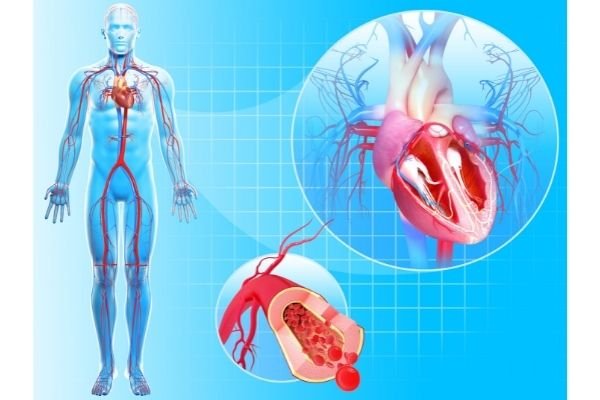
In simple words, a circulatory system in the human body is the system that delivers nutrients and oxygen to cells and takes away the wastes produced by the cells. We have listed down complete Circulatory System Facts for Kids that will help you in learning all about Circulatory Systems. You are going to learn about its definition, location, main organs, parts, functions, working, types, importance, diseases, and many other interesting facts about Circulatory Systems.
Circulatory System Facts For Kids
What Is A Circulatory System – Circulatory System Definition
- The circulatory system is also known as the cardiovascular system or just the vascular system. It consists of the heart and blood vessels.
- The circulatory system is responsible for the circulation of lymph and blood across the body.
- It transports oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to the rest of the body via blood arteries.
- Along with blood, the circulatory system carries nutrients to the body such as amino acids and electrolytes. It also transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, blood cells (red blood cells and white blood cells), and hormones.
- It is also responsible for maintaining optimum blood pH, stabilizing normal body temperature, and maintaining homeostasis.
- The circulatory system is divided into two systems: The blood circulatory system and the lymph circulatory system.
- The blood circulatory system transports blood all over the body. Blood consists of plasma, blood platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells.
- The lymphatic system circulates lymph. Lymph consists of recycled excess blood plasma that has been filtered from the interstitial fluid and returned to the lymphatic system.
- Humans and other vertebrates have a closed circulatory system which means that the blood stays in the network of arteries, capillaries, and veins. On the other hand, some invertebrates have an open circulatory system.
Where Is The Circulatory System Located
- The circulatory system starts from the heart, goes around the body, and back into the heart. It is a loop that spreads throughout the body.
- In invertebrates, the circulatory system is closed, meaning no blood enters or leaves the system as it makes its journey around the body and back into the heart.
- The circulatory system starts when the heart is in the relaxation state, which is between two heartbeats.
What Does The Circulatory System Transport
- The circulatory system is responsible for transporting blood and lymph across the body. Along with blood and lymph, it carries oxygen, hormones, and nutrients and removes waste materials such as carbon dioxide from the cells.
- The circulatory system works in one direction only. It starts from the heart, moves across the body, and ends back in the heart.
Circulatory System Main Organs
- The circulatory system consists of two main organs: the heart and the lungs.
- These organs make up the circulatory system and help in transporting blood, nutrients, and hormones to and from cells.
What Are The Parts Of the Circulatory System
The circulatory system is a complex system consisting of the following parts:
Heart
- The heart is a muscular organ that helps to transport blood across the body via a network of blood vessels.
Learn more: Human Heart Facts for Kids
Lungs
- The lungs are a pair of air-filled and spongy organs, where gases in the blood are exchanged.
- Carbon dioxide-rich blood is carried to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries. Here, carbon dioxide is removed and oxygen is added to the blood. The oxygen-rich blood is then transported back to the heart through the pulmonary veins.
Arteries
- Arteries are blood vessels that are the pathways for oxygen-rich blood to move away from the heart, towards the body.
Veins
- Veins are blood vessels that carry oxygen-poor blood from the body back into the heart.
Capillaries
- They are tiny blood vessels that help in the exchange of oxygen, nutrients, and waste products (such as carbon dioxide and other gases) between the circulatory system and the body.
What Is The Circulatory System Made Up Of
- The circulatory system is made up of three independent systems working together: the heart (cardiovascular system), lungs (pulmonary system), and arteries, veins, and coronary vessels (systemic system).
- It primarily consists of blood vessels that spread across the heart, lungs, and the body to transport oxygen, nutrients, and hormones and remove waste products such as carbon dioxide.
- Arteries in the circulatory system are blood vessels that move blood away from the heart while veins are the blood vessels that bring blood back into the heart.
- Capillaries are small blood vessels responsible for providing oxygen to the cells and removing carbon dioxide.
Circulatory System Cells
- The circulatory system is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, and blood platelets.
- Red blood cells consist of a protein called hemoglobin, responsible for carrying oxygen.
- White blood cells help to protect the body from infections and other diseases. It is an essential part of the immune system.
- Blood platelets are tiny cell fragments in the blood that help the body form clots to stop bleeding.
Circulatory System Arteries
- Arteries are small blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart towards the body.
- The biggest human artery is called the aorta. It is responsible for carrying blood away from the heart and transporting oxygen and nutrients to the brain, muscles, and other cells.
- Arteries of the circulatory system are thick and elastic because blood is constantly being pumped from the heart with high pressure.
- There are two types of arteries: elastic arteries which are located closer to the heart where the blood pressure is highest and muscular arteries that are present away from the heart where the blood pressure is lower.
- Arteries are further divided into arterioles that connect to blood capillaries and help in the exchange of oxygen and nutrients between the blood and body cells. They also remove waste products like carbon dioxide.
Human Arterial System
- The arteries are blood vessels that take oxygen-rich blood away from the heart and towards the brain and other body organs.
- The arteries are a part of the circulatory system that plays an essential role in allowing the body to function properly. They transport blood, oxygen, and nutrients around the body.
- The human arterial system is divided into systemic arteries and pulmonary arteries.
- The systemic arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the whole body, while the pulmonary arteries carry oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs.
- The arterial system also helps to maintain the balance of proteins and keeps the immune system healthy.
- A deteriorated arterial system can lead to complications such as myocardial infarction and even stroke.
Which Is The Largest And The Main Artery Of The Circulatory System
- Aorta is the largest and the major artery of the circulatory system. It is located right on the top of the heart.
- Its main function is to carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
- If the aorta fails to perform its function correctly, the whole body’s blood supply will be threatened.
Circulatory System Lungs – Function Of Lungs In Circulatory System
- The lungs do more than just fill up with air when you breathe. They also play a vital role in moving oxygen into the bloodstream and taking waste products, such as carbon dioxide out of it.
- Blood moves in and out of the lungs via pulmonary arteries and veins. It is where the gas exchange occurs.
- Oxygen-poor blood from the heart is carried to the lungs via pulmonary arteries and after oxygen has been added to it and carbon dioxide has been removed, the blood is carried back to the heart via pulmonary veins.
- Without lungs, blood would be useless and the circulatory system would never be able to perform its function properly.
What Is The Main Function Of The Circulatory System
- The main function of the circulatory system is to provide oxygen and nutrients to the body and remove toxins and waste products, such as carbon dioxide from it.
Function Of Heart In Circulatory System – What Does The Heart Do In The Circulatory System
- The heart is a pump that transports blood all around the body. It is the main part of the circulatory system as the majority of the functions start from the heart and also end in the heart during circulation.
- The heart beats 60 to 80 times per minute and with each beat, the heart sends blood across the body providing oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to all cells and tissues.
- The heart sends oxygen-poor blood to the lungs where it picks up oxygen and is sent back to the heart so that it can be delivered to the brain and the rest of the body.
- The blood capillaries, attached to the heart are responsible for the movement of blood around the body and back to the heart. This process is known as circulation.
- The heart completes a single circulation in less than 60 seconds.
How The Circulatory System Works
- The circulatory system is a loop that starts from the heart, goes around the body, and ends back in the heart.
- It is a closed system which means that the blood does not enter or leave the system at any point during circulation.
- Circulation of blood across the body occurs via the arterial system that consists of arteries, arterioles, and blood capillaries, while blood is returned to the heart via the venous system that consists of veins and venules.
- Blood from the heart passes to the capillaries via the aorta of the heart. The speed and pressure of the blood are adjusted so that it flows continuously because there is a constant exchange of oxygen and nutrients in the capillaries.
- After the oxygen-rich blood has been supplied to the cells, its oxygen content is reduced and waste content is increased by picking up toxins and carbon dioxide along the way.
- This blood is sent back to the heart to pick up oxygen from the lung, sent again for circulation, and the cycle repeats.
Types Of Circulatory System
- There Are Two Types of Circulatory systems: The pulmonary circulatory system and the systemic circulatory system.
- Pulmonary circulation is responsible for moving blood between the heart and the lungs. It transports oxygen-depleted blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen and release carbon dioxide. After that, the oxygen-rich blood flows back to the heart.
- Systemic circulation is responsible for providing oxygen and nutrients to the cells and picking up carbon dioxide and waste products.
Open And Closed Circulatory System
| Open Circulatory System | Closed Circulatory System |
| Hemolymph is present instead of blood. | Blood is present. |
| The hemolymph directly swims in the organs and tissues. | The blood is present in closed vessels and does not circulate openly. |
| There are no blood vessels or capillaries in this system. | Blood vessels and capillaries are present in this system. |
| The blood and interstitial fluid mix and cannot be easily distinguished. | Blood and interstitial fluid do not mix and can be easily distinguished. |
| The respiratory pigment is absent. | The respiratory pigment is present. |
| Blood flow is slow and irregular. | Blood flow is rapid and regular. |
| This system is present in invertebrates, such as mollusks and arthropods. | This system is present in annelids and some vertebrates. |
| Snails, clams, cockroaches, and spiders have open circulatory systems. | Humans, cats, squids, and earthworms have closed circulatory systems. |
Open Circulatory System Definition
- The open circulatory system is a type of circulatory system in which the blood flows freely in the body instead of being sealed tight in arteries and veins.
- The blood is open to the environment, such as the digestive tract and other places in the body.
- This system is primarily found in invertebrates.
Closed Circulatory System
- In the closed circulatory system, blood does not enter or leave the system during its journey from the heart to the body and back to the heart. In this system, there is a continuous flow of blood through the loop again and again.
- Closed circulatory systems are common among vertebrates and a few invertebrates, such as earthworms.
Double Circulatory System – Double Circulation Definition
- A double circulatory system has two separate circuits and the blood moves through the heart twice.
- The first circuit is the pulmonary circuit, which is present between the heart and lungs.
- While the second circuit is the systemic circuit and is present between the heart and other organs.
- The circulatory system of humans is a double circulatory system.
Why Is Blood Circulation In Human Heart Called Double Circulation
- Blood circulation in the human heart is called double circulation because blood moves through the heart twice via two circuits: the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit.
- First, oxygen-poor blood from the heart is sent to the lungs to pick up oxygen. The oxygen-rich blood from the lungs moves back to the heart, after which it is pumped again into different parts of the body. Thus, the blood passes twice through the heart to make one complete round through the body.
Types Of Blood Circulation
- There are two types of circulation in the body: Pulmonary Circulation and Systemic Circulation.
- Pulmonary circulation is responsible for moving blood between the heart and the lungs, while systemic circulation is responsible for moving blood between the heart and the rest of the body.
Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation
| Pulmonary circulation | Systemic circulation |
| It involves the circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs. | It involves the circulation of blood between the heart and the rest of the body. |
| It transports oxygen-poor blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen. | It transports the oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body |
| In the pulmonary circulation, blood is pumped by the right ventricle and received by the left atrium of the heart. | In the systemic circulation, blood is pumped by the left ventricle and received by the right atrium of the heart. |
| It is responsible for returning oxygen-rich blood, back into the heart. | It is responsible for returning oxygen-poor blood to the heart. |
Pulmonary Circulatory System
- The pulmonary system is the part of the circulatory system which carries oxygen-depleted blood away from the heart, to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
- It brings the oxygen-rich blood back to the left atrium and ventricle of the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body.
- The pulmonary circulatory system consists of blood vessels, called pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins.
Coronary Circulation Of Heart
- Coronary circulation of the heart refers to the circulation of blood in the blood vessels that supply the myocardium wall of the heart.
- The coronary circulatory system consists of blood vessels called coronary arteries and coronary veins.
- The coronary arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, while the coronary veins remove the oxygen-poor blood.
Systemic Circulation Definition
- Systemic circulation refers to the process of carrying oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to all body parts and oxygen-poor blood back to the heart.
- It consists of blood vessels called arteries, arterioles, capillaries, veins, and coronary vessels.
- The circulatory system fights infections and helps to stabilize body temperature.
Why Is The Circulatory System Important
The circulatory system is important for several reasons:
- It pumps blood all over the body and keeps us alive.
- It provides oxygen supply to the body and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
- It supplies nutrients and hormones to the cells of the body.
- The circulatory system removes infections and toxins from the body.
- The circulatory system also transports platelets or thrombocytes, which make blood clots in case of injury and prevent blood loss.
- The circulatory system plays an important role in thermoregulation.
- It maintains the fluid balance within the body and keeps it working properly.
How Does The Circulatory System Work With Other Systems
- The circulatory system works with many other systems as all body systems are connected.
Nervous System
- The nervous system incorporates the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. The heart beats because the brain tells it to do so.
- When it beats, it pumps blood throughout the body and provides nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and removes waste.
Learn more: Nervous System Facts for Kids
Digestive System
- The digestive system is in charge of breaking down food and absorbing nutrients from it. These nutrients are supplied to the cells via the bloodstream.
- Minerals and vitamins are also absorbed into the bloodstream as they strengthen the bones and the immune system.
Muscular System
- The heart is a muscular organ and is the main component of the circulatory system.
- It expands and contracts to pump blood throughout the body.
Respiratory System
- The respiratory system is in charge of supplying oxygen to the body.
- Oxygen enters the body through the lungs and is sent to the bloodstream via blood vessels. At the same time, carbon dioxide is removed from the blood and exhaled.
Skeletal System
- The skeletal system contains red blood cells and white blood cells, produced in the bone marrow.
- They are part of the bloodstream and carry oxygen to the cells and fight off diseases and infections.
Endocrine System
- The endocrine system produces hormones. These hormones travel through the circulatory system to reach their destination.
Immune System
- The immune system contains white blood cells and antibodies. They travel inside the bloodstream to destroy any infection and fight off sickness.
Diseases Of The Circulatory System
Some diseases of the circulatory system are as follows:
Atherosclerosis
- It occurs when there is the build-up of plaque in the arteries. This can damage the circulatory system and disrupt blood flow around the heart and body.
- Factors that contribute to atherosclerosis are high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, an unhealthy diet, and obesity.
- If atherosclerosis only affects the arteries of the heart, it is called coronary artery disease. Whereas, if it affects arteries in other parts of the body, it is called peripheral artery disease.
Varicose veins
- It happens when the veins responsible for carrying oxygen-poor blood to the heart fail to perform their function. As a result, oxygen-depleted blood starts to accumulate in the veins, causing them to become swollen.
- Varicose veins most commonly occur in the lower legs.
Heart attack
- It occurs when the heart is unable to receive enough oxygen required for proper activity.
- Lack of oxygen causes heart cells to die and lose their function.
Heart valve problems
- Heart valves are responsible for controlling blood flow in the heart. Leaky or blocked (stenotic) valves lead to heart valve problems, causing the heart to be less efficient at pumping blood around the body.
How To Keep Your Circulatory System Healthy
- It is important to maintain a healthy circulatory system because without it the body will not be able to function.
- It is essential to maintain a healthy weight and to prevent obesity or malnutrition as both of these conditions can impact the circulatory system.
- If you want healthy circulation, avoid smoking as it damages the lungs and the heart hence, damaging the circulatory system.
- Exercise is vital for healthy blood circulation. Even 30 minutes of light exercise most days of the week will keep the heart and the circulatory system fit.
- A healthy diet that is low in fats and cholesterol and consists of lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is excellent for the circulatory system as it makes the blood flow easy and regular.
- Processed foods and fast food contain trans fats and saturated fats which are bad for the heart and should be avoided completely.
- Salt and alcohol intake should be limited to keep the circulatory system healthy.
- Stress also plays a huge role in weakening the circulatory system. This is why it is important to get good sleep, stay relaxed, and self-care to reduce stress.
Label The Circulatory System
- Capillaries in the lungs
- Pulmonary vein
- Pulmonary artery
- Left atrium of the heart
- Right atrium
- Left ventricle
- Right ventricle
- Aorta (main artery)
- Vena cava (main vein)
- Blood capillaries in the body
Fun Facts About The Circulatory System
- The circulatory system is composed of a network of blood vessels spread around the body in a loop that starts and ends at the heart.
- The main organs of the circulatory system are the heart, lungs, and blood vessels.
- Blood from the heart is pumped to the lungs, where it is oxygenated and transported back to the heart. This oxygen-rich blood is transported to the rest of the body.
- Blood contains red blood cells, white blood cells, and blood platelets.
- Human blood is red while some arthropods and mollusks have blue-colored blood.
- Blood vessels in the brain selectively allow the passage of molecules and metabolic products into the brain and make up the blood-brain barrier. The blood-brain barrier is responsible for keeping viruses and pathogens away from the brain.
- There are no blood vessels in the cornea of the eyes because they can obstruct vision.
- The size of the blood vessels is controlled by temperature and weather. In winter, blood vessels become constricted to retain heat while, during summertime, they expand to release heat.
- Blood vessels only contain a single type of muscle tissue, called smooth muscle tissue.
- Eating dark chocolate is good for the heart because it contains antioxidants.
Interesting Facts About The Circulatory System
- The circulatory system is a biological system that transports blood across the body.
- It is also called the vascular system or the cardiovascular system.
- The circulatory system is composed of two main components: systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation.
- If all the blood vessels in the human circulatory system are laid out in a straight line, it would be 60,000 miles in length.
- Humans have enough blood vessels in the body to wrap around the Earth, approximately 2.5 times.
- An average adult human has 192 ounces of blood flowing through his circulatory system.
- Each tiny drop of blood contains about 5 million red blood cells.
- Red blood cells have a short life span and spend about 4 months circulating throughout the body, feeding almost 60 trillion other body cells.
- It takes 20 seconds for a single blood cell to circulate the body once.
- The heart pumps about 5 liters of blood in one minute.
- The blood pressure of humans changes throughout the day. It is the lowest while sleeping and highest in the afternoon.
What Is The Cardiovascular System – Cardiovascular System Definition
- The cardiovascular system is a system that pumps blood throughout the body. It consists of the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins.
What Is The Function Of The Cardiovascular System
- The cardiovascular system performs many important functions:
- It permits blood to flow around the body and provides oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
- It helps to remove carbon dioxide from the cells.
- It also gets rid of any metabolic waste and sends it to the excretory system for disposal.
- The cardiovascular system also transports immune cells and protects the body against any disease and infection.
- It also transports platelets, which help to clot blood in case of an injury and stop the bleeding.
Parts Of The Cardiovascular System
- The cardiovascular system is a transport system of the body. It has three main components: the heart, blood vessel, and blood itself.
- The heart is the pumping organ, while the blood vessels are the delivery routes that transport blood around the body.
- Blood contains oxygen and nutrients required for cells to perform their function.
Cardiovascular System Major Organs
- The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood itself. The main organ involved in this system is the heart that pumps the blood all over the body and maintains its functions.
Anatomy Of Cardiovascular System
- The main constituent of the cardiovascular system is the heart. It is present between the lungs and its main function is to pump blood to the brain and body.
- The pericardium is a structure that covers the heart and protects it from shock.
- The heart wall is composed of the cardiac muscle, which is a special type of muscle only found in the heart.
- The blood vessels of the heart carry blood from the heart to the body and from the body back into the heart.
- Arteries are the vessels that carry blood away from the heart, while veins are the vessels that carry blood back to the heart.
- Capillaries are tiny vessels that join arteries and veins together.
- Aorta is the largest blood vessel of the body and it is responsible for pumping blood around the body.
- The four chambers of the heart: right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle and left ventricle work together to circulate blood around the body and also receive the blood that is coming back to the heart.
How Does The Cardiovascular System Work
- The body requires oxygen and nutrients to perform its function. It needs blood to acquire these things.
- The body also needs to remove waste products like carbon dioxide from the cells.
- The cardiovascular system helps the body achieve all this. Veins help to deliver oxygen-poor blood to the heart.
- The right atrium pumps this used blood into the right ventricle where it moves through the pulmonary arteries and enters the lungs to pick up fresh oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide.
- This oxygen-rich blood is now ready to use by the body. It drains into the left atrium and from there, it is moved to the left ventricle.
- The left ventricle pumps this freshly oxygenated blood into the aorta, which then transports it to the rest of the body.
Why Is The Cardiovascular System Important
- The cardiovascular system is important for delivering oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to the cells and organs of the body.
- It is essential for removing waste products from the body and fighting against infections and diseases.
- It helps the body to meet the demands of activity, exercise, and stress.
- It is also important for thermoregulation meaning maintaining body temperature.
- The cardiovascular system enables the body to achieve fluid balance.