structure in the whole universe is the human brain.
- The human brain is made up of more than 100 billion neurons and each neuron is linked with approximately 10 thousand other neurons.
- In the condition of hard thinking, the human brain uses about 50% of the oxygen and energy, while at rest the brain uses about 20% of the body’s energy.
- As the human brain is divided into two halves, the right and left. The right part controls the left side movements of the body while the left part controls the right side.
- The language area is usually found on the left side of the brain.
- The survival capability of the human brain without oxygen is only 5 to 6 minutes.
- The length of the blood vessels within the brain is about 100,000 miles.
- Neurons develop at a rate of approximately 250,000 per minute during the early developmental stage.
- It is believed that dreams are a combination of neurological and psychological factors and imagination, which is proof of the brain working during sleep.
- The human brain is about 3 times bigger than the brain of other mammals of the same body size.

 The human brain has an average size of about 140 mm (14 cm) in width and 167 mm (16.7 cm) in length.
The human brain has an average size of about 140 mm (14 cm) in width and 167 mm (16.7 cm) in length.