Raccoons are intelligent and curious animals well known for destroying gardens and making a mess at garbage cans. They have a unique black mask of fur covering their eyes that makes them look like cute bandits. We have gathered complete Raccoon Facts For Kids that will help kids in learning all about Raccoons. They are going to learn its scientific name, taxonomy, etymology, evolution, species, appearance, characteristics, features, size, weight, lifespan, habitat, diet, lifecycle, reproduction, adaptations, predators, conservations status, and many other interesting facts about Racoons.
Raccoon Facts For Kids
1. What Is A Raccoon
- A raccoon ( or raccoon) is a nocturnal mammal species indigenous to North America.
- It is also known as the North American raccoon, common raccoon, northern raccoon, or just coon.
- It is a medium-sized animal and the largest of all the species of the Procyonidae family.
- It has a distinctive facial mask, ringed tail, and extremely nimble front paws.
- A raccoon is well-known for its intelligence.
- It is primarily a nocturnal animal and remains active at night time.
- It is an omnivore and consumes invertebrates, small vertebrates, and plant matter.
- There are also two other raccoon species in the genus Procyon, however, they are not well-known and are indigenous only to the trophic regions.

2. Raccoon Scientific Name
- “Procyon lotor” is the scientific name of the raccoon.
3. Raccoon Classification – Raccoon Taxonomy
- The following is the scientific classification or taxonomy of raccoon:
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Subphylum | Vertebrata |
| Class | Mammalia |
| Order | Carnivora |
| Family | Procyonidae |
| Genus | Procyon |
| Species | Procyon lotor |
4. Raccoon Etymology
- The word ‘raccoon’ was derived from a Powhatan or Virginia Algonquian word.
- It was recorded as “aroughcun” in the Powhatan words list by John Smith.
- In the list of William Strachey, it was recorded as ‘arathkone’.
- It is also recognized as a reflex of a proto-Algonquian word “ahrah-koon-em”, which means “[The] one who rubs, scrubs, and scratches with its hands”.
- In many other languages, the raccoon’s name is based on its characteristic dousing behavior along with a term used for bear in that language. For example; in the German language, the name of a raccoon is Waschbär, which means ‘wash bear’. In Chinese, it is Huan Xiong (浣熊), which also means ‘wash bear’. In Italian, it is orsetto lavatore meaning ‘little washer bear’. In Hebrew, it is dvivón róchetz (דביבון רוחץ), which means ‘washing-bear. In Japanese, the name of the raccoon is araiguma (洗熊 (あらいぐま), which means ‘washing-bear’.
- In Russian, the raccoon’s name is based exclusively on its washing behavior; poloskun (полоскун), which means “rinser”.
5. Raccoon Evolution
- Fossil evidence found in Bulgaria and Russia reveals that the first known individuals of the family Procyonidae lived in Europe about 25 million years ago during the late Oligocene epoch.
- Structure similarities between the skull and tooth of Procyonids and weasels suggest that both probably share a common ancestor, however, the molecular analysis indicated a close relationship of raccoons with bears.
- At least 6 million years later during the early Miocene epoch, the existing Procyonids species at that time crossed the Bering Strait Bridge or Beringia and were probably distributed in Central America.
- In 2006, the genetic analysis indicated that raccoons have a close relationship with ringtails.
- About 2.5 million years ago, the ancestors of the common raccoon migrated from the tropical and subtropical regions to farther north regions. A fossil discovery in the Great Plains (USA) that dates back to the mid-Pliocene epoch has been confirmed that migration.
- Procyon rexroadensis is considered the most recent ancestors of the common raccoons. It was a large Blancan raccoon found in the Rexroad Formation (a geological formation in Kansas that preserve fossils belonging to the Neogene period). It was characterized by having a large lower jaw and narrow back teeth.
6. Raccoon Characteristics – Raccoon Features
- The body length of raccoons without tails ranges between 16 and 28 inches (40 to 70 cm).
- They have a bushy ringed tail with an average length of 10 inches (25 cm).
- Their height at the shoulders ranges between 9 and 12 inches (23 to 30 cm).
- Their usual body weight is between 10 and 30 pounds. However, it varies greatly and depends on the habitat they live in.
- Raccoons have grey to brown fur on their bodies.
- They are well-known for a distinct mask-like black fur on their face around the eyes, which sharply contrast with the white fur on faces.
- Their locomotion method is considered as plantigrade, however, they can stand on their hind limbs to examine things with their front paws.
- Raccoons have a compact body and short legs, due to which they can not run fast or jump high.
- They have an unusual ability to rotate their hind limbs at 180°.
- They have a dual cooling system to thermoregulate. They can sweat and pant at a time to dissipate heat.
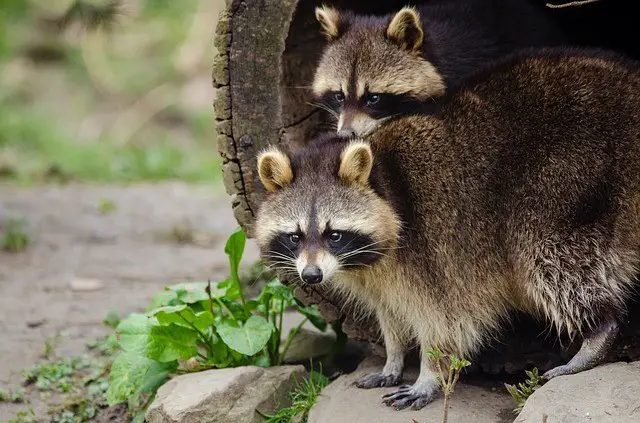
7. What Does A Raccoon Look Like – Raccoon Appearance
- A raccoon is a medium-sized animal with grey to brown fur and a ringed tail.
- It has a black mask of fur around its eyes, a black color strip running from its forehead to nose, and a white face region around its eyes and nose.
- Its two slightly round ears have a white color border.
- It has a short skull with a voluminous braincase and a broad face.
- It has short legs and black-color paws with 5 digits and a bushy tail.
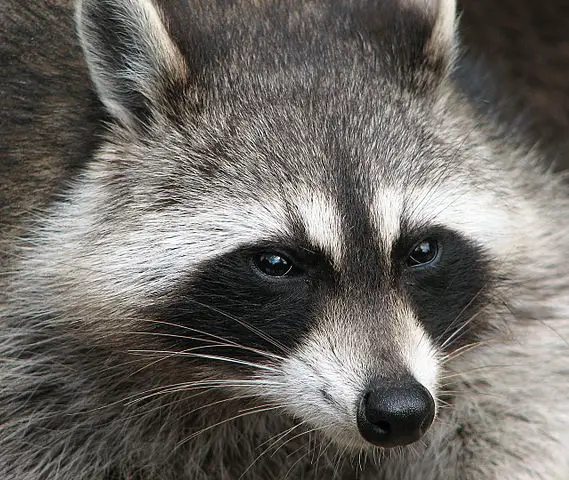

8. What Color Are Raccoons – Raccoon Colors
- The body fur of a raccoon ranges from grey to brown.
- The German population of raccoons has commonly a very dark coat color.
- The color of the face is white with a distinct black color mask around the eyes and a black stripe running from the forehead to the nose tip.
- The ears have a border of white color.
- Its tail has alternating rings of light and dark colors.
- It is assumed that raccoons quickly recognize the posture and facial expressions of other individuals of their species, because of visible face masks and ringed tails.
- It is also assumed that the dark mask helps reduce glare (difficulty to see things in the presence of bright light, such as the direct or reflected light of car headlamps at night) and thus intensifying their night vision.
9. Average Weight Of A Raccoon – Raccoon Weight
- The weight of an adult raccoon considerably changes with habitat.
- The usual weight range of a raccoon is between 10 and 30 pounds (5 and 12 kg).
- The average body weight tends to be from 7 to 19 pounds (3.5 to 9 kg).
- The recorded heaviest raccoon in the wild was weighed up to 62.6 pounds (28.4 kg).
- The specimens found in south Florida are the smallest, while those found in the northern limits are the largest.
- Male individuals usually have 15 to 20% more bodyweight than females.
- Raccoons eat much in summer and store fats in their body. That is why a raccoon has as much as twice bodyweight at the start of winter than in spring.
10. What Is The Size Of A Raccoon – Raccoon Size
- The size of the raccoons’ hindquarters ranges between 16 to 28 inches (40 and 70 cm).
- Their tail usually measures from 8 to 10 inches (20 to 25 cm), however, it can be as large as 16 inches (40 cm).
- Their average body length from head to tail ranges from 23.7 to 37.5 inches (60 to 95 cm).
- Their height at the shoulder is between 9 and 12 inches (23 and 30 cm).
- The recorded largest raccoon was measured 55 inches (140 cm). It was also the largest-sized Procyonid.
How Tall Is A Raccoon – Raccoon Height
- A raccoon has 9 to 11 inches (23 to 30 cm) height at shoulders.
11. Types Of Raccoons – Raccoon Species
- There are three species of raccoons in the genus Procyon. They are:
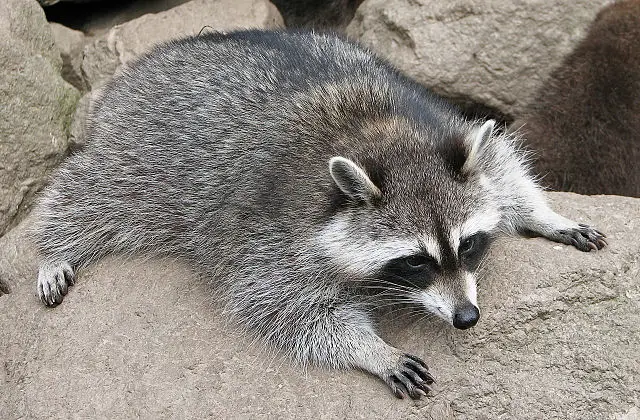
The common raccoon (Procyon lotor)
- It is the most well-known type of raccoon.
- It is also known as the Northern raccoon and is distributed from southern Canada to Panama.
- This species has also been introduced to the Japanese archipelago and continental Europe.
- They live in the wild and can easily adapt to various habitats in the city.

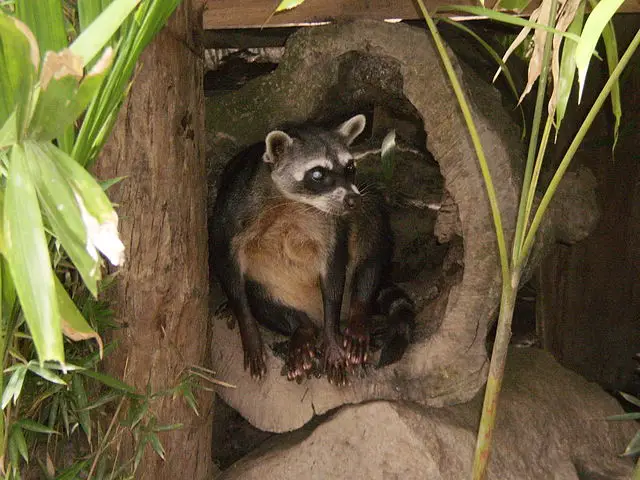
The crab-eating raccoon (Procyon cancrivorus)
- This species of the raccoon is found in the marshy and jungle regions of South and Central America.
- A genetic study revealed that the lineage of crab-eating raccoons and common raccoons probably separated around 4.2 million years ago.

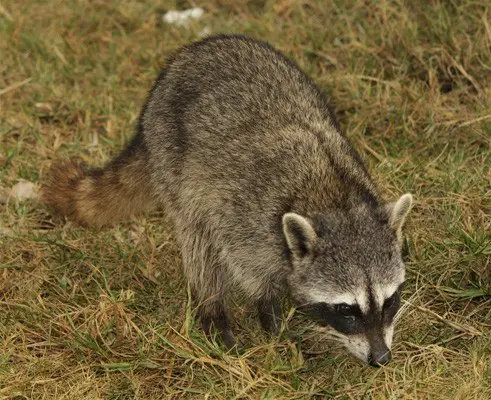
The Cozumel raccoon (Procyon pygmaeus)
- This species of the raccoon is also known as a pygmy raccoon.
- It is found only on Cozumel island, Mexico.
- It is a critically endangered species of the raccoon.

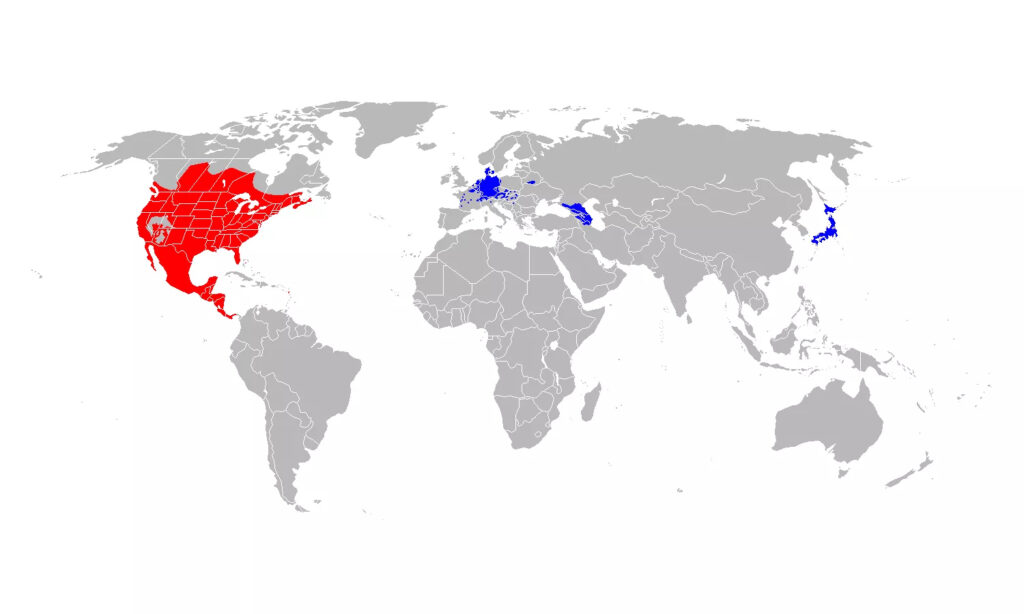
12. Where Do Raccoons Live – Raccoon Habitat
- The habitat range of raccoons is from Canada to Panama throughout North America.
- Outside North America, they are distributed in Germany, Japan, and the former Soviet Union.
- Raccoons are found in most of the US states, except for the parts of the Rocky Mountains, Arizona, Utah, and central Nevada.
- They flourish in highly wooded areas, as they rely on vertical structures to climb when they feel threatened.
- They do not like to live in open terrains and regions with a high amount of beech trees, as the bark of beech trees is so smooth for climbing.
- Raccoons prefer the hollow parts of trees and rock crevices for sleeping, spending winter, and as a litter den.
- If there are no such dens, raccoons use the burrows of other animals, tree crotches, or dense undergrowth of vegetation.
- The lowland deciduous or mixed forests along with marshes and lakeshores sustain the highest population density of raccoons (51.8 raccoons per square mile), as a lot of amphibians and crustaceans are found there, which is an important food source of raccoons.
- Prairies and upland hardwood forests have a very low population density.
- Raccoons can easily adapt to urban areas as a habitat. Such areas provide a large number of sleeping areas, such as cottages, attics, garages, abandoned houses, and hollow trees in gardens. In urban areas, they easily get their food in the form of leftovers from municipal waste, fruits, and insects.
13. Where Do Raccoons Live In The World – Raccoon Habitat Map
14. Where Do Raccoons Live During The Day – Raccoon During Day
- Raccoons are primarily nocturnal and spend most of their daytime resting.
- In forests, they spend their day sleeping in trees or hollow parts of fallen trees.
- In urban regions, they take shelter in abandoned houses and cars, attics, barns, sheds, and underneath woodpiles.
- Raccoons usually have multiple dens and they move between them every two days.
15. Do Raccoons Live In Trees
- Yes, raccoons live in the hollow parts of the trees.
- They also use tree crotches if there is no hollow region.
- Raccoons also need vertical structures or long trees to climb when they feel threatened.

16. How Long Do Raccoons Live – Raccoon Lifespan – Raccoon Life Expectancy
- The lifespan of common raccoons in the wild is 1.8 to 3.1 years.
- Their lifespan depends on various local conditions, such as traffic volume, the severity of the weather, and hunting.
- About half of the young ones do not survive until their first birthday.
- After surviving for the age of one year, the rate of their mortality reduced to between 10% and 30%.
- Crab-eating raccoons are known to live for more than 5 years in the wild.
- Cozumel raccoons also live for as much as 5 years in the wild.
How Long Do Raccoons Live In Captivity – Raccoon Lifespan In Captivity
- The lifespan of raccoons in captivity is more than 20 years.
Average Age Of Raccoon – Raccoon Age
- The average age of raccoons in the wild is 2 to 3 years.
17. What Do Raccoons Eat – Raccoon Diet
- Raccoons are omnivores in nature and their diet is composed of up to 40% invertebrates, 27% vertebrates, and 33% plant matter.
- The invertebrates they consume are insects, worms, crustaceans, and mollusks.
- The vertebrates they eat are small animals, such as rats, squirrels, poultry, fish, snakes, and frogs.
- The plant matter they consume includes vegetables, fruits, grains, berries, and nuts.
- During spring and early summer, they mostly eat insects, worms, and other animals available.
- In the late summer and autumn, they prefer to eat fruits and calorie-rich nuts, such as walnuts and acorns to build up the fat needed in the winter.
- It is a popular belief that raccoons like to eat large and active prey, such as mammals and birds, however, they eat large animals only occasionally.
- Their favorite prey is the one they can catch easily, especially amphibians, fish, and birds’ eggs.
What Do Raccoons Like To Eat – Raccoons Favorite Food
- In the wild, a raccoon prefers to prey and eat the things it can easily catch, especially fish, amphibians, and birds’ eggs.
- In the wild, a raccoon is a severe predator of birds’ eggs and it is usually kept away from the nests of endangered birds species.
- Fruits, berries, nuts, grains, vegetables, eggs, and poultry are the favorite foods of raccoons.
- If a large variety of food is available (such as in captivity), they like to eat sweets, peanuts, peanut butter, fruits, cat and dog food, and bread.
What Do Raccoons Eat In Captivity – Raccoon Diet In Captivity
- In captivity, raccoons are fed with vegetables, fruits, nuts, and cat or dog food.
- Water should be kept with their food, as they like to douse their food before eating.
What Do Raccoons Eat In The Winter
- In the winter, raccoons will eat many things they find.
- They consume plants, small animals, insects, birds’ eggs, and even human garbage.
- Their usual diet in the winter is corn, acorns, fruits, insects, small animals, and injured water-fowls.
- They would also eat many other things if available.
18. What Do Baby Raccoons Eat – Baby Raccoon Diet
- In the wild, the only regular diet of the baby raccoon is their mother’s milk.
- In captivity, a baby raccoon is fed KMR (Kitten Milk Replacement) with a bottle from birth to 7 weeks.
- From 7 to 8 weeks, cereals are introduced into their diet.
- After 9 weeks, baby food is added to their diet.
- From 10 to 12 weeks, a large variety of fruits and vegetables is cut into small pieces and cooked chicken is given along with bottle feeding.
- After 13 weeks, a baby raccoon is usually weaned from the bottle feeding and is fed with solid food.
19. What Can Raccoons Not Eat
- Raccoons can eat everything good for their health.
- However, they should not be overloaded with unhealthy foods and treats, as it can cause obesity and other health issues in them.
20. Raccoon Life Cycle
- The life cycle of a raccoon starts when the younger ones reach sexual maturity and mate.
- The kits are born after a gestation period of 63 to 65 days.
- The kits are born in an underdeveloped form and depend on the mother for food and protection.
- The younger ones reach sexual maturity at the age of about one year.
- Raccoons live for an average age of 2 to 3 years in the wild.
21. How Do Raccoons Reproduce – Raccoon Reproduction
- The mating season of raccoons is between late winter and early spring (between late January and mid-March).
- The pregnant females give birth to a litter of kits after a gestation period of 63 to 65 days.
- A litter usually has 2 to 5 kits.
- The average size of litter greatly changes with habitat. In Alabama, it is 2.5 while in Northern Dakota it is 4.8.
- Litters of large sizes are usually born in regions with high mortality rates.
- Mothers feed their kits usually for 16 weeks.
22. Baby Raccoon Facts
-
What Is A Baby Raccoon Called
- A baby raccoon is called a kit.
- Sometimes, it is also called a cub.
-
What Does A Baby Raccoon Look Like
- A baby raccoon looks like an adult raccoon but is of a much smaller size.
- The babies can not open their eyes at the time of birth.
- They have light-colored fur and a visible mask.
- A baby raccoon is born deaf and blind.
- It has a light fur and a visible mask.
- At birth, it has a size of up to 4 inches (10 cm) and weighs between 2.1 and 2.6 oz (60 to 75 g).
- After 18 to 23 days of its birth, its ear canals open while its eyes open after a few days for the first time.
- A kit depends on its mother for food and protection.
- After 6 to 9 weeks, its weight reaches 2 pounds (1 kg) and it starts coming outside of the den and also starts eating solid food.
- At this age, the mother decreases the intervals of feeding kits with her milk.
- A kit is usually weaned at the age of 16 weeks.
- A kit and all its brothers and sisters in a litter separate from the mother after their mother has shown them the feeding grounds and dens.
23. Raccoon Adaptations
Raccoon Physical Adaptations
- The following are the main physical adaptations of raccoons:
Paw structure
- The dexterous paws of a raccoon are its major physical adaptation.
- The structure of its front paws is almost human-like, which makes it capable to fulfill complex tasks.
- Due to such a paw structure, a raccoon can easily search for its food.
- They can turn their hind limbs at 180°. This ability make them efficient climbers.
Solid bones and nimble body
- A raccoon has solid bones and a nimble body structure, which provides them protection against falls. They are observed ignoring up to 40 feet drops to the ground.
- Their nimble body structure also allows them to run as fast as 15 miles per hour despite having short legs.
Dental system
- Raccoons have a well-adapted dental system to their omnivorous diet.
- They have 40 teeth with a dental formula: 3.1.4.2 /3.1.4.2.
- They do not have extremely sharp and pointed carnassials like those of full carnivore animals.
- They also do not have much-wide molars like those of herbivore animals.
Dark mask
- The dark mask of raccoons makes their night-vision intense by reducing glare.
Dual-cooling system
- Raccoons have a unique system of thermoregulation; a dual cooling system. They can sweat and pant at a time to dissipate heat.
Raccoon Behavioral Adaptations
- A raccoon is fully adapted to eat about anything it found; from insects, mice, plants, and fruits to human garbage.
- This behavioral adaptation allows them to live in a variety of environments. When cities are built in their natural habitats, they have no problem living there. They are even comfortable living in the basement or attic of someone’s home.
- Another unique behavioral adaptation of a raccoon is dousing its food before eating. The scientific name “Procyon lotor” means “washer dog”, which is given to it because of its dousing behavior.
- Raccoons are primarily nocturnal creatures and remain active at night. This behavior protects them from their natural predators and humans.
- During the winter season, raccoons can go into torpor (lethargy or a state of physical and mental inactivity). This ability allows them to survive harsh winter conditions and food scarcity.
- Raccoons also eat high-calorie diets during autumn to build their body weight and store fat reservoirs for winter.
Raccoon Adaptations In Deciduous Forest
- A raccoon is well-adapted to live in every type of habitat.
- Deciduous forest is the natural habitat of raccoons.
- They nest in hollow trees there and climb trees to forage and escape from predators.
What Eats A Raccoon – Raccoon Predators
- Bobcats, coyotes, great horned owls, American black bears, cougars, American alligators, grey wolves, golden and bald eagles, black hawk-eagles, and ornate hawk-eagles eat raccoons.
- In North America, the natural cause of their death on a large scale is canine distemper disease.
- In urban areas, they fall victim to heavy vehicular traffic and excessive hunting, which accounts for about 90% of their deaths.
Raccoon Natural Predator
- Bobcats, coyotes, and great horned owls are the natural predators of raccoons.
- In Florida, they sometimes become prey to the large carnivore animals, such as cougars and American black bears.
- Sometimes, raccoons become a supplemental prey item to grey wolves.
- In the southeast regions, raccoons are the favorite prey of American alligators.
- Golden and bald eagles also sometimes prey on raccoons.
- In the tropic regions, black hawk-eagles and ornate hawk-eagles prey raccoons.
- In the regions of the former Soviet Union where they were introduced, their major predators are lynx, wolves, and Eurasian eagle-owls.
24. Are Raccoons Endangered – Raccoon Endangered
- No, raccoons are not endangered and their current population trend is increasing.
25. Raccoon Conservation Status
- The conservation status of the raccoon on the IUCN Red List is “Least Concern”.
26. Fun Facts About Raccoons – Weird Facts About Raccoons
- A group of raccoons is known as gaze or nursery.
- The paw structure of raccoons is similar to human hands.
- The scientific name of the raccoon is based on its dousing behavior.
- Raccoons do not like tomatoes to eat.
- Raccoons are very vocal and can make more than 50 different voices to communicate.
- Their lifespan in captivity is much longer than in the wild.
- In the USA, raccoons are believed to be one of the primary carriers of rabies disease.
27. Interesting Facts About Raccoons
- The most distinctive features of raccoons; facial mask, ringed tail, and nimble front paws, are themes in the Native American mythologies.
- Raccoons are famous for their intelligence. Research reveals that they can remember the tasks’ solution for up to 3 years.
- Raccoons are quite clean animals. They douse their food before eating and dig holes for sanitary waste disposal.
- Raccoons are resourceful solvers of problems.
- They use their sense of touch to locate things.
- Raccoons found in the cities are observed to be more clever than those found in other regions.
- The raccoon is one of the animal species that have benefited from the spread of humans and can be found across the world.
- Raccoons are astonishingly adaptable and can easily adapt to the new environment of their stolen natural habitat.
- Car accidents are the most significant reason for the deaths of raccoons.
- Raccoons can climb down with head first direction. They can rotate their hind limbs at 180 degrees.
29. FAQs About Racoons
What Does Raccoon Poop Look Like
- The poop of raccoons looks like the droppings of little dogs.
- It has a bad smell, dark color, and usually contains undigested food items.
What Do You Feed Baby Raccoons
- Baby raccoons are fed with KTM (Kitten Milk Replacement).
What Are Raccoons Good For
- Raccoons are good for eating pests, wasp larvae, and small rodents.
Can You Have A Pet Raccoon
- Yes, many people keep a raccoon pet.
- However, in many states of the USA, it is illegal to have a pet raccoon.
How To Get A Raccoon Out Of Your House
- Open all the doors and windows of your house and wait until a raccoon gets out on its own.
- If it is difficult to open everything, take a broom and usher it out.
- If raccoon does not get out of any other way, call a company of wildlife removal.
Do Raccoons Climb Trees
- Yes, raccoons are excellent climbers and climb trees.
What Keeps Raccoons Away
- Pepper spray, as raccoons do not like peppers.
- Ammonia spray
- Mothballs
- Predator urine
Can Raccoons Climb Walls
- Yes, raccoons are excellent climbers and can climb walls and vertical structures.
Do Raccoons Eat Turtles
- Yes, raccoons will eat turtles if they are found.
Do Owls Eat Raccoons
- Yes, owls eat raccoons.









