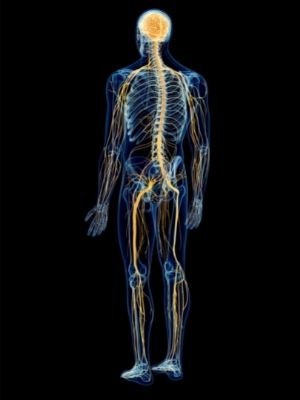
The nervous system in the human body is a sophisticated network of nerves and cells that connects the brain and spinal cord to other parts of the body. We have listed down complete Nervous System Facts for Kids that will help you in learning all about the Nervous System. You are going to learn about nerves, types of nerves, nervous tissue, nervous system, its location, parts, organs, functions, working, types, importance, the wonders of the human brain and many other interesting facts about Nervous Systems.
Nervous System Facts For Kids
What Are Nerves
- A nerve is a cable-like structure composed of a bundle of nerve fibers known as axons.
- Nerves are the building blocks of the peripheral nervous system.
- Nerves transmit electrical impulses and their primary function is to control and coordinate all parts of the body.
What Do Nerves Look Like
- Nerves look like threads or long cables.
What Are Nerves Made Of
- Nerves are made of nerve fibers or axons (myelinated and unmyelinated) and Schwann cells.
- A dense sheet of connective tissue surrounds every axon within the nerve and is known as the endoneurium. Within the endoneurium, a low-protein liquid (the endoneurial fluid) surrounds every individual axon. This fluid builds a blood-nerve-barrier and performs the same function as the cerebrospinal fluid performs in the Central Nervous System and builds the blood-brain-barrier.
- The axons are grouped into bundles, known as fascicles. A layer of connective tissue wraps each fascicle and is known as the perineurium.
- The entire nerve has then a final wrapping of a layer of connective tissue, known as the epineurium.
Types Of Nerves In The Human Body
In the human body, there are three types of nerves:
- Autonomic nerves control the involuntary (reflex or automatic) and partially voluntary (partial reflex or partial automatic) functions of the human body, such as heart rate, temperature, blood pressure, and digestion.
- Motor nerves control the actions and movements of our bodies. It passes information from the brain and spinal cord to muscles.
- Sensory nerves pass information back from the muscles and skin to the spinal cord and brain. In the brain, the information is then processed and we feel pain, heat, touch, or other sensations.
What Is The Function Of Nerves
- The major function of the nerves is to transmit information in the form of electrochemical impulses.
- Individual neurons that build a nerve convey this information.
- The impulse travels from one neuron to another through crossing a synapse.
- The impulses travel extremely fast, at the speed of up to 120 m/s with some myelinated neurons.
What Is Peripheral Nerves
- Nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system are the peripheral nerves.
- 43 paired nerves form the peripheral nervous system; 12 cranial nerve pairs and 31 pairs of spinal nerves.
How Many Nerves Does The Human Body Have
- The number of nerves in the human body is more than 7 trillion.
Largest Nerves In Human Body
- The largest nerves in the human body are the sciatic nerves.
- They start from the lower back and travel through the entire legs to the heels of the feet.
- Sciatic nerves are also the thickest nerves in the human body.
What Is Nervous Tissue
- Nervous tissue is the major tissue component of the nervous system.
- Nervous tissue is made up of neurons (nerve cells) and neuroglial cells (also called glial cells or just glia).
- Neurons generate and transmit impulses, while neuroglial cells are the supportive cells that help in the propagation of nerve impulses and also provide nutrients and protection to the neurons.
- In the central nervous system (CNS), four types of neuroglial cells are found that are; astrocytes, microglial cells, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes. The tissue types are; grey matter and white matter.
- In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), two types of neuroglial cells are found which are; satellite cells and Schwann cells.
What Is The Function Of Nervous Tissue
- The function of nervous tissue is the conduction of electric signals across tissues. In such a way, it forms the communication network of the nervous system.
- In the central nervous system (CNS), grey matter (that has synapses) is vital for the processing of information.
- White matter has myelinated axons that connect and assist nerve impulses between grey matter regions in the central nervous system.
- The ganglion tissue in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) has cell bodies and dendrites. It has relay points for the impulses of nerve tissue.
- The nerve tissue has bundles of myelinated axons and conveys action potential nerve impulses.
- In simple words, nervous tissue is responsible to control and coordinate many activities of our body. It stimulates our muscle contractions, makes us aware of the environment, and plays the main role in memory, reasoning, and emotions.
Where Is Nervous Tissue Found
Nervous tissue is found in the:
- Brain (grey matter and white matter)
- Spinal cord
- Nerves (ganglion tissue and nerves)
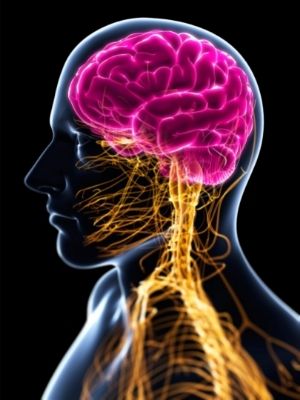
What Is A Nervous System
- The nervous system is an extremely complex part of the animal body.
- It is a system composed of organized groups of cells specialized for the transmission of electrochemical signals to and from different body parts. In such a way, it coordinates the actions and sensory information of the animal.
- The nervous system makes organisms capable of detecting changes that occur within their body and in the environment.
Where Is The Nervous System Located
- The nervous system is divided into two parts based on location; the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- The brain and spinal cord are parts of the central nervous system (CNS) located in the skull and vertebral column.
- While the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nerves and ganglia that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to the rest of the body.
What Are The Parts Of The Nervous System
- The nervous system of vertebrates has two major parts:
- Central nervous system (CNS), which is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral nervous system (PNS), which is made up of nerves branching off from the spinal cord and extending to all body parts.
What Is The Nervous System Made Up Of
The nervous system is made up of two types of cells:
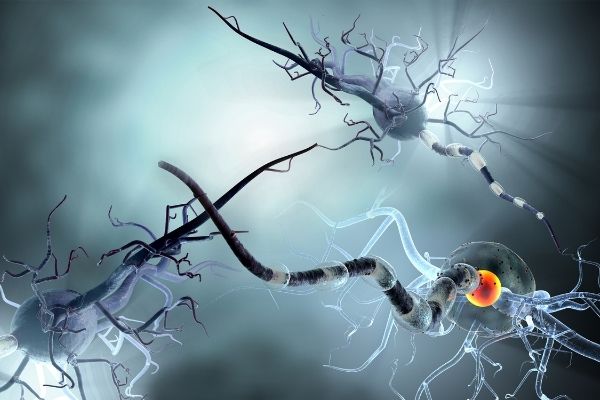
Neurons
- Neurons are special types of cells that are the major component of nervous tissue.
- The most fundamental feature of the neurons is they are designed to communicate and transmit information to other cells (nerve cells, muscles, and gland cells).
- Most neurons are composed of a cell body, an axon, and dendrites.
- Neurons communicate with other neurons or other target cells through synapses. A synapse is a membrane-to-membrane structure or junction with special molecular machinery that passes a rapid transmission of chemical or electrical signals.
- Neurons are the basic working units of the central nervous system, especially of the brain.
- There are hundreds of different types of neurons in humans. However, they are typically classified into three types based on function;
- Motor neurons are those neurons whose cell bodies are found in the motor cortex, brainstem, or spinal cord. While their axons are extending to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to control effectors. These neurons convey signals from the central nervous system to the effector organs (muscles and glands).
- Sensory neurons are those neurons whose cell bodies are found in the dorsal ganglia region of the spinal cord. They modify specific types of stimuli into action potentials through their receptors (a process known as sensory transduction). The action potentials are then transmitted from the peripheral nervous system (PNS) to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Interneurons are those neurons that are involved in the connection of two brain regions. These neurons enable communication between motor or sensory neurons and the central nervous system (CNS). Interneurons play an important role in the processes of reflexes, neurogenesis, and neuronal oscillations.
Glial cells
- Glial cells are the supportive cells in the nervous system.
- They provide nutrition, maintain homeostasis, participate in the formation of myelin, and are also involved in signal transmission.
- The most important roles of glial cells are to support neurons and to keep them in place.
- The total number of glial cells in the human brain is estimated to be equal to neurons. However, their proportion changes in the different regions of the brain.
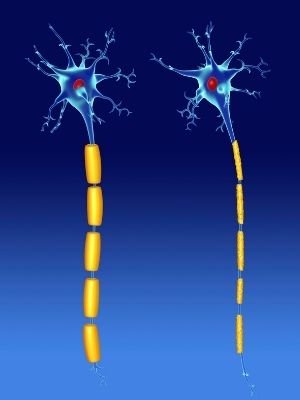
- Oligodendrocytes (found in the central nervous system) and Schwan cells (found in the peripheral nervous system) are extremely important types of glial cells. These cells generate myelin sheath (layers of fatty substance around the axons) and also provide electrical insulation, which makes neurons able to transmit action potential in a much more quick and efficient way.
What Organs Are In The Nervous System
- The brain and spinal cord are the major organs in the nervous system.
What Is The Function Of The Nervous System – What Does The Nervous System Do
The following are the major functions of the nervous system:
Controlling All Three Types Of Muscles
- The nervous system can cause the contraction and relaxation of all the three types of muscles found in the human body; cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscles.
- In this way, it controls body movements, blood pressure, and digestion.
Controlling The Internal Environment Of The Body
- The nervous system controls the internal environment of the body and maintains its homeostasis and temperature.
Controlling Glands
- The nervous system also controls the secretion of hormones from the glands.
- In this way, it controls the growth, metabolism, and blood sugar level.
Learning And Memory
- The acquisition of knowledge or skills is known as learning. While memory is the expression of the acquired knowledge or skill.
- Learning and memory are one of the major functions of the nervous system.
Controlling The Digestive System
- The enteric nervous system (ENS) found in the digestive tract works somewhat independently from the brain and spinal cord.
- This system is responsible for the autonomous (self-governed) functions of digestion.
What Is The Main Function Of The Nervous System
- The primary function of the nervous system is the control and communication of information all-over the body.
- It is done through the extraction of information from the environment by the use of sensory receptors.
- In the form of sensory input, the information is then sent to the central nervous system (CNS).
- The central nervous system (CNS) then integrates the information and determines a suitable response.
What Does The Nervous System Control
- The nervous system controls the entire body functions of an organism.
- From the movement and balance of the body to the thinking and thought processes, the nervous system controls all functions of the body.
How Does Nervous System Work
The nervous system works in the following way:
Sensation
- The sensation is the major function of the nervous system, in which information is received about the environment.
- Inputs are gained about what is occurring outside the body (sometimes, inside the body).
- The nervous system then registers the existence of change or a special event in the environment (called stimulus) through homeostasis.
- The major senses are five; touch, smell, taste, hearing, and sight.
- The stimuli for the sense of touch are mechanical or physical that make contact with the skin.
- In the hearing sense, the perception of sound is also a physical stimulus.
- Stimuli in the case of sight are light.
- While in the case of smell and taste, the stimuli are chemical substances that may be ions, molecules, or compounds.
Response
- Based on the received stimuli, the nervous system makes a response.
- A response would be a movement of mussels. For example, a quick withdrawal of hand from a hot thing.
- The nervous system controls the contraction of all three types of muscles (cardiac, smooth, and skeletal muscles).
- Neural control of glands is also a response. For example, in the case of high environmental temperature, the eccrine and merocrine sweat glands found in the skin are stimulated to produce and excrete sweat and keep body temperature normal.
- The responses are of two types: voluntary (conscious) and involuntary (unconscious). An example of a voluntary response is the contraction of skeletal muscle. While cardiac muscle regulation, glands activation, and smooth muscle contraction are examples of involuntary responses.
Integration
- The information of the received stimuli is communicated with the central nervous system (CNS) where it is processed. This is known as integration.
- In the central nervous system (CNS), the received stimuli are integrated or compared with; other stimuli, the memories of previous stimuli, or the state or position of a person at a specific time.
- This then leads to the generation of a specific response.
What Does The Brain Do In The Nervous System
- In the nervous system, the brain acts as a central computer and controls all the functions. While the other parts of the nervous system act as a network and relay information back and forth from the brain to different body parts.
- It is the brain that controls; what a person thinks and feels, how a person learns different skills, how a person remembers skills and information, the way a person talks, and the way a person moves.
- The brain also controls functions in our body we are less aware of, such as heart beating, breathing, and digestion of food.
- In short, the brain is the command center of our body.
What Is The Main Function Of Spinal Cord
- The main function of the spinal cord is to receive messages from the body and send it to the brain, and from the brain to the body.
- The spinal cord acts as a pathway for sensory information and transports it between the body and brain.
Division Of Nervous System – Types Of Nervous System
The nervous system is mainly divided into two parts or types:
- The Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
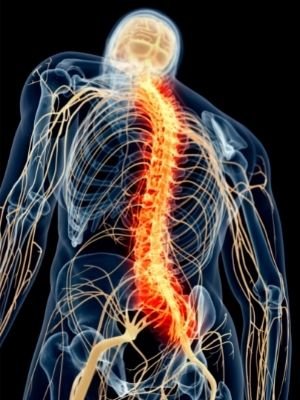
What Is The Central Nervous System
- The central nervous system (CNS) is part of the nervous system that controls most of our body functions.
- It is primarily composed of the brain and spinal cord.
- It is called the central nervous system because it integrates the information received as well as coordinates and affects the activities of all body parts.
What Makes Up The Central Nervous System – What Is The Central Nervous System Made Up Of
- The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system (CNS).
- The CNS then consists of grey and white matter, which can be observed on brain tissue without a microscope.
- The grey matter is composed of neurons and unmyelinated nerve fibers or axons (unmyelinated axons do not have any Milne sheet and conduct impulses with low velocity), glial cells, synapsis, and capillaries.
- The white matter is mainly composed of myelinated axons, and also has glial cells (mostly the oligodendrocytes). The white color of white matter is due to myline, which is a fatty substance. White matter has more glial cells than grey matter.
Where Is The Central Nervous System
- The central nervous system (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
- The brain is located in the cranial cavity within the skull, where it is protected by the cranium.
- While the spinal cord moves down from the back region of the brain, in the center of the spine, and ends in the lumbar region of the lower back. It is protected by the vertebrae.
- A triple-layered protective membrane known as meninges covers both the brain and spinal cord. This membrane provides a supportive framework and also protects the CNS from any mechanical injury.
What Is The Function Of The Central Nervous System – What Does The Central Nervous System Do
- The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
- The brain acts as the central computer of the body and controls most of the body’s functions.
- The major functions of the body that brain control includes: thoughts, memory, learning, speech, attention and concentration, awareness, problem-solving, judgment, self-monitoring, planning, emotions, behavior, understanding language, sequencing, organizations, differentiation (identification of shapes, sizes, and colors), consciousness and arousal, heart rate, breathing, cycles of sleep and awakening, senses (touch, vision, hearing, smell, and test), body movement and balance, movement of the muscles (legs, arms, fingers), the release of some hormones, body temperature.
- The major function of the spinal cord is to communicate other body parts with the brain. We can say that the spinal cord is a communication pathway between the brain and body.
What Is The Peripheral Nervous System
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of the two parts of the nervous system (the other is the central nervous system).
- It lies outside the brain and spinal cord, and that is why it is called the peripheral (outlying or outer).
- Its major function is to connect limbs and other organs to the central nervous system (CNS).
- Unlike the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system is vulnerable to mechanical injuries and toxins because no hard structure (such as vertebral column or skull) or any blood-brain barrier protects it.
- The peripheral nervous system is divided into two parts based on function; the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system.
What Is The Peripheral Nervous System Made Up Of – What Does The Peripheral Nervous System Consist Of – What Makes Up The Peripheral Nervous System
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is made up of nerves and ganglia.
- Nerves are cable-like bundles of axons or nerve fibers.
- While ganglia are the groups of the cell bodies of neurons.
What Does The Peripheral Nervous System Do – What Is The Function Of The Peripheral Nervous System
- The major function of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is to connect limbs, organs, and skin to the central nervous system (CNS).
- It acts as a relay and conveys information between the central nervous system (CNS) and the rest of the body.
What Is The Somatic Nervous System
- The somatic nervous system is a part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and is also known as the voluntary nervous system.
- This part of the nervous system is involved in the voluntary control of body movements through skeletal muscles.
- The somatic nervous system is composed of the sensory (afferent) nerves and the motor (efferent) nerves.
- Sensory nerves work to convey sensations from the body to the central nervous system (CNS).
- While the motor nerves work to send out commands from the central nervous system (CNS) to the body and thus causing the stimulation of muscle contraction.
- All the non-sensory neurons linked with the skin and skeletal muscles are also included in the somatic nervous system.
What Does The Somatic Nervous System Do – What Is The Function Of The Somatic Nervous System
- The major function of the somatic nervous system is to control voluntary movements and reflex arcs.
- It takes information through the sensory system and sends it to the central nervous system (CNS), through the sensory nerves.
- In the central nervous system (CNS), the information is integrated and commands are sent out to the muscles and organs through the motor nerves.
- The muscles are then stimulated to contract and the organs move in a specific way.
- For example, a person is going on a path and spots a muddy region ahead. His visual system receives the information of the muddy region and conveys it to his brain. The brain sends signals to the muscles to take action. The person turns in his direction and successfully avoids the muddy region and becomes prevented from a possible dangerous slip and fall.
- The somatic nervous system also controls the reflex arcs, without any commands from the brain. This occurs through a direct connection between a nerve pathway and the spinal cord.
- An example of the reflex arc is jerking the hand after an accidental touch with a hot thing.
What Does The Somatic Nervous System Control
- The somatic nervous system controls the voluntary muscular movements of the body.
- It is also associated with reflex arcs.
What Is The Autonomic Nervous System
- The autonomic nervous system is also known as the involuntary nervous system.
- It is part of the peripheral nervous system that is associated with involuntary ( unconscious) control of the internal organs through the smooth muscles.
- The autonomic nervous system regulates body functions, such as respiratory rate, heart rate, digestion, urination, sexual arousal, and pupillary response.
- This system is also associated with the control of fight-or-flight response.
- The autonomic nervous system is further divided into three branches: the sympathetic nervous system, the parasympathetic nervous system, and the enteric nervous system.
What Does The Autonomic Nervous System Do – What Is The Function Of The Autonomic Nervous System – What Does The Autonomic Nervous System Control
The autonomic nervous system controls the involuntary functions of the body that are vital for survival.
The following are some major internal processes of the body that are controlled by the autonomic nervous system:
- Heart rate
- Breathing rate
- Blood pressure
- Body temperature
- Digestion
- Metabolism
- Balancing the amount of water and electrolytes (sodium and calcium)
- Fluid production (sweat, tears, saliva)
- Sexual response
- Urination
- Defecation
What Controls The Autonomic Nervous System
- A lower sub-region of the brainstem, known as medulla oblongata, is a main control center of the autonomic nervous system.
- The autonomic functions are integrated with the hypothalamus, which perceives the autonomic regulatory feedback from the limbic system.
What Is The Sympathetic Nervous System
- The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three branches of the autonomic nervous system.
- It regulates the unconscious actions of the body.
- The sympathetic nervous system is described as complementary to the parasympathetic nervous system because the effects of both the nervous systems on some organs are opposite.
- Two types of neurons are associated with the signal transmission through the sympathetic nervous system. They are known as preganglionic neurons and postganglionic neurons. Preganglionic neurons originate in the spinal cord (in the thoracolumbar division) and move to a ganglion. Here they synapse with postganglionic neurons. The postganglionic neurons then spread across most of the body parts.
What Does The Sympathetic Nervous System Do
- The sympathetic nervous system remains constantly active and regulates many homeostatic mechanisms. Tissues in about every organ system have a supply of the sympathetic nerve fibers, which is involved in the regulation of at least some functions. For example, gut motility, relaxing the bladder, speed up of the heart rate, and dilation of the eye pupils.
- The sympathetic nervous is the primary mechanism to stimulate the “fight-or-flight” response of the body. In the situation of stress or danger, it directs the rapid voluntary response of the body. It causes a heavy secretion of the hormones (adrenaline), which increases the heart rate, sending more blood to the muscles, dilates bronchioles in the lungs, and profuse sweating.
What Does The Sympathetic Nervous System Control
- The sympathetic nervous system controls:
- Relaxation of bladder
- Mortality of gut
- Speeding up of heart rate
- Dilation of the eye pupils
- Activation of sweat secretion
What Is The Parasympathetic Nervous System
- The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the three branches of the autonomic nervous system.
- It stimulates the “feed and breed” or the “rest-and-digest” activities of the body, which occurs when the body is relaxed, especially after eating. The activities it stimulates include; digestion, urination, defecation, sexual arousal, salivation, and lacrimation (tears).
- The parasympathetic nervous system is described as antagonistic to the sympathetic nervous system because its effects on some organs are opposite to that of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Nerve fibers involved in the signal transmission of the parasympathetic nervous system originate from the central nervous system (CNS).
What Does The Parasympathetic Nervous System Do
- The parasympathetic nervous system promotes the rest and digestion activities of the body, when the body is at rest, feeding, and relaxed.
- It increases digestion and decreases heart rate and respiratory rate.
- It undoes the effects of the sympathetic nervous system after a stressful condition.
- The stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system causes:
- Decrease of the heart rate and blood pressure
- Bronchial muscle contraction
- Increase in digestion
- Increase urine secretion
- Increase the production of mucus and saliva
- Contraction of pupils
What Happens When The Parasympathetic Nervous System Is Activated
- The activation of the parasympathetic nervous system causes a relaxed and calm feeling in the mind and body.
- Its activation immediately reduces the sense of stress and anxiety.
What Is The Enteric Nervous System
- The enteric nervous system, which is also known as the intrinsic nervous system, is one of the three branches of the autonomic nervous system.
- It is composed of a net-like system of neurons that controls the functions of the gastrointestinal tract.
- The enteric nervous system can work independently from the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
- It can operate independently from the CNS (the brain and spinal cord). However, it has a two-way connection with the central nervous system and works in harmony with it to control the digestive system according to the demands of the local and entire body’s physiological conditions.
- The neurons of the enteric nervous system control the secretion of the gastrointestinal enzymes as well as the motor functions of the digestive system.
- Because of its extent and a higher level of self-governance, it is also known as the second brain.
Human Nervous System Diagram
Why Is The Nervous System Important
- The nervous system is fundamental for every function of our body. It plays a role in almost every aspect of our body’s health and comfort.
- When we move, our muscles contract and pull on our bones to create movement. However, it is our nervous system that stimulates the muscles and causes their contraction. Without the neural command from the nervous system, our muscles would simply not work. When someone experiences a severe injury on the spinal cord, it often leads to paralysis of the body below the injury point. Because the nerves become damaged and the body parts below the injury point can no longer receive messages from the nervous system.
- The nervous system stimulates and controls the functions of every tissue and every organ in our body. It controls our heart rate and blood pressure. It controls our breathing rate and makes sure that the oxygen supply to the blood is stable. It controls our digestive system. It controls metabolism, body temperature, and the balance of water and electrolytes. It also controls growth and development as well as reproduction.
- The nervous system guides our daily activities, such as sleeping and waking up. It also controls complex processes of our body, such as thinking, memory, reading, emotions, and behavior.
- Simply, the nervous system is extremely important because every tissue and every organ of our body depends on the commands from the nervous system to work properly.
Why Is The Nervous System Like A Telegraph
- Neurons are specialized cells that are the basic functional units of the nervous system.
- Neurons act like telegraph wires and transfer messages in the form of electrochemical impulses all over the body.
- They make links with other cells and are used to carry and receive information. That is why the nervous system is like a telegraph.
Fun Facts About The Nervous System
- The basic functional units of the nervous system are the neurons, which are specialized cells.
- In the human body, there are more than 7 trillion neurons.
- The number of neurons in the human body is greater than the number of stars in the Milky Way.
- There are four types of neurons, which are programmed to perform different tasks. Sensory neuron (transmit signals from outer body parts to CNS), motor neurons (transmit signals from the CNS to the outer body parts), receptor neurons (convert environmental stimuli, such as light, heat, touch, and sound to electrochemical impulses), and interneurons (transmit signals from one neuron to another).
- Nerves can be considered as the electrical wiring of the human body. They transmit signals between the brain, spinal cord, and all other parts of the human body.
- The alpha motor neurons within the spinal cord are the fastest signal transmitters of the body. They transmit signals at a speed of about 268 miles per hour.
- The brain makes only about 2% of the human body weight, however, it consumes 20% of the total body energy.
- Damage to nerves is often permanent because they can not divide or replace themselves.
- Sciatic nerves are the largest and thickest nerves in our body. They run from the spinal cord and end in the toes on each side of the body.
- The axons of some neurons have a fatty insulating layer, known as myline sheet. Myline sheet allows the transmission of nerve impulses faster with less energy consumption.
- If all the neurons found in an adult human are lined up, its length would be about 965 kilometers.
- The enteric nervous system controls our digestive system. It is also sometimes described as a second brain, because of its extent and degree of autonomy.